Topic perimeter word problems: Perimeter word problems are a fantastic way to enhance your math skills while solving real-world scenarios. This article will guide you through various examples and techniques, helping you understand and master the concept of perimeter. Get ready to boost your confidence in math with these practical and engaging problems!
Table of Content
- Perimeter Word Problems
- Introduction to Perimeter Word Problems
- Basic Perimeter Concepts
- Understanding Shapes and Their Perimeters
- Rectangle Perimeter Problems
- Square Perimeter Problems
- Triangle Perimeter Problems
- Perimeter of Regular Polygons
- Composite Shape Perimeter Problems
- Perimeter Problems with Missing Dimensions
- Real-Life Applications of Perimeter
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- Advanced Perimeter Word Problems
- Tips and Tricks for Solving Perimeter Problems
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Conclusion and Further Reading
- YOUTUBE: Video giới thiệu về các bài toán từ ngữ liên quan đến chu vi, giúp học sinh hiểu và giải quyết các bài toán một cách dễ dàng.
Perimeter Word Problems
Understanding perimeter word problems involves determining the total distance around a two-dimensional shape. These problems can vary in complexity and are useful in real-life situations such as fencing a yard or framing a picture. Below are various examples and solutions to help understand how to solve perimeter word problems.
Basic Perimeter Problems
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \):
- Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Example: If \( l = 5 \, \text{cm} \) and \( w = 3 \, \text{cm} \), then \( P = 2(5) + 2(3) = 10 + 6 = 16 \, \text{cm} \).
- Find the perimeter of a square with side length \( s \):
- Formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Example: If \( s = 4 \, \text{cm} \), then \( P = 4(4) = 16 \, \text{cm} \).
Intermediate Perimeter Problems
- Calculate the perimeter of a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \):
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Example: If \( a = 3 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 4 \, \text{cm} \), and \( c = 5 \, \text{cm} \), then \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{cm} \).
- Find the perimeter of a regular pentagon with side length \( s \):
- Formula: \( P = 5s \)
- Example: If \( s = 2 \, \text{cm} \), then \( P = 5(2) = 10 \, \text{cm} \).
Advanced Perimeter Problems
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle given its area \( A \) and length \( l \):
- Area formula: \( A = l \times w \)
- Solve for width: \( w = \frac{A}{l} \)
- Perimeter formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Example: If \( A = 20 \, \text{cm}^2 \) and \( l = 4 \, \text{cm} \), then \( w = \frac{20}{4} = 5 \, \text{cm} \) and \( P = 2(4) + 2(5) = 8 + 10 = 18 \, \text{cm} \).
- Find the perimeter of a composite shape consisting of a rectangle and a semicircle with diameter \( d \):
- Rectangle perimeter: \( P_{\text{rect}} = 2l + 2w \)
- Semicircle perimeter (excluding diameter): \( P_{\text{semi}} = \pi r \) where \( r = \frac{d}{2} \)
- Total perimeter: \( P = P_{\text{rect}} + P_{\text{semi}} \)
- Example: If the rectangle has \( l = 8 \, \text{cm} \), \( w = 4 \, \text{cm} \), and the semicircle has \( d = 4 \, \text{cm} \), then \( r = 2 \, \text{cm} \).
- \( P_{\text{rect}} = 2(8) + 2(4) = 16 + 8 = 24 \, \text{cm} \)
- \( P_{\text{semi}} = \pi(2) = 2\pi \, \text{cm} \)
- Total \( P = 24 + 2\pi \approx 24 + 6.28 = 30.28 \, \text{cm} \)
Practice Problems
- A rectangular garden has a length of 10 meters and a width of 6 meters. What is the perimeter?
- A square has a side length of 7 meters. Calculate its perimeter.
- The sides of a triangle are 5 cm, 12 cm, and 13 cm. Find its perimeter.
- A regular hexagon has a side length of 3 cm. Determine the perimeter.
- A rectangle has an area of 36 square meters and a length of 9 meters. Find its perimeter.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter Word Problems
Perimeter word problems are an essential part of geometry that help students understand the concept of measuring the total distance around various shapes. These problems not only enhance mathematical skills but also apply to real-world scenarios such as determining the length of fencing needed for a garden or the border length of a picture frame.
