Topic basketball court perimeter: The basketball court perimeter is crucial for understanding the game's layout and strategic play. It includes the key dimensions and markings that define player movements and game rules. By exploring the perimeter, players and enthusiasts can appreciate the intricacies that make basketball an engaging and competitive sport.
Table of Content
- Basketball Court Perimeter
- Introduction to Basketball Court Perimeter
- Dimensions and Markings
- NBA Court Specifications
- Detailed Court Markings
- Additional Equipment
- FIBA Court Specifications
- NCAA Court Specifications
- High School Court Specifications
- Center Circle
- The Key (Paint Area)
- Three-Point Line
- Free Throw Line and Circle
- Half-Court Line
- Backboard and Rim
- Court Surfaces and Flooring
- FAQs on Court Dimensions
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách đo đạc sân bóng rổ và giới thiệu các tham số quan trọng của sân bóng rổ.
Basketball Court Perimeter
The perimeter of a basketball court encompasses the boundary lines and includes various crucial markings essential for gameplay. Understanding the dimensions and markings of different basketball courts helps in grasping the game rules and play areas. Here are the detailed dimensions and markings for various levels of play:
NBA Basketball Court Dimensions
- Length: 94 feet
- Width: 50 feet
- Three-point line: 23.75 feet from the basket at the top of the arc, 22 feet at the corners
- Free-throw line: 15 feet from the backboard
- Key (paint area): 16 feet wide
WNBA Basketball Court Dimensions
- Three-point line: 22.15 feet from the basket at the top of the arc, 21.65 feet at the corners
High School Basketball Court Dimensions
- Length: 84 feet
- Three-point line: 19.75 feet from the basket
- Key (paint area): 12 feet wide
NCAA Basketball Court Dimensions
FIBA Basketball Court Dimensions
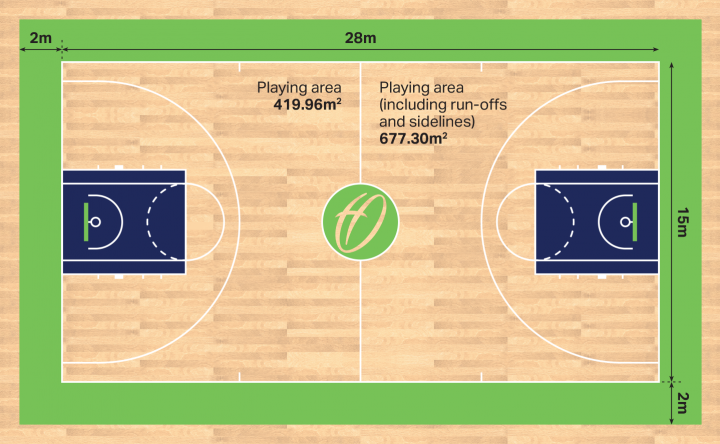
- Length: 28 meters (91.86 feet)
- Width: 15 meters (49.21 feet)
- Three-point line: 6.75 meters (22.15 feet) from the basket
- Free-throw line: 4.6 meters (15.09 feet) from the backboard
- Key (paint area): 4.9 meters (16.08 feet) wide
Additional Markings
- Baseline: The boundary at each end of the court
- Sideline: Defines the lateral boundaries of the court
- Half-court line: Divides the court into two equal sections
- Free throw line: Positioned 15 feet from the backboard
- Frontcourt/Backcourt: Designated areas relative to each team’s basket
- Driving and rebounding lanes: Key zones for penetrating defenses and positioning for rebounds
- Elbows and free throw line extended: Strategic points on the court
The History of Basketball Court Dimensions
Since its invention by James Naismith in 1891, basketball court dimensions have evolved significantly. The initial courts used peach baskets as goals, which were later replaced by metal hoops and backboards. Over the years, court sizes and markings have been standardized to ensure consistent gameplay across different levels.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Basketball Court Perimeter
The basketball court perimeter is a crucial aspect of the game, encompassing all the key measurements and lines that define the playing area. Understanding the dimensions and markings of a basketball court is essential for players, coaches, and fans alike. This guide provides a detailed overview of the various components that make up the perimeter of a basketball court, ensuring a clear understanding of the game's layout.
- Overall Court Dimensions: The standard size for an NBA and NCAA basketball court is 94 feet long and 50 feet wide, while high school courts are slightly smaller, typically measuring 84 feet by 50 feet.
- The Three-Point Line: The distance from the basket to the three-point line varies by level of play. In the NBA, it is 23.75 feet at the top of the key and 22 feet at the corners. For NCAA men's games, the distance is 20.75 feet, and for high school, it is 19.75 feet.
