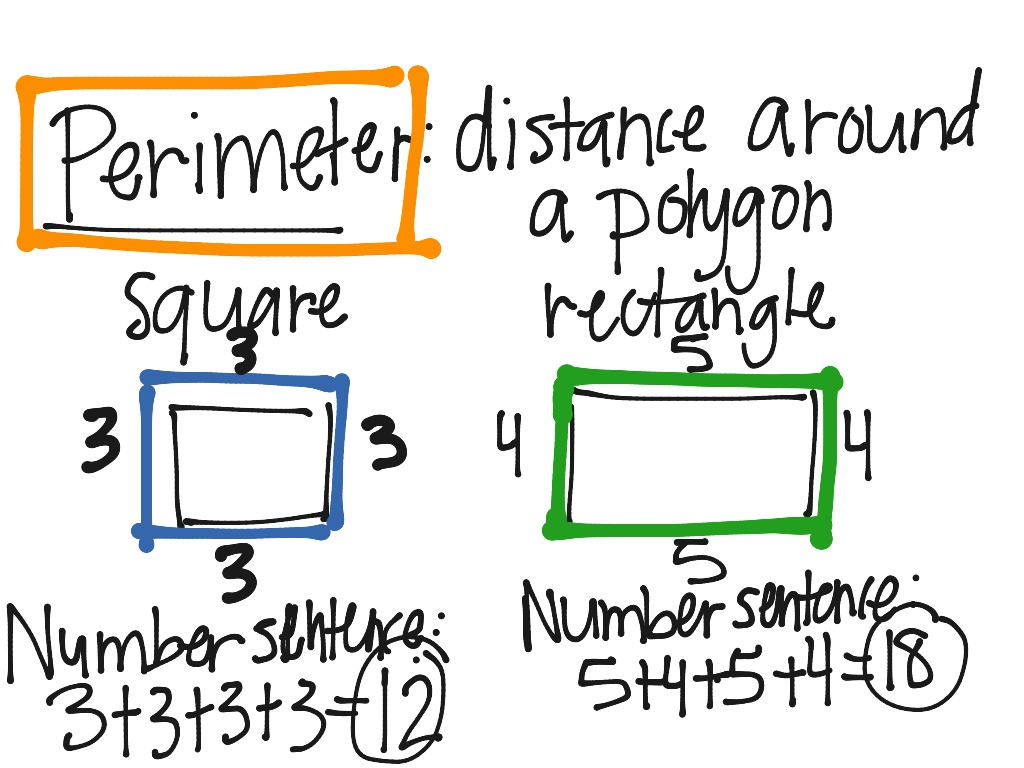
Topic how to work out the perimeter of a semicircle: Learning how to work out the perimeter of a semicircle is essential for solving geometry problems and practical applications. In this guide, we'll walk you through the simple steps and formulas needed to accurately calculate the perimeter of a semicircle, ensuring you understand the concepts and can apply them with ease.
Table of Content
- How to Work Out the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Understanding the Semicircle
- Properties of a Semicircle
- Calculating the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Example Calculation
- Basic Definitions
- Formula for Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Example Calculations
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Applications in Real Life
- Advanced Topics
- Practice Problems
- YOUTUBE:
How to Work Out the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle is the total length around the shape. A semicircle is half of a circle combined with the diameter of the circle. To calculate the perimeter, you need to know either the radius or the diameter of the semicircle.
Formula to Calculate the Perimeter
The formula to find the perimeter (P) of a semicircle is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Or, if you know the diameter (d):
\[ P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \]
Here, \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159, \( r \) is the radius, and \( d \) is the diameter of the semicircle.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the diameter (d) or radius (r) of the semicircle.
- Use the radius in the formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- If you have the diameter, first find the radius by dividing the diameter by 2.
- Plug the radius into the formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \) and calculate the perimeter.
Example Calculation
Let's say the diameter of a semicircle is 10 cm. First, find the radius:
\[ r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10 \, \text{cm}}{2} = 5 \, \text{cm} \]
Now use the radius to find the perimeter:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
\[ P = 3.14159 \times 5 \, \text{cm} + 2 \times 5 \, \text{cm} \]
\[ P = 15.70795 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} \]
\[ P = 25.70795 \, \text{cm} \]
Perimeter Table for Different Diameters
| Diameter (d) | Radius (r) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 cm | 5 cm | 25.71 cm |
| 20 cm | 10 cm | 51.42 cm |
| 30 cm | 15 cm | 77.13 cm |
Conclusion
By following these steps and using the provided formulas, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any semicircle. This method is applicable whether you have the radius or diameter of the semicircle. Practice with different values to become more comfortable with the calculations.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle is the total length of its boundary, which consists of the curved edge, half of the circumference of a full circle, and the straight edge, the diameter. Calculating the perimeter involves understanding both these components and using the formula:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle. This formula can also be written as:
\( P = r (\pi + 2) \)
Here are the steps to find the perimeter of a semicircle:
- Find the half the circumference of the circle using the formula \( \pi r \).