The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides of a two-dimensional shape. The general formula for calculating the perimeter depends on the type of shape:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: \( P = 4s \) where \( s \) is the side length.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Regular polygons: \( P = n \times s \) where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the side length.
Here are the steps to solve perimeter word problems effectively:
- Read the Problem Carefully: Understand what is being asked and identify the shape involved.
- Identify the Dimensions: Note the given dimensions and what needs to be calculated.
- Apply the Appropriate Formula: Use the formula for the perimeter of the shape involved.
- Perform the Calculations: Substitute the known values into the formula and solve for the perimeter.
- Check Your Work: Review the problem and your calculations to ensure accuracy.
Let's look at an example:
Example Problem: A rectangular garden has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. What is the perimeter?
Solution:
- Identify the shape: Rectangle
- Given: \( l = 8 \, \text{m} \), \( w = 5 \, \text{m} \)
- Formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Calculation: \( P = 2(8) + 2(5) = 16 + 10 = 26 \, \text{m} \)
- Answer: The perimeter of the garden is 26 meters.
By practicing perimeter word problems, you can improve your problem-solving skills and gain confidence in tackling various mathematical challenges.
Basic Perimeter Concepts
The concept of perimeter is fundamental in geometry, representing the total distance around a two-dimensional shape. Understanding and calculating the perimeter is crucial for solving various real-world problems, from fencing a yard to framing a picture.
Perimeter can be calculated for different shapes using specific formulas. Here are the basic formulas for common shapes:
- Rectangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is given by: \[ P = 2l + 2w \] where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: The perimeter \( P \) of a square is given by: \[ P = 4s \] where \( s \) is the side length.
- Triangle: The perimeter \( P \) of a triangle is the sum of its side lengths: \[ P = a + b + c \] where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the side lengths.
- Regular Polygons: For a regular polygon with \( n \) sides, each of length \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) is: \[ P = n \times s \]
- Circle (Circumference): The perimeter (circumference) \( C \) of a circle is: \[ C = 2\pi r \] where \( r \) is the radius.
Understanding these formulas is the first step in solving perimeter word problems. Let’s break down the steps to solve these problems:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of shape for which the perimeter needs to be calculated.
- Note the Given Dimensions: Identify and list the dimensions provided in the problem (e.g., length, width, side length, radius).
- Select the Appropriate Formula: Choose the correct formula based on the shape identified.
- Substitute the Values: Plug the given dimensions into the selected formula.
- Calculate the Perimeter: Perform the arithmetic operations to find the perimeter.
- Verify the Answer: Double-check the calculations to ensure accuracy.
Let's go through an example:
Example Problem: Calculate the perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 meters.
Solution:
- Identify the shape: Square
- Given: \( s = 7 \, \text{m} \)
- Formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Calculation: \( P = 4(7) = 28 \, \text{m} \)
- Answer: The perimeter of the square is 28 meters.
Mastering these basic perimeter concepts will build a strong foundation for tackling more complex perimeter word problems.
Understanding Shapes and Their Perimeters
Understanding the perimeters of different shapes is fundamental to solving perimeter word problems. The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. Below, we will discuss how to find the perimeters of various basic shapes.
Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding together the lengths of all four sides. For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 2l + 2w \]
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units, the perimeter would be:
\[ P = 2(5) + 2(3) = 10 + 6 = 16 \text{ units} \]
Perimeter of a Square
A square has four equal sides. If each side has length \( s \), the formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 4s \]
For example, if each side of a square is 4 units long, the perimeter would be:
\[ P = 4(4) = 16 \text{ units} \]
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. For a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
For example, if a triangle has sides of lengths 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units, the perimeter would be:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ units} \]
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
A regular polygon has all sides of equal length. If a regular polygon has \( n \) sides each of length \( s \), the formula for the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = n \cdot s \]
For example, if a regular hexagon (6 sides) has each side of length 2 units, the perimeter would be:
\[ P = 6 \cdot 2 = 12 \text{ units} \]
Examples and Practice
- Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with length 8 units and width 5 units.
- Find the perimeter of a square with each side measuring 7 units.
- Determine the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 6 units, 7 units, and 8 units.
- What is the perimeter of a regular pentagon with each side measuring 3 units?