- The Free-Throw Line: The free-throw line is 15 feet away from the backboard across all levels of play, allowing players a standardized distance for shooting free throws.
- The Key (Paint Area): The key, also known as the paint, is 16 feet wide in the NBA and 12 feet wide in NCAA and high school courts. This area is crucial for offensive and defensive play strategies.
- Center Circle: Located at midcourt, the center circle has a diameter of 12 feet and is where the game begins with a jump ball. It also serves as a reference point during gameplay.
- Restricted Area Arc: This semi-circular area under the basket prevents defensive players from drawing charging fouls within its boundaries. The radius of the arc is four feet in the NBA and three feet in NCAA games.
Dimensions and Markings
A basketball court's dimensions and markings vary slightly depending on the governing body, such as the NBA, NCAA, or FIBA. Here, we detail the measurements and markings common across various levels of play.
| Governing Body | Length (feet) | Width (feet) | Key Width (feet) | 3-Point Line (feet) | Free Throw Line (feet) | Rim Height (feet) |
| NBA | 94 | 50 | 16 | 23.75 | 15 | 10 |
| NCAA | 94 | 50 | 12 | 20.75 | 15 | 10 |
| FIBA | 91.9 | 49.2 | 16 | 22.15 | 15.09 | 10 |
| High School | 84 | 50 | 12 | 19.75 | 15 | 10 |
Key dimensions are critical for understanding the layout and play mechanics of a basketball court. The key width is larger in the NBA compared to the NCAA and high school courts, allowing for different playing strategies.
- Center Circle: The center circle has a diameter of 12 feet in most courts.
- 3-Point Line: The distance for the 3-point line varies, being farthest in the NBA at 23.75 feet.
- Free Throw Line: Consistently 15 feet from the backboard across all levels.
These standardized dimensions ensure consistency in gameplay, allowing players to transition between different levels without significant adjustment to court layout. The restricted arc under the basket, a 4-foot radius area where charging fouls cannot be drawn, is also a notable feature in professional and college courts.
NBA Court Specifications
The NBA court is designed with specific dimensions and markings to ensure a standardized playing environment. These specifications are critical for maintaining consistency across all games and venues. Below is a detailed overview of the NBA court's key features:
| Feature | Specification |
| Court Length | 94 feet (28.65 meters) |
| Court Width | 50 feet (15.24 meters) |
| Free Throw Line | 15 feet (4.57 meters) from the backboard |
| Three-Point Line | 23.75 feet (7.24 meters) from the basket at the top of the key, 22 feet (6.7 meters) in the corners |
| Key (Paint Area) | 16 feet (4.88 meters) wide |
| Basket Height | 10 feet (3.05 meters) from the court surface |
| Backboard | 6 feet (1.83 meters) wide by 3.5 feet (1.07 meters) high |
| Restricted Area | 4 feet (1.22 meters) radius from the center of the basket |
Detailed Court Markings
- Sidelines: The outer boundary lines running the length of the court.
- Baselines/End Lines: The boundary lines running width-wise at the ends of the court.
- Center Circle: A circle with a 6-foot radius used for the opening tip-off.
- Three-Point Line: An arc extending 23.75 feet from the basket, with a shorter 22 feet distance in the corners.
- Free Throw Line: Positioned 15 feet from the backboard, where free throws are taken.
- Key (Paint Area): The rectangular area below the basket extending 16 feet wide.
- Restricted Area: A semi-circular area 4 feet from the basket where defensive players cannot draw charges.

Additional Equipment
- Backboard: A transparent rectangle 6 feet wide and 3.5 feet high with a 2-inch white rectangle centered behind the basket.
- Baskets: Pressure-release NBA-approved metal rings 18 inches in diameter, with nets 18 inches long.
- Scoreboard: Digital displays synchronized with the game clock and shot clock.
- Lighting: LED lights outlining the backboard to indicate game and shot clock expirations.
These specifications ensure that NBA games are played on a uniform court, providing a consistent and fair playing environment for all teams and players.
