Topic area and perimeter worksheets with answers pdf: Discover our comprehensive collection of area and perimeter worksheets with answers in PDF format. Perfect for students and educators, these resources simplify geometry concepts and provide ample practice. Enhance your understanding and ace your exams with these easy-to-download, expertly crafted worksheets. Start mastering area and perimeter today!
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets with Answers (PDF)
- Introduction
- Basic Concepts
- Area and Perimeter of Rectangles
- Area and Perimeter of Squares
- Area and Perimeter of Triangles
- Area and Perimeter of Circles
- Compound Shapes
- Word Problems
- Mixed Exercises
- Interactive Geometry Tools
- Advanced Geometry Worksheets
- YOUTUBE:
Area and Perimeter Worksheets with Answers (PDF)
Enhance your geometry skills with these comprehensive worksheets focused on area and perimeter. Suitable for students of various grade levels, these worksheets come with answers to aid in learning and self-assessment. Download the PDFs and start practicing today!
Topics Covered
- Calculating the area of rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles
- Determining the perimeter of various shapes
- Word problems involving area and perimeter
- Mixed exercises for comprehensive practice
Example Problems
Below are some examples of the types of problems included in the worksheets:
-
Rectangles
Calculate the area and perimeter of a rectangle with length \( l = 8 \, \text{cm} \) and width \( w = 5 \, \text{cm} \).
Solution:
Area: \( A = l \times w = 8 \, \text{cm} \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 40 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Perimeter: \( P = 2(l + w) = 2(8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) = 26 \, \text{cm} \)
-
Triangles
Calculate the area of a triangle with base \( b = 10 \, \text{cm} \) and height \( h = 6 \, \text{cm} \).
Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \, \text{cm} \times 6 \, \text{cm} = 30 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
-
Circles
Calculate the area and circumference of a circle with radius \( r = 7 \, \text{cm} \).
Area: \( A = \pi r^2 = \pi \times 7^2 \, \text{cm}^2 = 49\pi \, \text{cm}^2 \approx 153.94 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Circumference: \( C = 2\pi r = 2\pi \times 7 \, \text{cm} = 14\pi \, \text{cm} \approx 43.98 \, \text{cm} \)
Downloadable PDF Worksheets
Click the links below to download the worksheets in PDF format:
Answer Keys
For self-assessment, refer to the answer keys provided:
Additional Resources
For more practice and in-depth learning, check out these additional resources:

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is fundamental in geometry and everyday life. These measurements are essential for calculating the space within a boundary and the distance around it, respectively. Whether designing a garden, building a house, or solving math problems, mastering these concepts is crucial. Our comprehensive guide offers a variety of worksheets to help students practice and perfect their skills in calculating the area and perimeter of different shapes.
The worksheets provided in this guide cover a range of shapes including rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles, as well as compound shapes. Each worksheet is designed to help students grasp the basic concepts and progressively tackle more complex problems. The step-by-step approach ensures a solid understanding and the ability to apply these skills in various contexts.
For each shape, we start with the basic formulas:
- Rectangles: Area = length × width, Perimeter = 2 × (length + width)
- Squares: Area = side2, Perimeter = 4 × side
- Triangles: Area = 1/2 × base × height, Perimeter = sum of all sides
- Circles: Area = π × radius2, Circumference = 2 × π × radius
Our worksheets include a variety of exercises such as:
- Finding the area and perimeter of given shapes
- Solving word problems that apply these concepts in real-life scenarios
- Identifying and calculating the area of compound shapes
Each worksheet comes with detailed answer keys to help students verify their solutions and understand any mistakes. This iterative learning process is designed to reinforce their skills and boost confidence in their mathematical abilities.
We also offer advanced geometry worksheets and interactive tools to challenge students and deepen their understanding of these concepts. Our downloadable PDF worksheets are perfect for classroom use or home study, ensuring that learners have access to quality educational materials wherever they are.
Embark on this learning journey and master the calculations of area and perimeter with our expertly crafted worksheets!
Basic Concepts
Understanding the basic concepts of area and perimeter is essential for solving various mathematical problems. Here, we provide a comprehensive guide to the fundamental principles of area and perimeter.
Area: The area is a measure of the space inside a two-dimensional shape. It is expressed in square units (e.g., cm2, m2).
- Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length (\( l \)) by its width (\( w \)). The formula is:
\( \text{Area} = l \times w \)
- Square: The area of a square is found by squaring the length of one of its sides (\( s \)). The formula is:
\( \text{Area} = s^2 \)
- Triangle: The area of a triangle is determined by multiplying the base (\( b \)) by the height (\( h \)) and then dividing by 2. The formula is:
\( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
- Circle: The area of a circle is calculated by squaring the radius (\( r \)) and multiplying by π (pi). The formula is:
\( \text{Area} = \pi r^2 \)
Perimeter: The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. It is expressed in linear units (e.g., cm, m).
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is found by adding twice the length and twice the width. The formula is:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 2l + 2w \)
- Square: The perimeter of a square is calculated by multiplying the length of one side by 4. The formula is:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 4s \)
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides (\( a \), \( b \), and \( c \)). The formula is:
\( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \)
- Circle (Circumference): The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is found by multiplying the diameter (\( d \)) by π (pi), or twice the radius by π. The formulas are:
\( \text{Circumference} = \pi d \) or \( \text{Circumference} = 2\pi r \)
By mastering these basic formulas, students can easily solve problems involving the area and perimeter of various shapes, enhancing their mathematical skills and understanding.
Area and Perimeter of Rectangles
Understanding the area and perimeter of rectangles is fundamental in geometry. Below are step-by-step instructions, examples, and practice problems to help you master these concepts.
Basic Formulas
- Area (A): \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Perimeter (P): \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Identify the length (l) and width (w) of the rectangle.
- To find the area, multiply the length by the width: \( A = l \times w \).
- To find the perimeter, add the length and width, then multiply by 2: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \).
Example Problems
Example 1: Find the area and perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 8 units and a width of 5 units.
- Solution:
- Area: \( A = 8 \times 5 = 40 \) square units
- Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times (8 + 5) = 2 \times 13 = 26 \) units
Example 2: A rectangle has a length of 12 cm and a width of 7 cm. Calculate the area and perimeter.
- Solution:
- Area: \( A = 12 \times 7 = 84 \) square centimeters
- Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times (12 + 7) = 2 \times 19 = 38 \) centimeters
Practice Problems
- A rectangle has a length of 15 units and a width of 10 units. Find the area and perimeter.
- Calculate the area and perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 9 cm and a width of 4 cm.
- A rectangle has dimensions of 20 meters by 8 meters. Determine the area and perimeter.
Answer Key
| Problem | Area | Perimeter |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 150 square units | 50 units |
| 2 | 36 square centimeters | 26 centimeters |
| 3 | 160 square meters | 56 meters |
Area and Perimeter of Squares
Understanding the area and perimeter of squares is essential in geometry. Here, we will explore the formulas and provide examples to help you master these concepts.
Formulas
- Area of a Square: \( \text{Area} = \text{side} \times \text{side} = \text{side}^2 \)
- Perimeter of a Square: \( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \)
Example Problems
-
Calculate the area and perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 feet.
- Area:
- Perimeter:
\[
\text{Area} = 5 \times 5 = 25 \text{ square feet}
\]\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ feet}
\] -
Find the area and perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 cm.
- Area:
- Perimeter:
\[
\text{Area} = 7 \times 7 = 49 \text{ square cm}
\]\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 7 = 28 \text{ cm}
\]
Practice Worksheets
Below are some practice worksheets to help you improve your skills in calculating the area and perimeter of squares:
Interactive Exercises
Engage with interactive tools and exercises to further enhance your understanding:
Conclusion
By practicing these worksheets and engaging with interactive tools, you can become proficient in calculating the area and perimeter of squares. Keep practicing to solidify your understanding and improve your mathematical skills.