Understanding these formulas and practicing with various shapes will help you master perimeter word problems.
Rectangle Perimeter Problems
Understanding the perimeter of a rectangle is crucial for solving various word problems. The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the outside of the rectangle. It is calculated by adding up all the sides of the rectangle. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is:
\( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
Below are steps and examples to help you solve perimeter problems involving rectangles:
Steps to Solve Rectangle Perimeter Problems
- Identify the length and width: Read the problem carefully to determine the dimensions of the rectangle.
- Use the perimeter formula: Apply the formula \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \) to find the perimeter.
- Substitute the values: Plug in the length and width into the formula.
- Perform the calculations: Carry out the arithmetic operations to find the perimeter.
- Include units: Don't forget to include the appropriate units in your final answer.
Example Problems
Here are a few example problems to illustrate the steps:
- Example 1: A rectangle has a length of 8 cm and a width of 5 cm. What is the perimeter?
- Example 2: The width of a rectangle is 6 cm less than its length. If the perimeter is 52 cm, what are the dimensions of the rectangle?
- Example 3: A rectangular garden is 3 times as long as it is wide. If the perimeter is 48 meters, what are the dimensions?
Using the formula: \( P = 2 \times (8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) = 2 \times 13 \, \text{cm} = 26 \, \text{cm} \)
Let the length be \( L \). Then, the width is \( L - 6 \, \text{cm} \). Using the perimeter formula:
\( 52 = 2 \times (L + (L - 6)) \)
Simplifying: \( 52 = 2 \times (2L - 6) \)
\( 52 = 4L - 12 \)
\( 64 = 4L \)
\( L = 16 \, \text{cm} \)
Therefore, the width is \( 16 - 6 = 10 \, \text{cm} \).
Let the width be \( W \). Then the length is \( 3W \). Using the perimeter formula:
\( 48 = 2 \times (W + 3W) \)
Simplifying: \( 48 = 2 \times 4W \)
\( 48 = 8W \)
\( W = 6 \, \text{meters} \)
Therefore, the length is \( 3 \times 6 = 18 \, \text{meters} \).
Practice Problems
- A rectangular playground has a length of 20 meters and a width of 15 meters. What is the perimeter?
- The perimeter of a rectangular swimming pool is 60 meters. If the width is 10 meters, what is the length?
- A picture frame is twice as long as it is wide. If the perimeter is 36 inches, what are the dimensions of the frame?
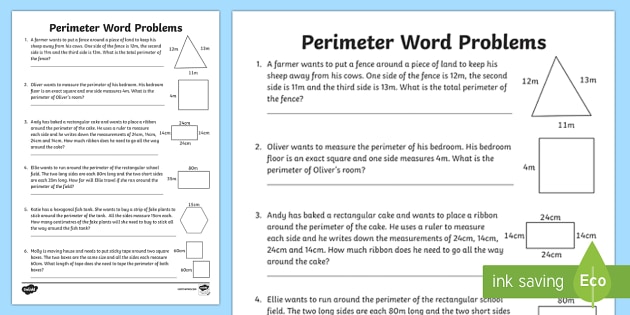
Square Perimeter Problems
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all its sides. Since a square has four equal sides, calculating its perimeter is straightforward using the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side length}
\]
Here is a step-by-step guide to solve square perimeter problems:
- Identify the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4 to get the perimeter.
Let's look at some examples:
-
Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 cm.
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 20 \, \text{cm}
\] -
Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 8 m.
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 8 \, \text{m} = 32 \, \text{m}
\]
In word problems, sometimes the perimeter is given and you need to find the side length. In such cases, use the formula:
\[
\text{side length} = \frac{\text{Perimeter}}{4}
\]
Example:
-
A square has a perimeter of 24 cm. What is the length of one side?
\[
\text{side length} = \frac{24 \, \text{cm}}{4} = 6 \, \text{cm}
\]
Practice Problems:
- Calculate the perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 inches.
- If the perimeter of a square is 40 meters, what is the length of one side?
- A garden in the shape of a square has a side length of 12 feet. Find its perimeter.
Solving these problems helps reinforce the concept of perimeter and the special properties of squares.