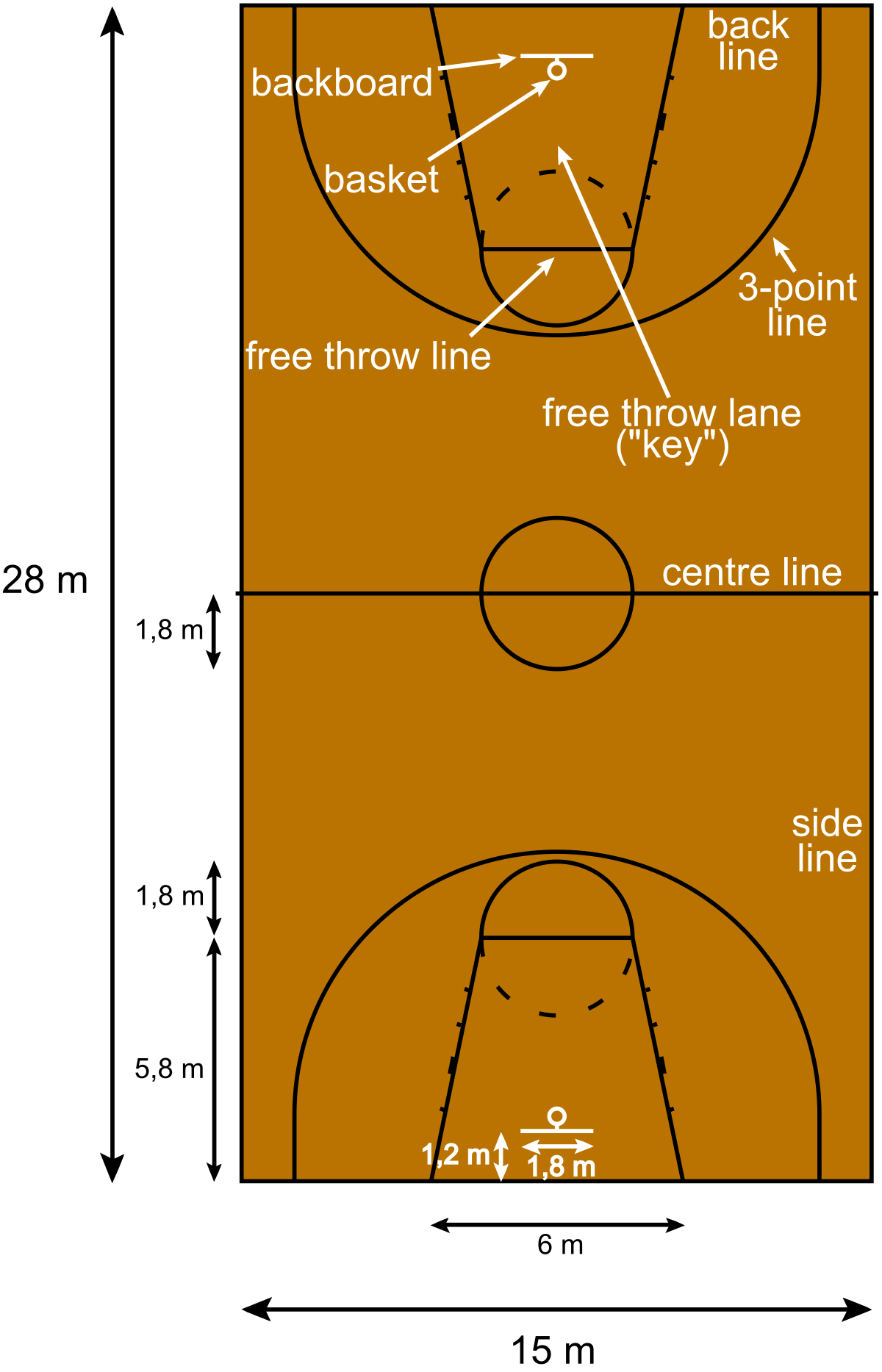
FIBA Court Specifications
The International Basketball Federation (FIBA) has specific dimensions and markings for basketball courts to ensure uniformity across international competitions. These specifications differ slightly from those of the NBA.
- The court measures 28 meters (91.86 feet) in length and 15 meters (49.21 feet) in width.
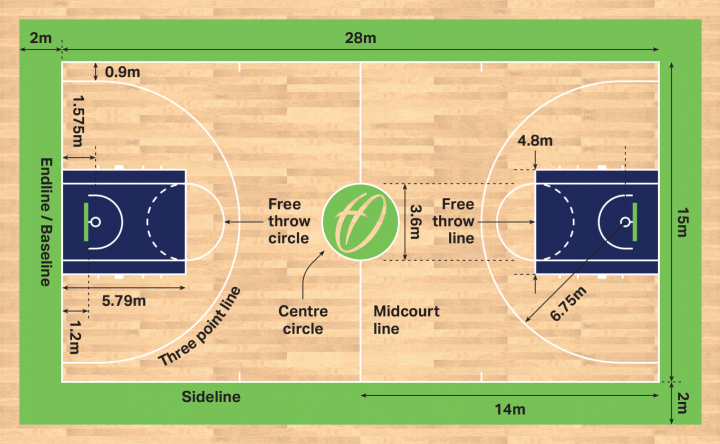
- The three-point line is 6.75 meters (22.15 feet) from the basket, except at the corners where it is 6.6 meters (21.65 feet).