- Find the length of the diameter, which is \( 2r \).
- Add these two values together to get the perimeter.
For example, if the radius of the semicircle is 7 cm, the perimeter would be calculated as:
\( P = \pi \times 7 + 2 \times 7 = 22 + 14 = 36 \) cm
It's important to note that the perimeter of a semicircle is not simply half the perimeter of a full circle because the straight edge (diameter) must be included in the calculation.
Understanding the Semicircle
A semicircle is a geometric shape that represents half of a circle. When a circle is divided by its diameter, it creates two equal halves, each known as a semicircle. The semicircle includes a curved edge, which is half of the circle's circumference, and a straight edge, which is the diameter of the circle.
Properties of a Semicircle
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its boundary.
- Diameter (d): The length of the straight edge, which is twice the radius (d = 2r).
- Central Angle: The angle subtended by the diameter, which is always 180 degrees.
- Area: The area of a semicircle is half of the area of a full circle, given by the formula: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \).
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a semicircle is the sum of half the circumference of the circle and the diameter, given by the formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r \).
Calculating the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle includes both the curved part (half of the circle's circumference) and the straight part (the diameter). The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) is:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle:
- Find the radius (r) of the semicircle.
- Calculate half the circumference of the circle using the formula: \( \frac{1}{2} \pi d \) or \( \pi r \).
- Find the length of the diameter (d) using the formula: \( d = 2r \).
- Add the values obtained in steps 2 and 3: \( \pi r + 2r \).
- Provide the appropriate unit based on the unit of the radius.

Example Calculation
Let's consider an example where the radius of the semicircle is 7 cm. Using the formula, we can calculate the perimeter as follows:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
\( P = \pi \times 7 + 2 \times 7 \)
\( P = 22 + 14 \)
\( P = 36 \, \text{cm} \)
Therefore, the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 cm is 36 cm.
Basic Definitions
A semicircle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that represents half of a circle. It is formed when a circle is divided into two equal halves by a diameter. The semicircle includes the arc, which is half the circumference of the circle, and the straight line of the diameter.
To understand the perimeter of a semicircle, it's essential to know some basic terms and formulas:
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its boundary. For a semicircle, the radius remains the same as that of the original circle.
- Diameter (d): The length of a straight line passing through the center of the circle, connecting two points on the boundary. The diameter is twice the radius, \( d = 2r \).
- Circumference of a Circle: The total length of the boundary of a full circle, given by the formula \( 2\pi r \).
- Perimeter of a Semicircle: The sum of the length of the arc (half of the circumference of the original circle) and the diameter. This is calculated using the formula \( \pi r + 2r \), which can also be written as \( r(\pi + 2) \).
Let's break down the steps to find the perimeter of a semicircle:
- Find the radius (r) of the semicircle.
- Calculate half the circumference of the original circle using the formula \( \pi r \).
- Add the diameter \( 2r \) to the half circumference to get the total perimeter: \( \pi r + 2r \).
- Express the final result with the appropriate unit of measurement.
For example, if the radius of a semicircle is 7 cm:
- Half the circumference = \( \pi \times 7 = 22 \) cm (using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \)).
- Diameter = \( 2 \times 7 = 14 \) cm.
- Total perimeter = \( 22 + 14 = 36 \) cm.
Thus, the perimeter of the semicircle is 36 cm.
Formula for Perimeter of a Semicircle
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle involves understanding a few basic geometric principles. The perimeter of a semicircle is the sum of half the circumference of a circle and the diameter of the circle. The formula can be expressed as:
Perimeter of a semicircle \( P \) is given by:
\( P = \pi r + d \)
Where:
- \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14159 or \(\frac{22}{7}\)
- \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle
- \( d \) is the diameter of the semicircle, which is equal to \( 2r \)
Hence, the formula can also be written as:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
Or, more compactly:
\( P = r (\pi + 2) \)
Let's break this down into steps for a clearer understanding:
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle using \( 2\pi r \).