Triangle Perimeter Problems
Understanding the perimeter of triangles is fundamental in solving many geometric problems. The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides. Here, we will explore different types of triangles and how to find their perimeters through various word problems.
Types of Triangles
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal.
- Scalene Triangle: All three sides are different.
- Right Triangle: One angle is 90 degrees.
Formula
The general formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Example Problems
-
Problem 1: Find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle with each side measuring 8 cm.
Solution:
- Each side length \( a = 8 \, \text{cm} \)
- Perimeter \( P = 3a \)
- \( P = 3 \times 8 = 24 \, \text{cm} \)
-
Problem 2: Find the perimeter of an isosceles triangle with equal sides of 5 cm and a base of 6 cm.
Solution:
- Equal sides \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Base \( b = 6 \, \text{cm} \)
- Perimeter \( P = 2a + b \)
- \( P = 2 \times 5 + 6 = 16 \, \text{cm} \)
-
Problem 3: A scalene triangle has sides of 7 cm, 8 cm, and 9 cm. Calculate its perimeter.
Solution:
- Sides \( a = 7 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 8 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 9 \, \text{cm} \)
- Perimeter \( P = a + b + c \)
- \( P = 7 + 8 + 9 = 24 \, \text{cm} \)
-
Problem 4: A right triangle has a perimeter of 144 cm, and its hypotenuse is 65 cm. Find the lengths of the other two sides.
Solution:
- Let the other two sides be \( x \) and \( y \).
- \( x + y + 65 = 144 \rightarrow x + y = 79 \)
- Using Pythagoras' theorem: \( x^2 + y^2 = 65^2 = 4225 \)
- Using the system of equations:
- \( (x + y)^2 = x^2 + y^2 + 2xy \)
- \( 79^2 = 4225 + 2xy \rightarrow 6241 = 4225 + 2xy \rightarrow 2xy = 2016 \rightarrow xy = 1008 \)
- Solving for \( x \) and \( y \): \( x \) and \( y \) can be 63 cm and 16 cm respectively.
- Check: \( 63 + 16 = 79 \) and \( 63^2 + 16^2 = 4225 \).
Practicing these problems will help you understand the methods to solve perimeter-related questions for triangles. Keep practicing with different values and configurations to strengthen your skills.
Perimeter of Regular Polygons
Regular polygons are shapes with all sides and all interior angles equal. The perimeter of a regular polygon is simply the sum of the lengths of all its sides. To calculate this, you can use the following formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = n \times s
\]
where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of one side.
Let's look at some common regular polygons and how to calculate their perimeters:
- Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has 3 equal sides.
- Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 3 \times s \)
- Example: If each side is 5 cm, then the perimeter is \( 3 \times 5 = 15 \) cm.
- Square: A square has 4 equal sides.
- Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times s \)
- Example: If each side is 7 cm, then the perimeter is \( 4 \times 7 = 28 \) cm.
- Regular Pentagon: A pentagon has 5 equal sides.
- Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 5 \times s \)
- Example: If each side is 6 cm, then the perimeter is \( 5 \times 6 = 30 \) cm.
- Regular Hexagon: A hexagon has 6 equal sides.
- Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = 6 \times s \)
- Example: If each side is 8 cm, then the perimeter is \( 6 \times 8 = 48 \) cm.
Steps to Solve Perimeter Word Problems for Regular Polygons:
- Identify the Shape: Determine if the shape is a regular polygon.
- Count the Sides: Find the number of sides (\( n \)).
- Measure One Side: Measure or identify the length of one side (\( s \)).
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula \( \text{Perimeter} = n \times s \).
- Calculate: Multiply the number of sides by the length of one side to find the perimeter.
Example Problem:
A regular octagon (8-sided polygon) has each side measuring 10 cm. Find its perimeter.
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 8 \times 10 = 80 \text{ cm}
\]
By following these steps and using the formula, you can easily solve any perimeter word problem involving regular polygons.
Composite Shape Perimeter Problems
Composite shapes are figures that consist of two or more basic geometric shapes. To solve perimeter problems involving composite shapes, follow these detailed steps:
Steps to Find the Perimeter of Composite Shapes
-
Identify the Shapes: Break down the composite shape into simpler geometric shapes like rectangles, triangles, or circles. This helps in visualizing and calculating the sides.
-
Label All Side Lengths: Ensure that every side length of the composite shape is labeled. If any side length is missing, use known properties or measurements of the shapes to determine the missing values.
-
Calculate Missing Lengths: Use the properties of the basic shapes within the composite shape to find any missing side lengths. For example, if two sides of a rectangle are known, the other two sides are the same.
-
Sum the Outer Side Lengths: Add up the lengths of all the outer sides of the composite shape to find the total perimeter. Only the outer edges of the shape should be included in this calculation.
Example Problems
Here are a few examples to illustrate the process:
Example 1: Composite Shape with Rectangles and Triangles
Consider a shape made up of a rectangle and a triangle:
- Rectangle: Length = 6 cm, Width = 4 cm
- Triangle: Base = 4 cm, Height = 3 cm
The perimeter of the composite shape is calculated as:
Example 2: L-Shape Composite
Consider an L-shaped figure made of two rectangles:
- First Rectangle: Length = 8 cm, Width = 4 cm
- Second Rectangle: Length = 4 cm, Width = 2 cm
The perimeter of the L-shaped composite shape is:
Tips for Solving Composite Shape Perimeter Problems
- Always double-check that all outer sides are included in your calculations.
- Use geometric properties to simplify finding missing lengths.
- Draw the shape and label all known dimensions to avoid confusion.
Practice Problems
Try solving these problems to enhance your understanding:
-
A composite shape is made up of two rectangles, one with dimensions 5 cm by 3 cm and the other with dimensions 7 cm by 2 cm. Calculate the perimeter.
-
Find the perimeter of a shape made up of a rectangle (10 cm by 4 cm) and a semicircle with a diameter of 4 cm.

Perimeter Problems with Missing Dimensions
Solving perimeter problems with missing dimensions involves determining the length of one or more sides of a shape when the total perimeter is given. Here’s a step-by-step guide to approaching these problems:
-
Understand the Problem
Read the problem carefully and identify the shape involved. Note down the given dimensions and the total perimeter.
-
Set Up the Perimeter Formula
Recall the perimeter formula for the given shape. For instance:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4s \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
-
Insert Known Values
Plug in the known side lengths and the given perimeter into the formula. Set up an equation to find the missing side.
- Example: For a rectangle with a perimeter of 20 units, length of 6 units, and unknown width \( w \):
\( 20 = 2(6 + w) \)
- Example: For a rectangle with a perimeter of 20 units, length of 6 units, and unknown width \( w \):
-
Solve for the Missing Dimension
Isolate the unknown variable and solve the equation.
- Continuing the example: \( 20 = 2(6 + w) \)
- \( 20 = 12 + 2w \)
- \( 20 - 12 = 2w \)
- \( 8 = 2w \)
- \( w = 4 \)
- Continuing the example: \( 20 = 2(6 + w) \)
-
Verify Your Solution
Check the calculated dimension by substituting it back into the original perimeter equation to ensure it satisfies the given perimeter.
- For the example above: \( 2(6 + 4) = 20 \) confirms the solution is correct.
Here are some additional practice problems to apply these steps:
- A square has a perimeter of 36 units. One side is missing. Find the length of the missing side.
- The perimeter of a triangle is 24 units. Two sides are 7 units and 8 units, respectively. Find the length of the third side.
- A rectangle has a perimeter of 50 units. One side is twice the length of the other side. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
Using these steps, you can systematically find the missing dimensions in perimeter problems and ensure your solutions are accurate.
Real-Life Applications of Perimeter
The concept of perimeter is widely used in various real-life scenarios. Understanding and calculating perimeter is crucial for many practical applications:
-
Construction and Architecture:
In building construction, calculating the perimeter of plots, rooms, and entire buildings is essential for determining the amount of materials needed, such as fencing, wiring, or piping. For instance, knowing the perimeter helps in estimating the length of the fence required to enclose a garden or the length of wiring needed for electrical installations.
-
Landscaping:
Landscapers use perimeter measurements to plan garden layouts, including the placement of plants, walkways, and borders. This ensures that the garden is well-organized and that the plants and features are evenly spaced.
-
Sports Fields:
In designing sports fields like soccer, basketball, or tennis courts, the perimeter is used to define the boundaries. Accurate measurements are crucial for maintaining standard dimensions, which are necessary for official competitions.
-
Home Improvement:
When painting a room, the perimeter helps in calculating the amount of paint needed for the walls. Similarly, for installing baseboards, crown molding, or other trim, the perimeter of the room determines how much material to purchase.
-
Fencing and Boundary Marking:
Farmers and property owners need to calculate the perimeter of their land to install fences. This helps in securing the property and keeping livestock within designated areas.
-
Transportation and Logistics:
In urban planning, the perimeter of roads and highways is important for designing efficient transportation networks. It also helps in estimating the materials required for road construction and maintenance.
By understanding these applications, students and professionals can appreciate the importance of perimeter calculations in everyday life and various industries.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Practicing perimeter problems helps to solidify understanding of the concepts and methods used to calculate the perimeter of various shapes. Below are several practice problems along with their solutions.
Problem 1: Perimeter of a Rectangle
Jason has a rectangular garden that is 10 meters long and 5 meters wide. What is the perimeter of his garden?
- Identify the length (l) and width (w) of the rectangle:
- Length (l) = 10 meters
- Width (w) = 5 meters
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \[ P = 2l + 2w \]
- Substitute the values: \[ P = 2(10) + 2(5) = 20 + 10 = 30 \]
- The perimeter of Jason's garden is 30 meters.
Problem 2: Perimeter of a Square
A square playground has each side measuring 8 meters. What is the perimeter of the playground?
- Identify the side length (s) of the square:
- Side length (s) = 8 meters
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a square: \[ P = 4s \]
- Substitute the value: \[ P = 4(8) = 32 \]
- The perimeter of the playground is 32 meters.
Problem 3: Perimeter of a Triangle
A triangular park has sides measuring 6 meters, 8 meters, and 10 meters. What is the perimeter of the park?
- Identify the lengths of the three sides:
- Side 1 = 6 meters
- Side 2 = 8 meters
- Side 3 = 10 meters
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a triangle: \[ P = a + b + c \]
- Substitute the values: \[ P = 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 \]
- The perimeter of the park is 24 meters.
Problem 4: Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
Each side of a regular pentagon is 7 centimeters long. What is the perimeter of the pentagon?
- Identify the side length (s) of the pentagon:
- Side length (s) = 7 centimeters
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon: \[ P = 5s \]
- Substitute the value: \[ P = 5(7) = 35 \]
- The perimeter of the pentagon is 35 centimeters.
Problem 5: Composite Shape Perimeter
A composite shape is made up of a rectangle and a semicircle. The rectangle has a length of 12 meters and a width of 6 meters. The semicircle is attached to one of the shorter sides of the rectangle. Find the perimeter of the composite shape.
- Identify the dimensions of the rectangle and the radius of the semicircle:
- Length of rectangle (l) = 12 meters
- Width of rectangle (w) = 6 meters
- Radius of semicircle (r) = 3 meters (since the semicircle's diameter is equal to the width of the rectangle)
- Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle (excluding the side where the semicircle is attached): \[ P_{\text{rect}} = 2l + w = 2(12) + 6 = 24 + 6 = 30 \text{ meters} \]
- Calculate the circumference of the semicircle: \[ P_{\text{semi}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 2\pi r = \pi r = \pi(3) = 3\pi \]
- Add the perimeter of the rectangle and the circumference of the semicircle: \[ P_{\text{total}} = 30 + 3\pi \approx 30 + 9.42 = 39.42 \text{ meters} \]
- The perimeter of the composite shape is approximately 39.42 meters.
Problem 6: Finding Missing Dimensions
The perimeter of a rectangle is 50 meters. If the length is twice the width, find the dimensions of the rectangle.
- Let the width be w and the length be 2w.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \[ P = 2l + 2w = 50 \]
- Substitute the known values: \[ 2(2w) + 2w = 50 \] \[ 4w + 2w = 50 \] \[ 6w = 50 \] \[ w = \frac{50}{6} \approx 8.33 \]
- Calculate the length: \[ l = 2w = 2(8.33) \approx 16.67 \]
- The dimensions of the rectangle are approximately 8.33 meters (width) and 16.67 meters (length).
Advanced Perimeter Word Problems
Advanced perimeter problems often involve more complex shapes and require a deeper understanding of geometric properties and algebraic techniques. Below are some example problems and solutions to help you master these advanced concepts.
Example Problems
-
Problem 1: The perimeter of a rectangular garden is 150 meters. The length of the garden is 5 meters more than twice the width. Find the dimensions of the garden.
Solution:
- Let the width be \( w \) meters.
- Then the length is \( 2w + 5 \) meters.
- The perimeter of a rectangle is given by \( P = 2(l + w) \).
- Substitute the known values: \( 150 = 2((2w + 5) + w) \).
- Simplify the equation: \( 150 = 2(3w + 5) \).
- Divide by 2: \( 75 = 3w + 5 \).
- Solve for \( w \): \( 3w = 70 \) and \( w = \frac{70}{3} = 23.33 \) meters (approximately).
- Find the length: \( l = 2(23.33) + 5 = 51.66 \) meters (approximately).
-
Problem 2: A triangle has sides in the ratio 3:4:5. If the perimeter of the triangle is 72 cm, find the length of each side.
Solution:
- Let the sides be \( 3x \), \( 4x \), and \( 5x \).
- The perimeter is given by \( P = 3x + 4x + 5x = 12x \).
- Substitute the known perimeter: \( 72 = 12x \).
- Solve for \( x \): \( x = \frac{72}{12} = 6 \) cm.
- Find the lengths of each side: \( 3x = 18 \) cm, \( 4x = 24 \) cm, and \( 5x = 30 \) cm.
-
Problem 3: The perimeter of a regular hexagon is 84 cm. Find the length of one side.
Solution:
- Let the length of one side be \( s \).
- The perimeter of a regular hexagon is given by \( P = 6s \).
- Substitute the known perimeter: \( 84 = 6s \).
- Solve for \( s \): \( s = \frac{84}{6} = 14 \) cm.
-
Problem 4: A trapezoid has bases of lengths 10 cm and 14 cm, and non-parallel sides of 7 cm and 9 cm. Find the perimeter of the trapezoid.
Solution:
- The perimeter of a trapezoid is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- Add the lengths of the bases and the non-parallel sides: \( 10 + 14 + 7 + 9 = 40 \) cm.
- The perimeter is 40 cm.
Practice Problems
- The perimeter of a rectangle is 200 meters. The length is 10 meters more than three times the width. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
- A triangle has sides in the ratio 2:3:4. If the perimeter is 54 cm, find the length of each side.
- The perimeter of a regular octagon is 96 cm. Find the length of one side.
- A trapezoid has bases of lengths 15 cm and 20 cm, and non-parallel sides of 8 cm and 12 cm. Find the perimeter of the trapezoid.
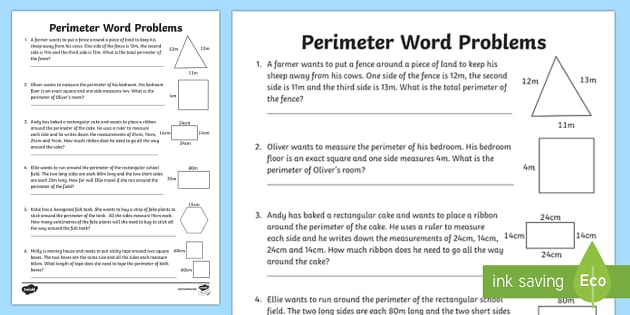
Tips and Tricks for Solving Perimeter Problems
Solving perimeter problems can be straightforward if you follow these tips and tricks:
- Understand the Shape: Identify the type of shape you are dealing with (e.g., rectangle, square, triangle). Each shape has a specific formula for calculating its perimeter.
- Know the Formulas: Familiarize yourself with the perimeter formulas for common shapes:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4s \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Regular Polygon: \( P = n \times s \) (where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the side length)
- Break Down Composite Shapes: For composite shapes, divide them into simpler shapes, calculate the perimeter of each part, and then combine the results appropriately.
- Use Algebra: If dimensions are missing, set up equations using variables and solve for the unknowns.
- Check Units: Ensure all measurements are in the same units before performing calculations. Convert if necessary.
- Draw and Label Diagrams: Visualize the problem by drawing and labeling all known and unknown dimensions. This helps in organizing information and making sense of the problem.
- Review and Double-Check: After solving, review each step and double-check calculations to avoid mistakes.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice with different types of perimeter problems improves accuracy and speed.
Here's a step-by-step example for solving a perimeter problem:
- Read the problem carefully and identify the shape involved.
- Write down the known dimensions and the perimeter formula for the shape.
- Substitute the known values into the formula.
- Solve for the unknown variable if necessary.
- Check your answer by verifying all steps and calculations.
Example Problem:
Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 8 cm and a width of 5 cm.
| Step 1: | Identify the shape - Rectangle |
| Step 2: | Write down the formula - \( P = 2(l + w) \) |
| Step 3: | Substitute the known values - \( P = 2(8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) \) |
| Step 4: | Simplify - \( P = 2(13 \, \text{cm}) = 26 \, \text{cm} \) |
| Step 5: | Verify the calculation |
With these tips and regular practice, you will be well-equipped to tackle any perimeter word problems with confidence and accuracy.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When solving perimeter word problems, students often make common mistakes that can lead to incorrect answers. Understanding these mistakes and learning how to avoid them is crucial for mastering perimeter problems. Here are some common pitfalls and tips to overcome them:
- Misidentifying Shapes:
Ensure you correctly identify the shape of the figure. For example, a square has equal sides, while a rectangle has opposite sides equal. Misidentifying the shape can lead to incorrect calculations.
- Incorrect Formula Application:
Each shape has a specific formula for calculating its perimeter. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is given by \( P = 2(l + w) \), while the perimeter of a square is \( P = 4s \). Make sure to use the correct formula for the shape you are working with.
- Units of Measurement:
Always pay attention to the units of measurement. Ensure that all dimensions are in the same units before performing any calculations. If the problem gives dimensions in different units, convert them to the same unit.
- Overlooking Missing Dimensions:
Sometimes, not all dimensions are provided directly. Use the given information and properties of the shape to find the missing dimensions. For example, if you know the perimeter of a square but not the side length, you can use \( s = \frac{P}{4} \).
- Ignoring Composite Shapes:
For composite shapes, break down the figure into simpler shapes, calculate the perimeter for each, and then sum them up. Be careful to not double-count the shared sides.
- Calculation Errors:
Double-check your arithmetic calculations. Simple addition or multiplication errors can lead to incorrect results. Revisit your steps to ensure accuracy.
- Misinterpreting Word Problems:
Read the word problem carefully to understand what is being asked. Look for keywords that indicate the shape and the dimensions involved. Sometimes drawing a diagram can help visualize the problem better.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and following these tips, students can improve their accuracy and confidence in solving perimeter word problems.
Conclusion and Further Reading
Understanding and solving perimeter word problems is a fundamental skill in geometry that applies to many real-world situations. Throughout this guide, we have covered various types of perimeter problems, from basic shapes to complex composite figures. By mastering these concepts, students can enhance their mathematical problem-solving abilities and apply these skills in practical contexts.
Here are some key takeaways to remember:
- Always start by identifying the shape and its dimensions.
- Use the appropriate perimeter formula for the given shape.
- Double-check your calculations to avoid common mistakes.
- Practice different types of problems to build confidence and proficiency.
For those looking to further their understanding and practice, here are some recommended resources:
- - Interactive exercises and detailed explanations to reinforce learning.
- - Step-by-step tutorials and examples to help grasp the concepts.
- - A variety of worksheets and problems to test your skills.
- - Engaging and challenging problems for advanced practice.
We hope this guide has been helpful in your journey to mastering perimeter word problems. Keep practicing, and don't hesitate to explore additional resources to further enhance your understanding. Happy learning!
Video giới thiệu về các bài toán từ ngữ liên quan đến chu vi, giúp học sinh hiểu và giải quyết các bài toán một cách dễ dàng.
Vấn Đề Từ Ngữ - Chu Vi
READ MORE:
Video về bài toán chu vi dành cho học sinh lớp 3, giúp các em hiểu và giải quyết các bài toán liên quan đến chu vi một cách hiệu quả.
Bài Toán Chu Vi | Toán Học | Lớp 3 - Kids Academy