- The free-throw line is 4.6 meters (15.09 feet) from the backboard.
- The key, also known as the shaded lane or restricted area, is a trapezoid shape, 4.9 meters (16.08 feet) wide at the free-throw line and 6 meters (19.69 feet) at the baseline.
- The no-charge semi-circle, located under the basket, has a radius of 1.25 meters (4.10 feet).
- The center circle, used for tip-offs, has a diameter of 3.6 meters (11.81 feet).
FIBA courts are designed to promote fluid and dynamic play, with slightly smaller dimensions than NBA courts to accommodate international play standards.
| Area | FIBA |
| Court Length | 28 meters (91.86 feet) |
| Court Width | 15 meters (49.21 feet) |
| Three-Point Line Distance | 6.75 meters (22.15 feet) |
| Free-Throw Line Distance | 4.6 meters (15.09 feet) |
| Key Width | 4.9 meters (16.08 feet) at free-throw line, 6 meters (19.69 feet) at baseline |
| No-Charge Semi-Circle Radius | 1.25 meters (4.10 feet) |
| Center Circle Diameter | 3.6 meters (11.81 feet) |
NCAA Court Specifications
The dimensions and specifications of an NCAA basketball court are carefully designed to ensure fair play and consistency across all games. Below are the detailed specifications for an NCAA basketball court:
Overall Court Dimensions
- Length: 94 feet
- Width: 50 feet
Key Areas and Markings
- Three-Point Line: The arc of the three-point line extends to 20 feet 9 inches from the center of the hoop.
- Free Throw Line: Located 15 feet from the backboard.
- Free Throw Lane (The Key): This area is 12 feet wide. The lane is also referred to as "the paint" and extends from the baseline to the free throw line.
Center Circle
The center circle is located at mid-court and has a radius of 6 feet, with an inner circle of 2 feet radius used for the jump ball at the start of the game.
Backboard and Rim
- Backboard Dimensions: 6 feet wide and 3.5 feet tall.
- Rim Height: The rim is set at a height of 10 feet from the floor.
Other Specifications
- Boundary Lines: All boundary lines are 2 inches wide, with the low block on the lane lines near the basket being 1 foot wide and 8 inches long.
- Restricted Area: An arc of 4 feet radius under the basket where defensive players cannot draw charging fouls.
These specifications ensure that the court meets the standards required for NCAA competitions, providing a consistent playing field for all athletes.
High School Court Specifications
The dimensions and markings of a high school basketball court are essential for ensuring consistency and fairness in the game. Below is a comprehensive guide to the specifications:
Court Dimensions
- The overall court size is 84 feet long and 50 feet wide.
- Junior high school courts may be smaller, typically 74 feet long and 42 feet wide.
Key Areas and Lines
- Foul Line: The foul line is 15 feet from the front of the backboard and 18 feet 10 inches from the baseline.
- The Key (Paint Area): The key is 12 feet wide, with the backboard extending 4 feet into it from the baseline.
- Three-Point Line: The three-point line is 19 feet 9 inches from the basket.
Backboard and Rim
- Backboard Dimensions: The backboard measures 6 feet wide by 42 inches high.
- Rim Height: The rim is 10 feet above the court surface.
- Rim Diameter: The diameter of the rim is 18 inches.
Additional Markings
- All line markings on the court are 2 inches wide.
- The center circle, used for the opening tip-off, has a radius of 6 feet.
Surface and Maintenance
High school basketball courts are typically made of wood or synthetic materials, ensuring durability and good performance. Proper maintenance, including regular dust mopping and spot cleaning, is crucial for preserving the court's condition and safety.
Maintaining the court involves daily dust mopping and immediate cleaning of any spills to prevent damage and ensure player safety. Additionally, walk-off mats at entrances help reduce dirt and moisture brought onto the court.
Center Circle
The center circle is a crucial part of the basketball court, serving as the starting point for the game with the initial tip-off. It is located at the midpoint of the court and has specific dimensions and features that are standardized across various levels of play.
- Dimensions: The center circle has a radius of 6 feet (1.83 meters).
- Location: It is situated directly in the center of the court, dividing it into two equal halves.
- Function: The primary function of the center circle is to host the jump ball at the beginning of each game and overtime period. It is also used for other jump ball situations that occur during the game.
Here's a detailed breakdown of the center circle specifications:
| Level of Play | Radius |
|---|---|
| NBA | 6 feet (1.83 meters) |
| NCAA | 6 feet (1.83 meters) |
| FIBA | 1.80 meters (5.9 feet) |
| High School | 6 feet (1.83 meters) |
The center circle is marked clearly on the court and is surrounded by a solid or broken line, depending on the level of play and the specific court design. This marking ensures that players, referees, and spectators can easily identify the area during gameplay.
The Key (Paint Area)
The key, also known as the paint or the restricted area, is a critical part of the basketball court located directly in front of each basket. It is used for several key aspects of the game, including scoring, defending, and rebounding. The dimensions and rules regarding the key can vary depending on the level of play.
Dimensions
- NBA: The key is 16 feet (4.88 meters) wide and extends 15 feet (4.57 meters) from the backboard to the free-throw line.
- NCAA: The key is 12 feet (3.66 meters) wide.
- High School: The key is also 12 feet (3.66 meters) wide.
- FIBA: The key is 16.08 feet (4.9 meters) wide.
Rules and Violations
There are specific rules associated with the key to ensure fair play:
- Three-Second Rule: An offensive player cannot stay in the key for more than three seconds while their team has possession of the ball. This rule is in place to prevent congestion and encourage movement.
- Defensive Three-Second Rule (NBA Only): A defender cannot remain in the key for more than three seconds unless they are actively guarding an opponent. Violations result in a technical foul.
- Restricted Area: A semi-circular area within the key where defensive players cannot draw charging fouls. This area promotes player safety by reducing collisions near the basket.
Strategic Importance
The key plays a significant role in both offensive and defensive strategies:
- Offensive Strategies: Players aim to score high-percentage shots within the key, often through layups or close-range jumpers. Dominating the key can lead to frequent scoring opportunities and force the defense to collapse, creating space for perimeter shots.
- Defensive Strategies: Controlling the key is crucial for preventing easy baskets. Teams often employ shot-blocking, physical play, and drawing charges to protect the paint. Effective defense in the key can force the opposition to take lower-percentage shots from outside.
Additional Markings
- Free Throw Lane: The area within the key extending from the baseline to the free throw line, where free throws are attempted.
- Elbows: The corners of the free throw line where it meets the lane lines. These are strategic points for setting up plays.
- Block: The area adjacent to the basket where players position themselves for rebounds during free throws.
Understanding the key's dimensions, rules, and strategic importance is essential for appreciating the complexities of basketball and the various tactics teams use to dominate this area of the court.
Three-Point Line
The three-point line, or arc, is a crucial feature of modern basketball courts, providing an added scoring dimension. Its position varies by league and competition, but it consistently serves to reward shots made from beyond the arc with three points.
- NBA: In the NBA, the three-point line forms an arc with a radius of 23.75 feet (7.24 meters) from the basket, but this distance shortens to 22 feet (6.70 meters) at the corners.
- FIBA: According to FIBA regulations, the three-point line is 6.75 meters (22.15 feet) from the basket, forming a uniform arc.
- NCAA (Men's): For NCAA men's basketball, the three-point line is set at 22.15 feet (6.75 meters) from the basket.
- NCAA (Women's): The NCAA women's three-point line is slightly closer, at 20.75 feet (6.32 meters) from the basket.
- High School: In U.S. high schools, the three-point line is 19.75 feet (6.02 meters) from the basket.
Arc Shape and Placement
The three-point line is not a perfect circle but an arc that is symmetrical about the center of the basket. Its radius ensures that all points on the line are equidistant from the basket, except for the straight sections at the corners of the court where the line becomes parallel to the sidelines. This adjustment is made to accommodate the court's rectangular shape.
Impact on Play
The introduction of the three-point line has significantly impacted basketball strategy, encouraging spacing and perimeter shooting. It also adds an exciting dynamic to the game, as teams often design plays specifically to create open three-point opportunities.
Measuring the Three-Point Line
- Mark the Center Point: Identify the center point directly beneath the basket, often referred to as the basket's center or the midpoint of the baseline.
- Set the Radius: Use a measuring tape to measure the correct distance from the basket's center to the arc's intended radius.
- Draw the Arc: Starting from the baseline, draw the arc with the measuring tape extended to the radius distance, marking points along the way to form a smooth curve.
- Extend to Corners: Draw straight lines from the endpoints of the arc to the sidelines, ensuring they are parallel to the baseline and maintain the required distance from the basket.
Key Considerations
- Uniformity: Ensure that the three-point line maintains a consistent distance from the basket across the entire court, except for the corner adjustments.
- Visibility: The line should be clearly visible and distinguished from other court markings to aid players and officials.
The three-point line's design and placement are essential for gameplay and vary slightly across different basketball governing bodies, but its fundamental role in enhancing the sport's scoring dynamics remains consistent.
Free Throw Line and Circle
The free throw line and circle are critical components of a basketball court, crucial for various gameplay elements including free throws and positioning during rebounds.
Free Throw Line Specifications
- Distance from Backboard: The free throw line is positioned exactly 15 feet (4.57 meters) from the backboard's front plane.
- Width: The line itself spans 2 inches (5 cm) in width, consistent with other court markings.
- Alignment: The free throw line is parallel to the baseline and runs across the width of the key (paint area).
Free Throw Circle Specifications
- Radius: The free throw circle has a radius of 6 feet (1.83 meters) from the center, which is the midpoint of the free throw line.
- Purpose: This circle is used to determine the positioning of players during a free throw attempt and defines the shooter’s area.
Layout and Measurement Steps
- Determine the Baseline: Begin by identifying the baseline and mark a point 15 feet (4.57 meters) from the backboard. This point will be the midpoint of the free throw line.
- Mark the Free Throw Line: Use a measuring tape to draw a line parallel to the baseline, ensuring it is 12 feet (3.66 meters) in length and centered on the point marked in step 1.
- Draw the Free Throw Circle: From the midpoint of the free throw line, use a string or measuring tape to draw a circle with a 6-foot (1.83 meters) radius.
Importance in Gameplay
The free throw line and circle are integral to the game, affecting both scoring and positioning:
- Free Throws: Players stand behind the free throw line to attempt unopposed shots awarded after certain fouls. This distance ensures a standardized shot across all levels of play.
- Rebounding Position: During a free throw, non-shooting players must stand outside the free throw circle and behind the free throw line extended until the ball is released.
Visual Representation
| Component | Measurement |
| Free Throw Line Distance from Backboard | 15 feet (4.57 meters) |
| Free Throw Line Length | 12 feet (3.66 meters) |
| Free Throw Circle Radius | 6 feet (1.83 meters) |
The free throw line and circle, with their precise measurements and placement, are fundamental in maintaining fairness and consistency in basketball, influencing both strategy and execution during play.

Half-Court Line
The half-court line, also known as the center line, is a critical feature of the basketball court, serving as a divider between the two halves of the court and playing a vital role in the game's rules and flow.
Location and Dimensions
- Placement: The half-court line is situated exactly halfway between the baselines, running parallel to them. It divides the court into two equal halves, each measuring 47 feet (14.33 meters) in length for an NBA court.
- Width: The line is typically 2 inches (5 cm) wide, consistent with other court markings.
Function and Rules
The half-court line plays several essential roles in basketball gameplay:
- Backcourt Violation: Once a team moves the ball across the half-court line into their frontcourt, they cannot return to the backcourt without committing a violation, promoting forward play and offensive momentum.
- Inbounding: The line is used during certain inbound plays, especially following a time-out or start of a quarter, where the ball is inbounded from the center or sideline near half-court.
- Over-and-Back Rule: Teams must advance the ball past the half-court line within a specific time frame (typically 8 or 10 seconds), encouraging quick and strategic play.
Center Circle Integration
At the midpoint of the half-court line lies the center circle, which is crucial for game starts and jump balls:
- Diameter: The center circle typically has a diameter of 12 feet (3.66 meters).
- Usage: The game begins with a jump ball at the center circle, and it may also be used for contested possession situations.
Marking and Measurements
- Determine Midpoint: Identify the exact midpoint of the court by measuring halfway between the baselines. Mark this point as the center of the half-court line.
- Draw the Line: Extend the line across the width of the court, ensuring it is straight and perpendicular to the sidelines. The total length of the line should match the width of the court, typically 50 feet (15.24 meters) for standard courts.
- Integrate Center Circle: From the midpoint of the half-court line, draw a circle with a radius of 6 feet (1.83 meters), ensuring it is centered on the line.
Visual Representation
| Component | Measurement |
| Half-Court Line Distance from Baselines | 47 feet (14.33 meters) for NBA |
| Half-Court Line Width | 2 inches (5 cm) |
| Center Circle Diameter | 12 feet (3.66 meters) |
The half-court line's strategic placement and clear marking are essential for ensuring the proper division of the court, guiding team strategies, and maintaining the flow of the game.
Backboard and Rim
The backboard and rim are fundamental components of a basketball court, forming the target area for scoring and significantly influencing the dynamics of the game.
Backboard Specifications
- Dimensions: The standard backboard measures 6 feet (1.83 meters) in width and 3.5 feet (1.07 meters) in height.