- Since a semicircle is half of a circle, divide the circumference by 2 to get \( \pi r \).
- Calculate the diameter of the circle, which is \( 2r \).
- Add the results of step 2 and step 3 to get the perimeter of the semicircle.
For example, if the radius of a semicircle is 7 units:
- Half of the circumference: \( \pi \times 7 = 21.99 \) units
- Diameter: \( 2 \times 7 = 14 \) units
- Perimeter: \( 21.99 + 14 = 35.99 \) units
Thus, the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 units is approximately 35.99 units.
Example Calculations
Here are detailed examples to illustrate how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle step by step.
Example 1
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 14 cm.
- Write down the formula: \( P = \pi r + 2r \)
- Substitute the radius into the formula: \( P = \pi \times 14 + 2 \times 14 \)
- Calculate the values: \( P = 3.14 \times 14 + 28 \)
- Simplify: \( P = 43.96 + 28 = 71.96 \, \text{cm} \)
Example 2
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 31 cm.
- Calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{31}{2} = 15.5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Write down the formula: \( P = \pi r + 2r \)
- Substitute the radius into the formula: \( P = \pi \times 15.5 + 2 \times 15.5 \)
- Calculate the values: \( P = 3.14 \times 15.5 + 31 \)
- Simplify: \( P = 48.67 + 31 = 79.67 \, \text{cm} \)
Example 3
Find the radius of a semicircle with a given perimeter of 48 cm.
- Write down the formula: \( P = \pi r + 2r \)
- Substitute the known perimeter into the formula: \( 48 = \pi r + 2r \)
- Factor out \( r \): \( 48 = r (\pi + 2) \)
- Solve for \( r \): \( r = \frac{48}{\pi + 2} = \frac{48}{3.14 + 2} = \frac{48}{5.14} \approx 9.34 \, \text{cm} \)
These examples highlight the straightforward process of calculating the perimeter of a semicircle using the formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \). Understanding and applying these steps will help solve similar problems with ease.
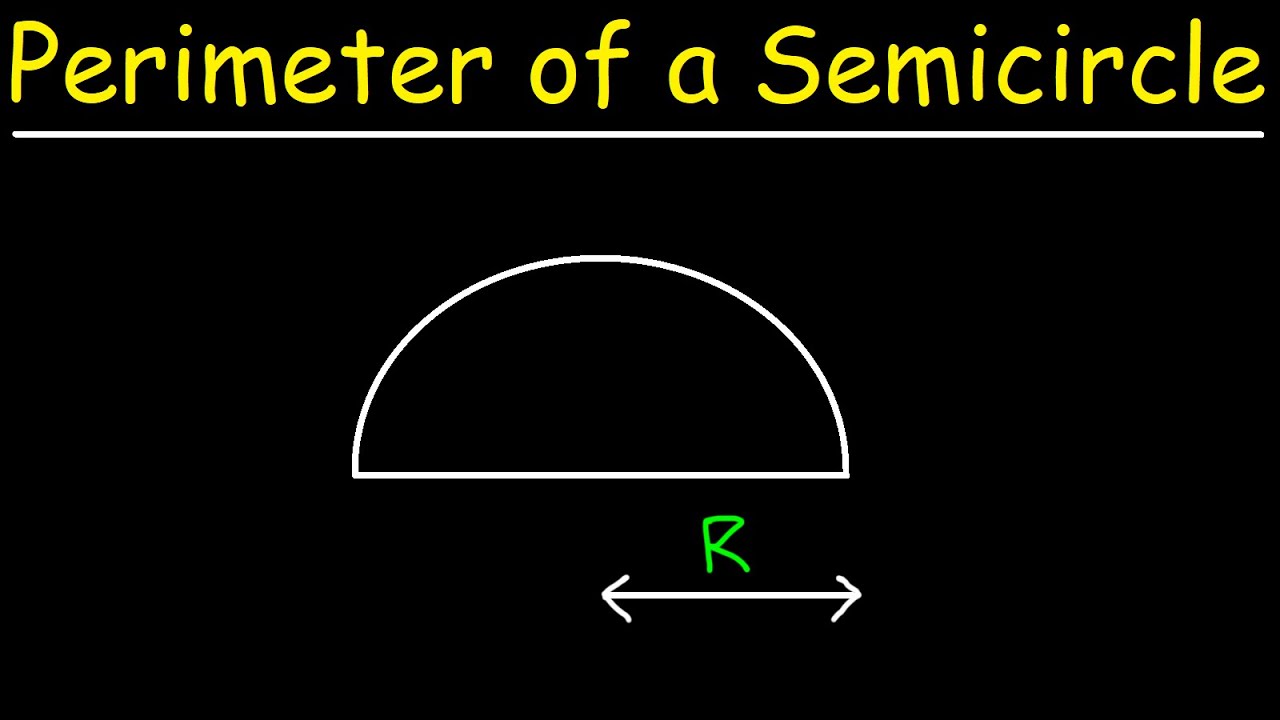
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle can be straightforward, but there are common mistakes that students and learners often make. Here are some of the frequent errors and how to avoid them:
- Incorrectly Calculating the Diameter:
The diameter is twice the radius. Ensure you correctly identify and use the diameter in your calculations. If the radius \( r \) is given, remember that the diameter \( d \) is \( d = 2r \).