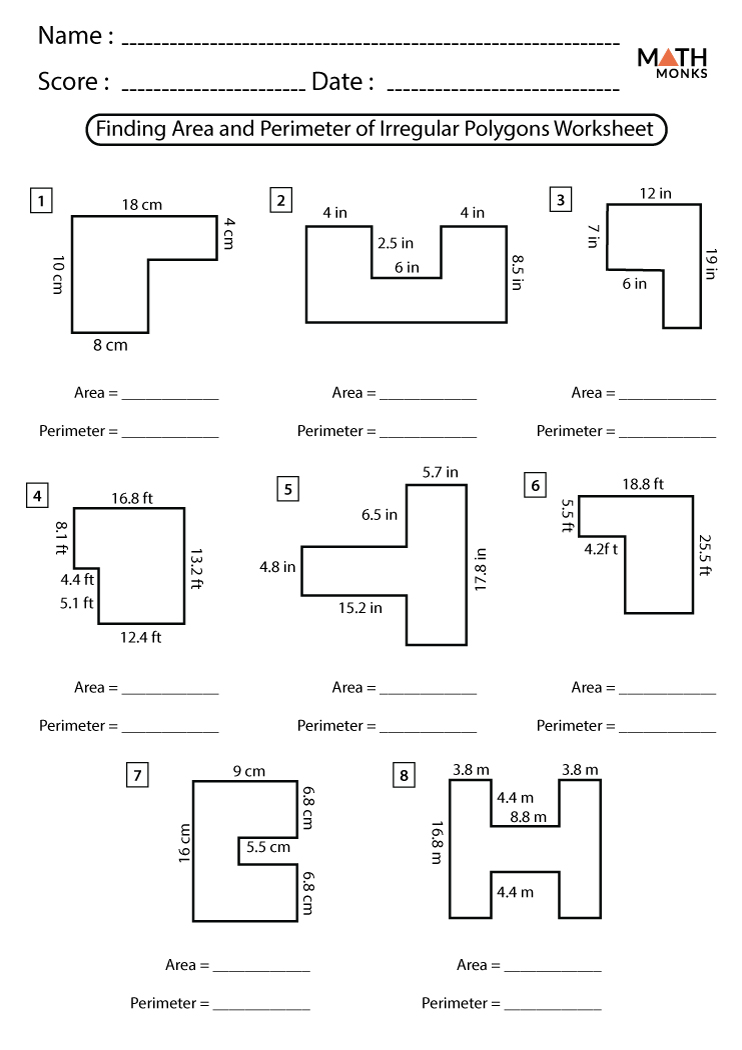
Area and Perimeter of Triangles
The area and perimeter of triangles are fundamental concepts in geometry. Understanding these concepts is crucial for solving various mathematical problems. Below are detailed explanations and formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of different types of triangles.
Types of Triangles
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal, and all three angles are 60 degrees.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal, and the angles opposite these sides are equal.
- Scalene Triangle: All three sides and angles are different.
Formulas for Area
- Equilateral Triangle:
The area \(A\) of an equilateral triangle with side length \(a\) is given by:
\[
A = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2
\] - Isosceles Triangle:
To find the area \(A\) of an isosceles triangle, you can use the base \(b\) and height \(h\):
\[
A = \frac{1}{2} b h
\] - Scalene Triangle:
For a scalene triangle, you can use Heron's formula. First, calculate the semi-perimeter \(s\):
\[
s = \frac{a + b + c}{2}
\]
Then, the area \(A\) is:
\[
A = \sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}
\]
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
Formulas for Perimeter
- Equilateral Triangle:
The perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = 3a
\]
where \(a\) is the length of a side. - Isosceles Triangle:
The perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = 2a + b
\]
where \(a\) is the length of the equal sides, and \(b\) is the base. - Scalene Triangle:
The perimeter \(P\) is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
Example Problems
Here are some example problems to practice calculating the area and perimeter of triangles.
- Example 1:
Find the area and perimeter of an equilateral triangle with side length 6 cm.
Solution:
Area:
\[
A = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 6^2 = 9\sqrt{3} \text{ cm}^2
\]
Perimeter:
\[
P = 3 \times 6 = 18 \text{ cm}
\] - Example 2:
Find the area and perimeter of an isosceles triangle with base 8 cm and height 5 cm, and the equal sides each 6 cm.
Solution:
Area:
\[
A = \frac{1}{2} \times 8 \times 5 = 20 \text{ cm}^2
\]
Perimeter:
\[
P = 2 \times 6 + 8 = 20 \text{ cm}
\] - Example 3:
Find the area and perimeter of a scalene triangle with sides 7 cm, 8 cm, and 9 cm.
Solution:
Semi-perimeter:
\[
s = \frac{7 + 8 + 9}{2} = 12 \text{ cm}
\]
Area:
\[
A = \sqrt{12(12 - 7)(12 - 8)(12 - 9)} = \sqrt{12 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3} = \sqrt{720} \approx 26.83 \text{ cm}^2
\]
Perimeter:
\[
P = 7 + 8 + 9 = 24 \text{ cm}
\]
Practice Worksheets
Download and practice with our worksheets to master the calculations of area and perimeter of triangles.
Area and Perimeter of Circles
Understanding the area and perimeter of circles is essential for solving various geometric problems. Below, we provide step-by-step explanations and examples to help you grasp these concepts effectively.
Key Concepts
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference.
- Diameter (d): The distance across the circle, passing through the center. It is twice the radius, \( d = 2r \).
- Circumference (C): The distance around the circle. It can be calculated using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \).
- Area (A): The amount of space enclosed within the circle. The formula for the area is \( A = \pi r^2 \).
Formulas
Here are the main formulas you'll need:
- Circumference: \( C = 2\pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \)
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
Example Problems
-
Example 1: Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
Using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \):
\[
C = 2 \times \pi \times 5 = 10\pi \approx 31.42 \, \text{cm}
\] -
Example 2: Find the area of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm.
First, find the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \, \text{cm} \).
Using the formula \( A = \pi r^2 \):
\[
A = \pi \times 5^2 = 25\pi \approx 78.54 \, \text{cm}^2
\]
Practice Exercises
Here are some exercises to help you practice finding the area and circumference of circles:
- Find the circumference of a circle with a radius of 7 cm.
- Find the area of a circle with a radius of 12 cm.
- Find the diameter of a circle with a circumference of 62.8 cm.
- Find the radius of a circle with an area of 314 cm².
Interactive Geometry Tools
Utilize online tools to visualize and calculate the area and circumference of circles. These tools can provide instant feedback and help you understand the relationships between radius, diameter, circumference, and area.
Additional Resources
For further practice, download worksheets and access online resources to deepen your understanding:
Compound Shapes
Compound shapes, also known as composite shapes, are shapes that are made up of two or more basic geometric shapes. To find the area and perimeter of compound shapes, it is essential to break them down into their simpler components.
Steps to Find the Area of Compound Shapes
- Identify and Separate the Shapes:
Look at the compound shape and identify the basic shapes that form it, such as rectangles, triangles, circles, etc.
- Calculate the Area of Each Basic Shape:
Use the appropriate formula for each shape:
- Rectangle: \(A = l \times w\)
- Triangle: \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\)
- Circle: \(A = \pi r^2\)
- Sum the Areas:
Add the areas of all the basic shapes together to find the total area of the compound shape.
Example Problem
Consider a compound shape consisting of a rectangle and a semicircle on top of the rectangle:
- Identify the Shapes:
The shape can be divided into a rectangle and a semicircle.
- Calculate the Area of the Rectangle:
If the rectangle has a length of 8 units and a width of 4 units:
\[ A_{\text{rectangle}} = l \times w = 8 \times 4 = 32 \, \text{units}^2 \] - Calculate the Area of the Semicircle:
If the semicircle has a diameter of 4 units, the radius is 2 units:
\[ A_{\text{semicircle}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi (2^2) = 2 \pi \approx 6.28 \, \text{units}^2 \] - Total Area:
Add the areas of the rectangle and the semicircle:
\[ A_{\text{total}} = 32 + 6.28 \approx 38.28 \, \text{units}^2 \]
Steps to Find the Perimeter of Compound Shapes
- Identify and Separate the Shapes:
Similar to finding the area, identify the basic shapes within the compound shape.
- Calculate the Perimeter of Each Basic Shape:
Use the appropriate formula for each shape, making sure to only include the outer edges that form the boundary of the compound shape:
- Rectangle: \(P = 2l + 2w\)
- Triangle: \(P = a + b + c\)
- Circle: \(P = 2\pi r\)
- Sum the Perimeters:
Add the lengths of the outer edges to find the total perimeter.
Example Problem
Consider the same compound shape (rectangle with a semicircle on top):
- Identify the Shapes:
Rectangle and semicircle.
- Calculate the Perimeter of the Rectangle:
If the rectangle has a length of 8 units and a width of 4 units:
\[ P_{\text{rectangle}} = 2l + 2w = 2(8) + 2(4) = 24 \, \text{units} \] - Calculate the Perimeter of the Semicircle:
Use the radius of 2 units:
\[ P_{\text{semicircle}} = \pi r = \pi (2) = 6.28 \, \text{units} \] - Total Perimeter:
Add the lengths of the outer edges, making sure to exclude the shared edge between the rectangle and the semicircle:
\[ P_{\text{total}} = 24 + 6.28 - 4 \approx 26.28 \, \text{units} \]
Word Problems
Solving word problems involving area and perimeter requires understanding the relationship between shapes and their dimensions. Here are some examples and steps to solve these problems:
Example 1: Rectangular Garden
Jane has a rectangular garden with a length of 12 meters and a width of 7 meters. She wants to put a fence around it and also wants to know the area for planting flowers.
- First, calculate the perimeter to find out how much fencing she needs:
Perimeter \( P = 2(l + w) \)
\( P = 2(12 \, \text{m} + 7 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 19 \, \text{m} = 38 \, \text{m} \)
- Next, calculate the area for planting:
Area \( A = l \times w \)
\( A = 12 \, \text{m} \times 7 \, \text{m} = 84 \, \text{m}^2 \)
Example 2: Circular Flower Bed
Sam wants to know the perimeter and area of a circular flower bed with a radius of 5 meters.
- Calculate the perimeter (circumference) using the formula:
Circumference \( C = 2\pi r \)
\( C = 2 \pi \times 5 \, \text{m} = 10 \pi \, \text{m} \approx 31.42 \, \text{m} \)
- Calculate the area:
Area \( A = \pi r^2 \)
\( A = \pi \times (5 \, \text{m})^2 = 25 \pi \, \text{m}^2 \approx 78.54 \, \text{m}^2 \)
Example 3: Composite Shape
A playground is composed of a rectangular area (20m by 10m) and a semicircular area with a diameter of 10m attached to one of the shorter sides.
- Calculate the area of the rectangular part:
Area \( A_{\text{rect}} = l \times w \)
\( A_{\text{rect}} = 20 \, \text{m} \times 10 \, \text{m} = 200 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Calculate the area of the semicircular part:
Radius \( r = \frac{d}{2} = 5 \, \text{m} \)
Area \( A_{\text{semi}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \)
\( A_{\text{semi}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi \times (5 \, \text{m})^2 = \frac{25\pi}{2} \, \text{m}^2 \approx 39.27 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Total area of the playground:
Total Area \( A_{\text{total}} = A_{\text{rect}} + A_{\text{semi}} \)
\( A_{\text{total}} = 200 \, \text{m}^2 + 39.27 \, \text{m}^2 = 239.27 \, \text{m}^2 \)
By breaking down each problem into smaller steps, you can easily solve complex word problems involving area and perimeter. Practice regularly with different shapes and scenarios to improve your skills.

Mixed Exercises
Mixed exercises on area and perimeter are designed to challenge students with a variety of problems that incorporate different shapes and compound figures. These exercises help in reinforcing the understanding of basic geometrical concepts while applying them to more complex problems. Below are some types of problems and examples:
- Calculate the area and perimeter of individual shapes like rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles.
- Solve problems involving the area and perimeter of compound shapes by breaking them down into simpler components.
- Apply formulas to find missing dimensions when given the area or perimeter.
- Work on real-life word problems to enhance practical understanding.
Example Problems
1. Simple Shapes
Calculate the area and perimeter of the following shapes:
- Rectangle with length 8 cm and width 5 cm.
- Square with side length 6 m.
- Triangle with base 10 cm and height 7 cm.
- Circle with radius 4 m.
Solutions:
- Rectangle:
- Area: \( A = l \times w = 8 \, \text{cm} \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 40 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(l + w) = 2(8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) = 26 \, \text{cm} \)
- Square:
- Area: \( A = s^2 = 6 \, \text{m} \times 6 \, \text{m} = 36 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( P = 4s = 4 \times 6 \, \text{m} = 24 \, \text{m} \)
- Triangle:
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \, \text{cm} \times 7 \, \text{cm} = 35 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( P = \text{sum of all sides} \) (needs the lengths of other sides)
- Circle:
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 = \pi \times 4^2 = 16\pi \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Circumference: \( C = 2\pi r = 2\pi \times 4 = 8\pi \, \text{m} \)
2. Compound Shapes
Calculate the area and perimeter of a compound shape formed by a rectangle and a semicircle:
- Rectangle with length 10 cm and width 6 cm, and a semicircle attached to one of the shorter sides with a radius of 3 cm.
