Topic what is 1/2 square: The concept of squaring a fraction like 1/2 can be confusing, but it's simple once you understand the process. In this article, we'll explore what it means to square 1/2, both in fraction and decimal forms, and provide practical examples to illustrate the calculations.
Table of Content
- Understanding 1/2 Squared
- Understanding the Concept of Squaring Fractions
- Calculating 1/2 Squared
- Square Calculator Tools
- Applications in Quilting
- Mathematical Properties and Examples
- Additional Resources and Further Reading
- YOUTUBE: How to Square a Number | What Does Squaring a Number Mean? | Exponents | Math with Mr. J
Understanding 1/2 Squared
When squaring a fraction like 1/2, you're essentially multiplying the fraction by itself. Here's a detailed explanation and steps to understand this calculation.
Mathematical Explanation
The square of a number \( x \) is \( x^2 \). For the fraction 1/2, this means:
\[
\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2 = \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{2} = \frac{1 \times 1}{2 \times 2} = \frac{1}{4}
\]
So, the fraction 1/2 squared equals 1/4 in fractional form.
Decimal Form
To convert the result to a decimal:
\[
\frac{1}{4} = 0.25
\]
Visual Representation
Visualizing the square of a fraction can help in understanding the concept better:
- If you imagine a square with a side length of 1/2, its area is the square of the side length.
- This means the area is \( \left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2 \), which is 1/4 of the total area if each side of the original square is 1 unit.
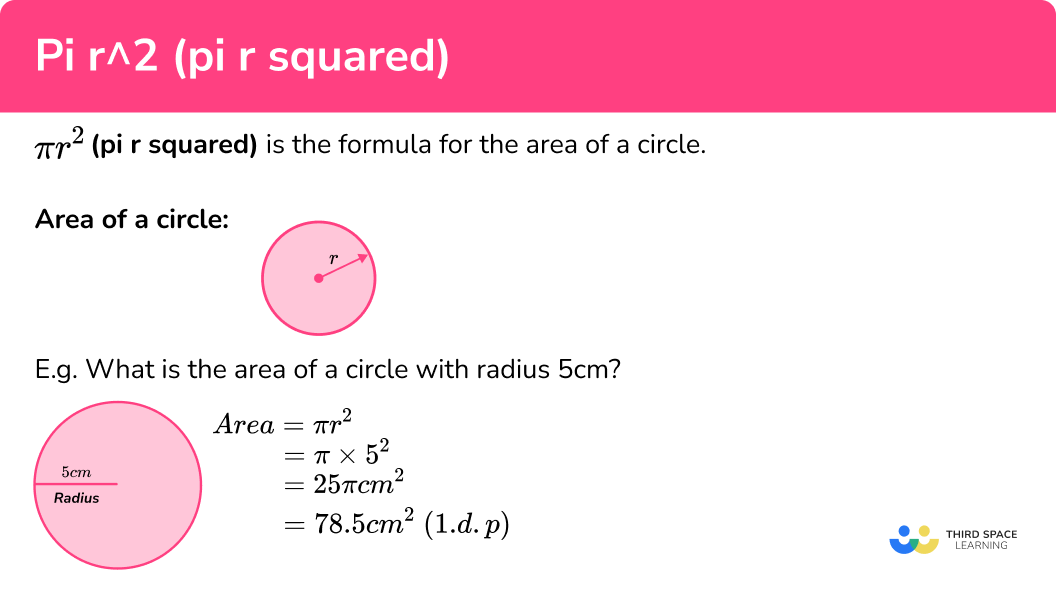
Application in Geometry
In geometry, squaring fractions is useful for calculating areas. For example:
- If you have a square with a side length of 1/2 unit, the area is \( \left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2 = \frac{1}{4} \) square units.
Additional Resources
For further reading, you can check these resources:
READ MORE:
Understanding the Concept of Squaring Fractions
Squaring fractions is an essential mathematical operation that involves multiplying a fraction by itself. Here's a step-by-step guide to understand how to square fractions:
- Identify the Fraction: Let's take the fraction \( \frac{1}{2} \) as an example.
- Multiply the Fraction by Itself: To square the fraction, multiply \( \frac{1}{2} \) by \( \frac{1}{2} \).
- \( \left( \frac{1}{2} \right)^2 = \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{2} \)
- Multiply the Numerators: Multiply the numerators (top numbers) of the fractions.
- \( 1 \times 1 = 1 \)
- Multiply the Denominators: Multiply the denominators (bottom numbers) of the fractions.
- \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \)
- Combine the Results: The result of squaring the fraction \( \frac{1}{2} \) is \( \frac{1}{4} \).
- \( \left( \frac{1}{2} \right)^2 = \frac{1}{4} \)
- Convert to Decimal (Optional): For a decimal representation, divide the numerator by the denominator.
- \( \frac{1}{4} = 0.25 \)
Thus, squaring the fraction \( \frac{1}{2} \) results in \( \frac{1}{4} \) or 0.25 in decimal form.