- Material: Backboards are typically made from tempered glass or acrylic to provide durability and a consistent rebound surface.
- Mounting: The backboard is mounted 10 feet (3.05 meters) above the playing surface, with its lower edge aligned parallel to the baseline.
Rim Specifications
- Diameter: The basketball rim (or hoop) has an inside diameter of 18 inches (45.72 cm).
- Height: The rim is positioned 10 feet (3.05 meters) above the playing surface, aligned with the backboard.
- Net: A net, typically 15-18 inches (38-46 cm) in length, is attached to the rim to slow the ball's descent and provide visual confirmation of a successful shot.
Backboard Markings
The backboard features specific markings to aid in shot accuracy:
- Square: A rectangular shooter's square, measuring 24 inches (61 cm) in width and 18 inches (45.72 cm) in height, is centered behind the rim. This helps players aim bank shots more effectively.
- White Border: The perimeter of the backboard is often bordered with a white line to enhance visibility for players and officials.
Assembly and Installation Steps
- Install the Support Structure: Ensure the supporting pole or wall mount is securely anchored and aligned vertically. The support should be strong enough to withstand the forces exerted during play.
- Mount the Backboard: Attach the backboard to the support structure at a height of 10 feet (3.05 meters). Ensure it is level and centered over the playing area.
- Attach the Rim: Securely attach the rim to the backboard at the specified height of 10 feet (3.05 meters). Verify that the rim is level and that the net hangs properly.
- Align and Mark: Mark the shooter's square and perimeter lines on the backboard using appropriate measurements and ensure they are visible and centered.
Visual Representation
| Component | Measurement |
| Backboard Width | 6 feet (1.83 meters) |
| Backboard Height | 3.5 feet (1.07 meters) |
| Rim Diameter | 18 inches (45.72 cm) |
| Rim Height | 10 feet (3.05 meters) |
| Shooter's Square Width | 24 inches (61 cm) |
| Shooter's Square Height | 18 inches (45.72 cm) |
The precise design and installation of the backboard and rim are essential for ensuring accurate shooting and consistent play, making them indispensable components of the basketball court.
Court Surfaces and Flooring
The surface and flooring of a basketball court are critical for player performance, safety, and the overall gameplay experience. Various materials are used depending on the location and level of play.
Types of Court Surfaces
Basketball courts can be classified based on their surface materials, each offering unique characteristics:
- Hardwood: The preferred choice for professional and collegiate indoor courts, hardwood surfaces (typically maple) provide a smooth, resilient surface that offers excellent ball bounce and player traction.
- Concrete: Common for outdoor courts, concrete is durable and low-maintenance but can be hard on players' joints due to its rigidity.
- Asphalt: Often used in outdoor courts, asphalt offers a balance between durability and cost-effectiveness but may develop cracks over time.
- Rubber: Rubber surfaces, often used in multi-purpose or indoor courts, offer good shock absorption and traction, making them a popular choice for recreational facilities.
- Modular Tiles: These are interlocking tiles that can be used both indoors and outdoors, offering easy installation and maintenance, along with decent performance and flexibility.
Surface Preparation and Installation
- Base Preparation: Ensure the base is leveled and compacted. For indoor courts, a subfloor system is often installed to provide cushioning and structural support.
- Material Application: Depending on the chosen surface material, apply it following the manufacturer’s guidelines. For hardwood, this involves laying and securing planks; for concrete or asphalt, this includes pouring and smoothing the surface.
- Finish and Lines: Apply a protective finish to hardwood surfaces to enhance durability and provide a smooth playing surface. Paint the necessary court lines and markings according to the specified regulations for the level of play.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly inspect the court for any damage or wear. Maintain the surface by cleaning and addressing any issues like cracks or loose tiles promptly.
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance of the court surface is crucial for longevity and performance:
- Cleaning: Regularly sweep and mop indoor courts to remove dust and debris. Outdoor courts should be cleaned to remove dirt, leaves, and other debris.
- Repairs: Address any cracks or damages immediately to prevent further deterioration. For hardwood courts, refinishing may be required periodically to restore the surface.
- Weather Protection: For outdoor courts, ensure proper drainage to prevent water accumulation and damage. Consider covering or protecting the court during extreme weather conditions.
Visual Representation
| Surface Type | Characteristics |
| Hardwood | Smooth, resilient, high-performance |
| Concrete | Durable, rigid, low-maintenance |
| Asphalt | Cost-effective, durable, may crack |
| Rubber | Shock-absorbing, good traction, multi-purpose |
| Modular Tiles | Easy installation, flexible, suitable for indoor and outdoor |
Choosing the right surface and maintaining it properly is essential for ensuring a safe and enjoyable basketball experience. Each type of surface has unique benefits that cater to different levels of play and environments.
FAQs on Court Dimensions
Understanding the dimensions of a basketball court is essential for players, coaches, and enthusiasts. Here are some frequently asked questions regarding court dimensions and their answers:
1. What are the standard dimensions of an NBA basketball court?
The standard dimensions of an NBA basketball court are 94 feet (28.65 meters) in length and 50 feet (15.24 meters) in width. The court is divided into two halves by the half-court line.
2. How does a FIBA court differ in size from an NBA court?
A FIBA court is slightly smaller, measuring 28 meters (91.86 feet) in length and 15 meters (49.21 feet) in width. This difference impacts the spacing and play dynamics.
3. What are the dimensions of the key (paint area) on a basketball court?
The key, or paint area, typically measures 16 feet (4.88 meters) wide for NBA and FIBA courts and 19 feet (5.8 meters) from the baseline to the free throw line. For NCAA, the key width is 12 feet (3.66 meters).
4. How far is the three-point line from the basket?
- NBA: The three-point line is 23.75 feet (7.24 meters) from the basket at the top and 22 feet (6.7 meters) at the corners.
- FIBA: The line is 6.75 meters (22.15 feet) from the basket.
- NCAA: For men, it's 22.15 feet (6.75 meters), and for women, it's 20.75 feet (6.32 meters).
- High School: The distance is 19.75 feet (6.02 meters).
5. How high is the basketball rim from the court surface?
The rim is positioned 10 feet (3.05 meters) above the court surface across all levels of play, including NBA, FIBA, NCAA, and high school.
6. What is the size of the backboard on a basketball court?
The standard backboard dimensions are 6 feet (1.83 meters) wide and 3.5 feet (1.07 meters) high. It is centered above the basket and extends horizontally from the baseline.
7. How large is the free throw circle?
The free throw circle has a radius of 6 feet (1.83 meters) and is centered at the midpoint of the free throw line, which is 15 feet (4.57 meters) from the backboard.
8. What are the dimensions of the restricted area under the basket?
The restricted area arc, where players cannot draw charges, extends 4 feet (1.22 meters) from the center of the basket. This applies to NBA and NCAA rules.
9. How wide is the half-court line?
The half-court line is typically 2 inches (5 cm) wide and runs the entire width of the court, dividing it into two equal halves.
10. What are the dimensions of the center circle?
The center circle has a diameter of 12 feet (3.66 meters). It is used for jump balls at the start of the game and in certain tie situations.
11. Are there any differences in court dimensions for youth basketball?
Youth basketball courts can vary in size, but they are typically smaller than professional or collegiate courts to accommodate younger players. Common dimensions for youth courts are around 74 feet (22.56 meters) in length and 42 feet (12.8 meters) in width.
Visual Summary
| Component | NBA | FIBA | NCAA | High School |
| Court Length | 94 feet (28.65 meters) | 28 meters (91.86 feet) | 94 feet (28.65 meters) | 84 feet (25.6 meters) |
| Court Width | 50 feet (15.24 meters) | 15 meters (49.21 feet) | 50 feet (15.24 meters) | 50 feet (15.24 meters) |
| Three-Point Line | 23.75 feet (7.24 meters) top, 22 feet (6.7 meters) corners | 6.75 meters (22.15 feet) | 22.15 feet (6.75 meters) men, 20.75 feet (6.32 meters) women | 19.75 feet (6.02 meters) |
| Rim Height | 10 feet (3.05 meters) | 10 feet (3.05 meters) | 10 feet (3.05 meters) | 10 feet (3.05 meters) |
| Backboard Dimensions | 6 feet (1.83 meters) x 3.5 feet (1.07 meters) | 6 feet (1.83 meters) x 3.5 feet (1.07 meters) | 6 feet (1.83 meters) x 3.5 feet (1.07 meters) | 6 feet (1.83 meters) x 3.5 feet (1.07 meters) |
These FAQs cover the essential dimensions of a basketball court, helping to clarify the standards and variations across different levels of play. Proper understanding and adherence to these dimensions ensure consistency and fairness in the game.
Hướng dẫn cách đo đạc sân bóng rổ và giới thiệu các tham số quan trọng của sân bóng rổ.
Đo Đạc Sân Bóng Rổ / Các Tham Số của Sân Bóng Rổ
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu về chu vi của sân bóng rổ và các yếu tố ảnh hưởng đến nó.
Chu vi của Sân Bóng Rổ Là Bao Nhiêu?