- Omitting the Straight Edge:
When calculating the perimeter of a semicircle, it's essential to include the straight edge (diameter). The perimeter \( P \) of a semicircle is given by the formula:
\[ P = \pi r + d \] where \( d \) is the diameter.
- Using Incorrect Units:
Ensure all measurements are in the same units. Convert all measurements to the same unit before performing any calculations to avoid errors in the final perimeter value.
- Forgetting to Add Both Parts:
The perimeter of the semicircle includes both the curved part (half the circumference) and the straight edge (diameter). Some learners forget to add these two components together.
- Rounding Errors:
Be careful with rounding, especially if intermediate steps are required. Use appropriate precision and only round off the final answer to the required number of decimal places.
- Misinterpreting the Formula:
Understand and correctly apply the formula. The perimeter is not just the arc length but includes the straight edge as well. Ensure the formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \) is correctly used.
To avoid these common mistakes, follow these steps:
- Always double-check the given radius or diameter and convert them correctly.
- Ensure you include both the curved part and the straight edge in your calculations.
- Use consistent units throughout the problem.
- Carefully apply the formula and verify each step of your calculation.
- Review your final answer for accuracy and appropriate rounding.
Applications in Real Life
The perimeter of a semicircle has numerous practical applications across various fields. Understanding these applications can enhance comprehension and appreciation of this geometric concept. Here are some real-life scenarios where the perimeter of a semicircle is commonly used:
- Architecture and Construction:
Architects and builders frequently encounter semicircular structures such as arches, domes, and windows. Calculating the perimeter helps in determining the materials needed for construction and ensuring the design's stability and aesthetics. For instance, the perimeter calculation is crucial when designing arched doorways or windows, where precise measurements are necessary for fitting frames and glass.
- Landscaping and Garden Design:
In landscaping, semicircular designs are often used for pathways, garden beds, and decorative elements. Knowing the perimeter allows for accurate placement of borders, edging materials, and the overall layout. For example, creating a semicircular flower bed requires calculating the perimeter to determine the length of the edging material needed.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Design:
Manufacturers of items such as pipes, tubes, and cylindrical containers need to understand the perimeter of semicircular cross-sections for production and quality control. This knowledge ensures that components fit together correctly and function as intended. For example, in the production of semicircular gutters, calculating the perimeter helps in cutting materials to the correct dimensions.
- Urban Planning:
Urban planners use semicircular designs in various infrastructures, including roundabouts, parks, and amphitheaters. The perimeter calculation assists in planning and allocating space efficiently. For instance, designing a semicircular amphitheater involves calculating the perimeter to arrange seating and ensure clear sightlines for the audience.
- Art and Design:
Artists and designers often incorporate semicircular shapes into their work, from visual art compositions to interior design elements. Understanding the perimeter helps in creating balanced and harmonious designs. For example, when designing a semicircular mural, knowing the perimeter aids in planning the artwork's layout and dimensions.
These examples highlight the versatility and importance of understanding the perimeter of a semicircle in various real-world applications. Mastery of this concept can lead to more effective and efficient solutions in both professional and everyday contexts.
Advanced Topics
In this section, we will delve into some advanced topics related to the perimeter of a semicircle. These topics will enhance your understanding and help you apply the concept in more complex scenarios.
1. Perimeter of a Semicircle with an Added Border
Sometimes, you might encounter a semicircle that has an additional border or frame. To calculate the perimeter in such cases, follow these steps:
- Calculate the perimeter of the original semicircle using the formula: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Determine the width of the border.
- Add twice the width of the border to the diameter to get the new diameter: \( D_{new} = D + 2w \), where \( D \) is the original diameter and \( w \) is the width of the border.
- Calculate the new radius: \( r_{new} = \frac{D_{new}}{2} \).
- Use the new radius to calculate the perimeter of the larger semicircle: \( P_{new} = \pi r_{new} + 2r_{new} \).
- The total perimeter is the sum of the original perimeter and the perimeter of the border: \( P_{total} = P + (P_{new} - P) \).
2. Perimeter of a Semicircle Segment
A semicircle segment is a portion of a semicircle cut off by a chord. To find its perimeter:
- Find the length of the chord using the formula: \( c = 2 \sqrt{r^2 - h^2} \), where \( h \) is the height of the segment.
- Calculate the angle subtended by the segment at the circle’s center: \( \theta = 2 \arcsin(\frac{c}{2r}) \).
- Determine the arc length of the segment: \( L = r \theta \).
- The perimeter of the segment is the sum of the chord length and the arc length: \( P_{segment} = c + L \).
3. Perimeter of a Semicircle with Inner Radius
In some cases, you might need to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle that has a smaller semicircle removed from its center, creating an annulus shape. To find the perimeter of the annulus-shaped semicircle:
- Calculate the perimeter of the outer semicircle: \( P_{outer} = \pi R + 2R \), where \( R \) is the outer radius.
- Calculate the perimeter of the inner semicircle: \( P_{inner} = \pi r + 2r \), where \( r \) is the inner radius.
- The total perimeter is the difference between the outer and inner perimeters: \( P_{total} = P_{outer} - P_{inner} \).
4. Using Calculus to Derive the Perimeter
For those interested in a more mathematical approach, the perimeter of a semicircle can be derived using integral calculus. The process involves setting up an integral to calculate the arc length:
- Express the semicircle equation in Cartesian coordinates: \( y = \sqrt{r^2 - x^2} \).
- Set up the integral for the arc length: \( L = \int_{-r}^{r} \sqrt{1 + (\frac{dy}{dx})^2} \, dx \).
- Compute the derivative \( \frac{dy}{dx} \) and substitute into the integral.
- Simplify and solve the integral to find the arc length \( L = r\pi \).
- Add the diameter to obtain the total perimeter: \( P = r\pi + 2r \).
5. Perimeter of Composite Shapes Involving Semicircles
In practical applications, semicircles are often combined with other geometric shapes. Here’s how to calculate the perimeter for a common composite shape, a rectangle with semicircles on its ends:
- Determine the perimeter of the rectangle excluding the semicircles: \( P_{rect} = 2l \), where \( l \) is the length of the rectangle.
- Calculate the perimeter of the two semicircles, which together form a full circle: \( P_{semicircles} = \pi d \), where \( d \) is the diameter of the semicircles.
- The total perimeter is the sum of the rectangle’s perimeter and the semicircles’ perimeter: \( P_{total} = P_{rect} + P_{semicircles} \).
Practice Problems
To reinforce your understanding of calculating the perimeter of a semicircle, here are some practice problems. Try to solve them step-by-step and check your answers against the provided solutions.
Problem 1
Calculate the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 cm.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Substitute the given radius into the formula: \( P = \pi \times 7 + 2 \times 7 \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P = 7\pi + 14 \).
- Approximate using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P \approx 7 \times 3.14 + 14 = 21.98 + 14 = 35.98 \) cm.
Answer: The perimeter is approximately 35.98 cm.
Problem 2
A semicircle has a diameter of 10 inches. Find its perimeter.
- First, find the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \) inches.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Substitute the radius into the formula: \( P = \pi \times 5 + 2 \times 5 \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P = 5\pi + 10 \).
- Approximate using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P \approx 5 \times 3.14 + 10 = 15.7 + 10 = 25.7 \) inches.
Answer: The perimeter is approximately 25.7 inches.
Problem 3
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 15 meters, and then calculate the total perimeter when an additional 2 meters border is added around it.
- Calculate the perimeter of the original semicircle: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Substitute the given radius: \( P = \pi \times 15 + 2 \times 15 \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P = 15\pi + 30 \).
- Approximate using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P \approx 15 \times 3.14 + 30 = 47.1 + 30 = 77.1 \) meters.
- Determine the new radius with the added border: \( r_{new} = 15 + 2 = 17 \) meters.
- Calculate the perimeter of the larger semicircle: \( P_{new} = \pi \times 17 + 2 \times 17 \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P_{new} = 17\pi + 34 \).
- Approximate using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P_{new} \approx 17 \times 3.14 + 34 = 53.38 + 34 = 87.38 \) meters.
- The total perimeter is the new perimeter: \( P_{total} = 87.38 \) meters.
Answer: The total perimeter with the border is approximately 87.38 meters.
Problem 4
A semicircle is inscribed in a rectangle with a width of 12 cm. Find the perimeter of the semicircle.
- For an inscribed semicircle, the diameter of the semicircle is equal to the width of the rectangle: \( d = 12 \) cm.
- Find the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{12}{2} = 6 \) cm.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Substitute the radius into the formula: \( P = \pi \times 6 + 2 \times 6 \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P = 6\pi + 12 \).
- Approximate using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P \approx 6 \times 3.14 + 12 = 18.84 + 12 = 30.84 \) cm.
Answer: The perimeter is approximately 30.84 cm.
Problem 5
Given a semicircle with a radius of \( r \), express the perimeter formula and calculate the perimeter when \( r = 8 \) cm.
- Recall the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Substitute \( r = 8 \) cm into the formula: \( P = \pi \times 8 + 2 \times 8 \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P = 8\pi + 16 \).
- Approximate using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P \approx 8 \times 3.14 + 16 = 25.12 + 16 = 41.12 \) cm.
Answer: The perimeter is approximately 41.12 cm.
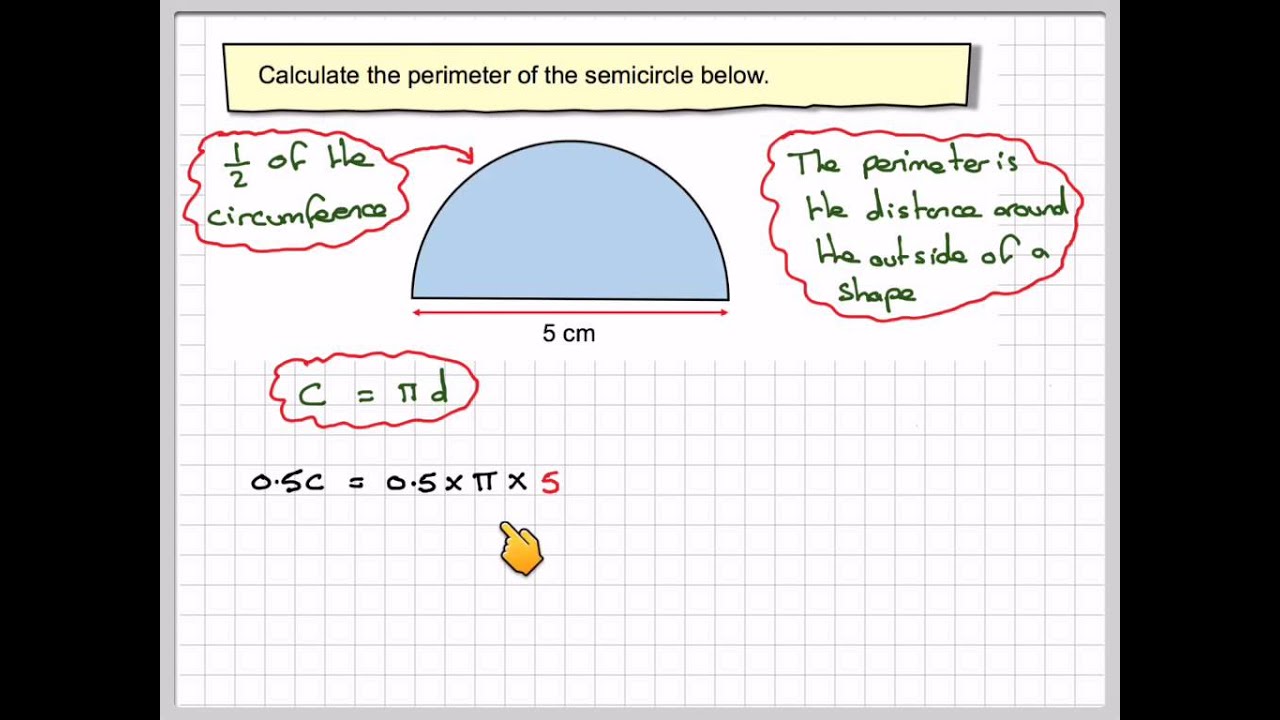
Cách Tính Chu Vi Hình Bán Nguyệt
READ MORE:
Chu Vi Hình Bán Nguyệt - Corbettmaths