Calculating 1/2 Squared
Squaring a fraction like 1/2 involves multiplying the fraction by itself. Here's a step-by-step explanation of the process:
- Start with the fraction: \( \frac{1}{2} \).
- Square the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number) separately: \( \left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2 = \frac{1^2}{2^2} \).
- Calculate the squares: \( 1^2 = 1 \) and \( 2^2 = 4 \).
- Combine the results to get the final fraction: \( \frac{1}{4} \).
Thus, the square of 1/2 is \( \frac{1}{4} \) in fraction form. Converting this to a decimal, we get:
- \( \frac{1}{4} = 0.25 \).
Therefore, squaring 1/2 results in 0.25 in decimal form.
Square Calculator Tools
Square calculator tools are essential for accurately computing the square of any given number. These tools are designed to simplify the calculation process, whether you're working with whole numbers, fractions, or decimals. Below is a detailed overview of various square calculator tools and their functionalities.
- Basic Square Calculators: Enter any number to quickly find its square. These calculators often allow input of positive or negative whole numbers, decimals, and fractions.
- Fraction Square Calculators: Specialized for fractions, these calculators simplify the process of squaring fractions. For example, squaring 1/2 results in 1/4, and this can be confirmed using these tools.
- Negative Number Calculators: These calculators handle the squaring of negative numbers by ensuring correct interpretation using parentheses to avoid ambiguity. For example, (-4)^2 = 16.
- Area of a Square Calculators: These tools help in finding the area of a square given various parameters such as the side length, diagonal, perimeter, or inradius. They also explain the formulas used in these calculations.
- Half Square Triangle Calculators: Used primarily in quilting, these tools assist in creating half-square triangles by calculating the necessary fabric measurements and providing step-by-step instructions for cutting and assembling the pieces.
Using these tools, users can perform accurate calculations efficiently, whether for academic purposes, DIY projects, or professional tasks. Explore different calculator tools to find the one that best suits your needs.
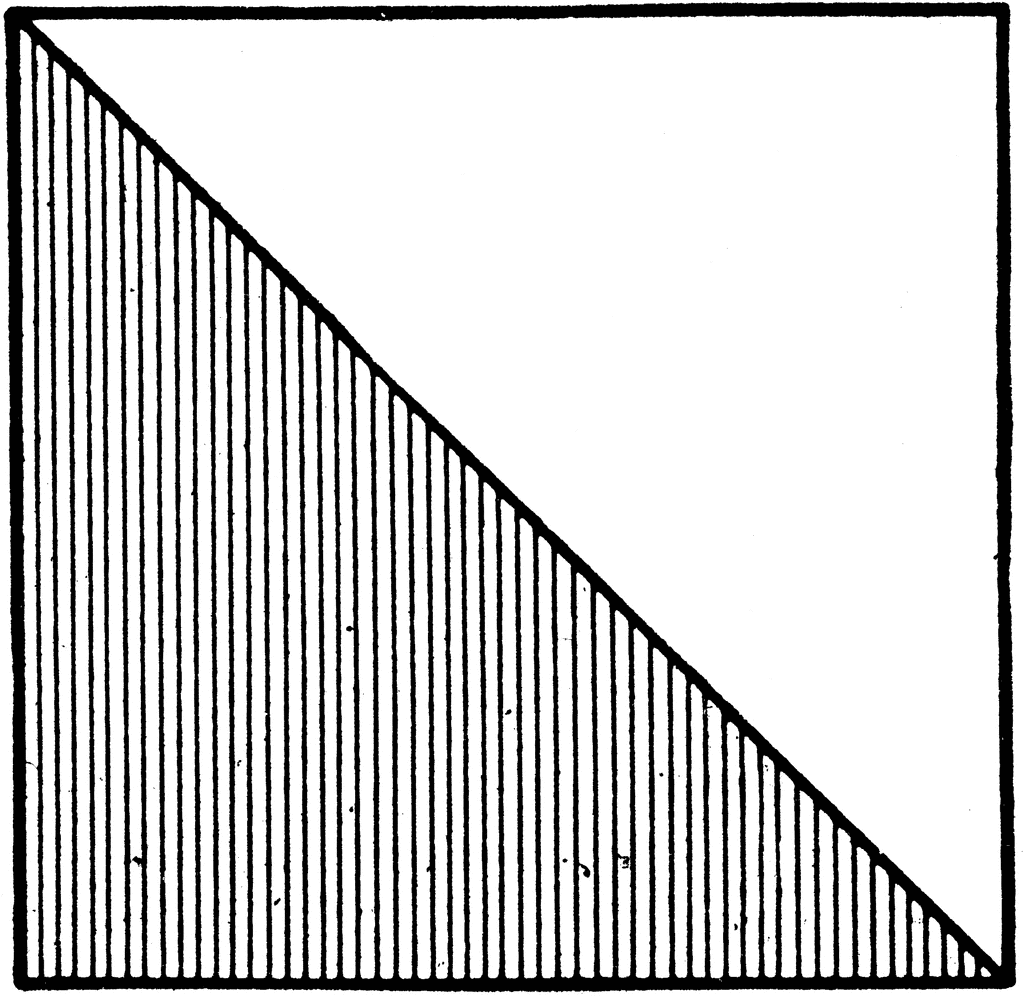
Applications in Quilting
Half-square triangles (HSTs) are a fundamental element in quilting, offering versatility and a range of design possibilities. They are created by combining two right-angle triangles to form a square, which can then be used in various quilt blocks and patterns. Here's a step-by-step guide on how HSTs are utilized in quilting:
- Creating Basic HST Units:
- Start with two squares of fabric, one light and one dark.