Solution:
- Area:
- Rectangle area: \( 10 \, \text{cm} \times 6 \, \text{cm} = 60 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Semicircle area: \( \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi \times 3^2 = \frac{9\pi}{2} \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Total area: \( 60 \, \text{cm}^2 + \frac{9\pi}{2} \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Perimeter:
- Rectangle perimeter (excluding the side attached to the semicircle): \( 10 \, \text{cm} + 6 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} = 26 \, \text{cm} \)
- Semicircle perimeter (half the circumference plus the diameter): \( \frac{1}{2} \times 2\pi r + 2r = 3\pi + 6 \, \text{cm} \)
- Total perimeter: \( 26 \, \text{cm} + 3\pi \, \text{cm} \)
3. Real-Life Word Problems
John wants to build a rectangular garden that is 12 meters long and 8 meters wide. He also plans to place a circular pond with a radius of 3 meters in one corner of the garden. Calculate the total area available for planting after the pond is added.
Solution:
- Garden area: \( 12 \, \text{m} \times 8 \, \text{m} = 96 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Pond area: \( \pi \times 3^2 = 9\pi \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Planting area: \( 96 \, \text{m}^2 - 9\pi \, \text{m}^2 \)
These examples illustrate a range of problems involving simple shapes, compound figures, and real-life applications, helping students to develop a comprehensive understanding of area and perimeter.
Interactive Geometry Tools
Enhance your learning experience with these interactive geometry tools designed to help students understand and practice calculating area and perimeter.
-
GeoGebra:
An interactive platform offering a range of tools to explore various geometric concepts. You can create and manipulate geometric shapes, measure areas and perimeters, and visualize mathematical principles. Visit to start exploring.
-
Desmos Geometry:
A versatile tool for constructing geometric shapes, examining properties, and performing calculations. Desmos Geometry allows users to dynamically manipulate figures and see real-time updates of their measurements. Access it at .
-
PhET Area Builder:
Developed by the University of Colorado, this simulation lets you create shapes using colorful blocks and explore the relationship between area and perimeter. It's an excellent tool for visualizing concepts and solving problems interactively. Try it out at .
-
SplashLearn:
Provides a variety of interactive exercises and games focused on area and perimeter. Students can learn through engaging activities that reinforce their understanding of these geometric concepts. Check out the resources available at .
-
Toy Theater - Area Perimeter Explorer:
This tool allows students to drag and drop blocks to form shapes, automatically calculating their area and perimeter. It's a great hands-on resource for visual learners. Explore this tool at .
Advanced Geometry Worksheets
Our advanced geometry worksheets provide comprehensive practice for students seeking to deepen their understanding of complex geometric concepts. These worksheets are designed to challenge students and help them master advanced topics in geometry. Below is an overview of the types of advanced geometry worksheets available:
-
Angles and Triangles
- Classifying and measuring angles
- Calculating triangle dimensions using the Pythagorean Theorem
- Trigonometric ratios (SOHCAHTOA) for determining angles and sides
-
Quadrilaterals and Polygons
- Classifying different types of quadrilaterals
- Calculating interior and exterior angles of polygons
- Understanding the properties of various polygons
-
Circles
- Identifying and calculating radius, diameter, and circumference
- Exploring theorems involving chords, tangents, and secants
- Finding areas of sectors and segments
-
Coordinate Geometry
- Plotting points and shapes on the Cartesian plane
- Calculating distances and midpoints
- Analyzing slopes and equations of lines
-
Transformations
- Translating, rotating, reflecting, and dilating shapes
- Understanding congruence and similarity through transformations
-
Solid Geometry
- Calculating surface area and volume of 3D shapes
- Exploring cross-sections of solids
These worksheets are suitable for advanced high school students and can be used for both classroom practice and homework assignments. They are designed to not only test students' knowledge but also to provide them with opportunities to apply geometric concepts in various contexts.
Downloadable PDF versions of these worksheets are available for easy printing and use in educational settings. These resources ensure that students have ample practice material to excel in geometry.
Toán học - Lớp 5: Chu vi - Giải quyết bài toán tìm cạnh thiếu
READ MORE:
Math-Salamanders: diện tích và chu vi của các hình chữ nhật