- Place the squares right sides together and draw a diagonal line from one corner to the opposite corner.
- Sew a seam 1/4 inch on either side of the drawn line.
- Cut along the drawn line to create two HST units.
- Press the seams towards the darker fabric.
- Design Possibilities:
- Combine HSTs to form various traditional quilt blocks such as pinwheels, chevrons, and stars.
- Use HSTs to create modern, geometric patterns with bold color contrasts.
- Incorporate HSTs into larger quilt designs to add texture and visual interest.
- Tools and Techniques:
- Use specialized rulers and templates to ensure accuracy and consistency in your HST units.
- Try different methods like the Easy 8 technique for efficient mass production of HSTs.
- Explore pre-cut fabric options to streamline the process and add variety to your quilt designs.
- Projects and Inspiration:
- Experiment with HSTs in small projects like table runners, pillows, and wall hangings to practice and perfect your technique.
- Look for quilt patterns and tutorials that incorporate HSTs to get inspired and expand your skills.
- Join quilting communities and participate in block exchanges or quilting bees to share ideas and learn from others.
Mathematical Properties and Examples
Understanding the mathematical properties and examples related to squaring fractions is crucial for a solid foundation in mathematics. This section will delve into the various properties that define fractions and how they behave when squared.
When we square a fraction, we multiply the fraction by itself. For example, squaring \( \frac{1}{2} \) involves the following steps:
- Write the fraction: \( \frac{1}{2} \)
- Multiply the fraction by itself: \( \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{2} \)
- Multiply the numerators: \( 1 \times 1 = 1 \)
- Multiply the denominators: \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \)
- Combine the results: \( \frac{1}{4} \)
Thus, \( \left( \frac{1}{2} \right)^2 = \frac{1}{4} \).
Here are some key properties and examples related to squaring fractions:
- Commutative Property: The order in which two numbers are multiplied does not change the product. For fractions, \( a \times b = b \times a \).
- Associative Property: The way in which numbers are grouped in multiplication does not change their product. For fractions, \( (a \times b) \times c = a \times (b \times c) \).
- Identity Property: The product of any number and one is the number itself. For fractions, \( a \times 1 = a \).
- Inverse Property: The product of a fraction and its reciprocal is one. For example, \( \frac{a}{b} \times \frac{b}{a} = 1 \).
Consider the following example to illustrate these properties:
If we square the fraction \( \frac{3}{4} \), we follow these steps:
- Write the fraction: \( \frac{3}{4} \)
- Multiply the fraction by itself: \( \frac{3}{4} \times \frac{3}{4} \)
- Multiply the numerators: \( 3 \times 3 = 9 \)
- Multiply the denominators: \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \)
- Combine the results: \( \frac{9}{16} \)
Therefore, \( \left( \frac{3}{4} \right)^2 = \frac{9}{16} \).
Understanding these properties helps in performing various mathematical operations with fractions, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in calculations.
Additional Resources and Further Reading
For those who wish to explore the topic of squaring fractions further, here are some valuable resources and additional reading materials:
- Online Calculators: Use online square calculators to practice and verify your results when working with fractions.
- Educational Videos: Platforms like Khan Academy and YouTube offer detailed video tutorials on the concept of squaring fractions and other mathematical operations.
- Math Textbooks: Refer to algebra and pre-algebra textbooks that cover the topic of fractions and their properties in detail.
- Interactive Math Websites: Websites such as Mathway and Wolfram Alpha provide interactive tools and step-by-step solutions for squaring fractions and other math problems.
- Practice Worksheets: Download and print practice worksheets from educational websites to improve your skills through repeated exercises.
- Tutoring Services: Consider using online tutoring services or local tutors who can provide personalized assistance and answer your specific questions.
By utilizing these resources, you can deepen your understanding and proficiency in working with fractions and their mathematical properties.
How to Square a Number | What Does Squaring a Number Mean? | Exponents | Math with Mr. J
Why does "x to the half power" mean square root?
Lesson 03 Units and Square Units - SimpleStep Learning
Square-0, Square-1, Square-2...!?
Square 1 to 20 || Listen and learn square of 1 to 20
Squares 1 to 50 || Learn 1 to 50 square root
READ MORE: