Topic perimeter of half a circle: Understanding the perimeter of a half circle is crucial for mastering geometry and its real-world applications. This guide simplifies the process, providing clear steps to calculate the perimeter efficiently. Whether for academic purposes or practical uses, learning this calculation will enhance your mathematical skills and confidence.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of Half a Circle
- Introduction to the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Understanding the Concept of a Half Circle
- Mathematical Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Step-by-Step Calculation of the Perimeter
- Using the Radius to Find the Perimeter
- Applications of the Half Circle Perimeter in Real Life
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practical Examples and Problem Solving
- Advanced Topics: Integrating with Full Circle and Sector Calculations
- Tips for Efficient Calculations
- Conclusion: Importance of Understanding Perimeter in Geometry
- YOUTUBE:
Perimeter of Half a Circle
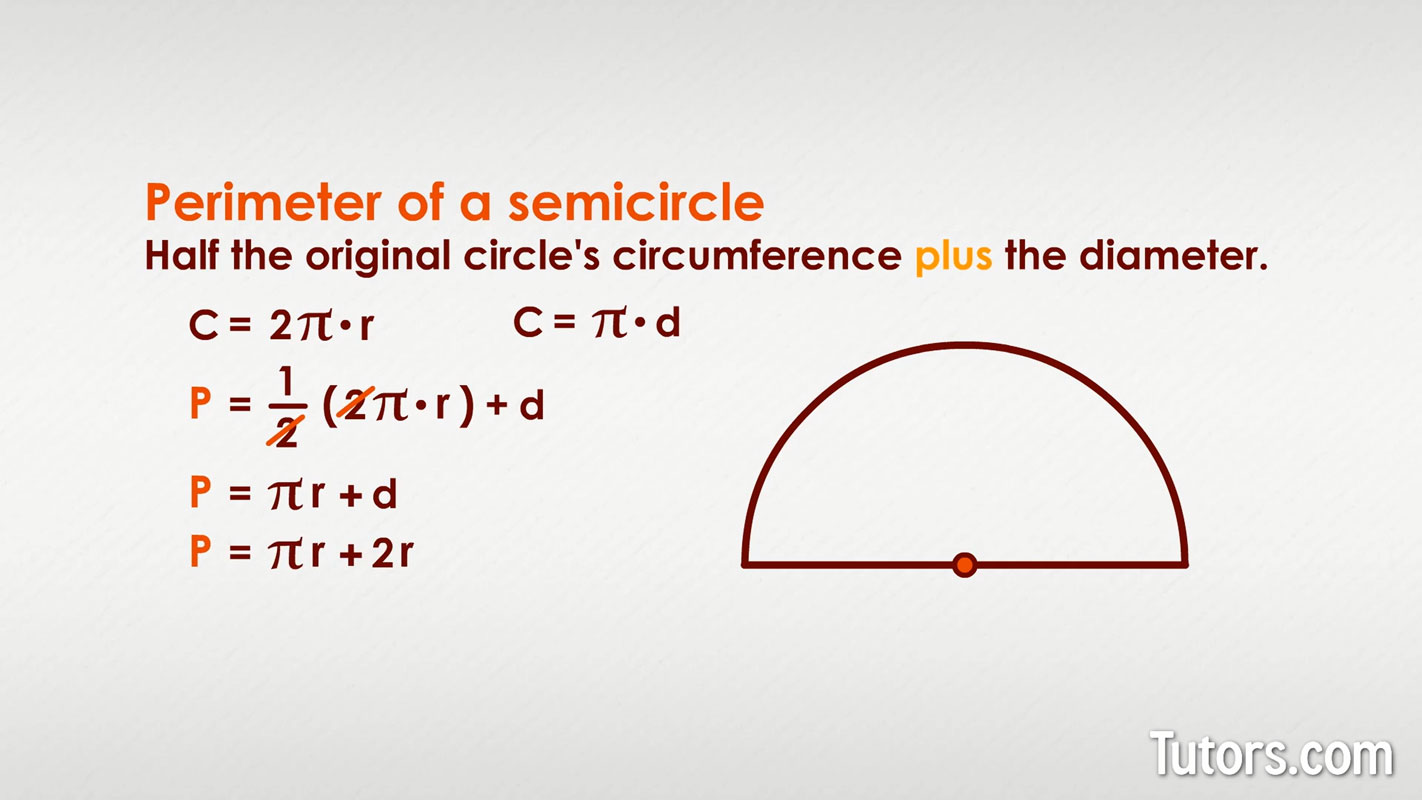
The perimeter (or circumference) of a half-circle includes the curved part of the half-circle as well as the diameter. The formula to calculate the perimeter of a half-circle is:
$$\text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r$$
Where:
- \( \pi \) : Pi (approximately 3.14159)
- r : Radius of the circle
Breaking it down:
- The curved part of the half-circle is half of the full circumference: $$\frac{1}{2}(2\pi r) = \pi r$$
- The diameter of the circle is twice the radius: $$2r$$
Adding these two components together gives the total perimeter:
$$\text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r = r(\pi + 2)$$
Thus, the perimeter of a half-circle is the sum of the half-circle's curved edge and its diameter.
| Radius (r) | Perimeter Formula | Perimeter Calculation |
| 1 | \(\pi + 2\) | 3.14159 + 2 = 5.14159 |
| 2 | \(2(\pi + 2)\) | 2(3.14159 + 2) = 10.28318 |
| 3 | \(3(\pi + 2)\) | 3(3.14159 + 2) = 15.42477 |

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Perimeter of a Half Circle
The perimeter of a half circle, also known as a semicircle, is a fundamental concept in geometry. It combines linear and curved measurements, making it an interesting calculation involving both the radius and the curved arc. This section will provide a clear understanding and step-by-step guide on how to calculate the perimeter of a half circle.
The formula to calculate the perimeter (or circumference) of a half circle is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Where:
- \( P \) is the perimeter of the half circle.
- \( r \) is the radius of the half circle.
- \( \pi \) is a constant (approximately 3.14159).
Let's break this down step by step:
- First, calculate the curved part of the half circle, which is half the circumference of a full circle. The formula for the circumference of a full circle is \( 2\pi r \). Since we are dealing with a half circle, the curved part is half of this, or \( \pi r \).
- Next, add the diameter of the circle to account for the straight edge of the half circle. The diameter is twice the radius, or \( 2r \).
- Combine these two components: the curved part (\( \pi r \)) and the straight part (\( 2r \)), resulting in the formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
Understanding this concept is crucial not only for academic purposes but also for various practical applications such as designing arches, bridges, or even calculating distances around circular tracks that are split in half.
Consider this table summarizing the components of the perimeter:
| Component | Formula | Description |
| Curved part | \( \pi r \) | The arc length of the half circle |
| Straight part | \( 2r \) | The diameter of the circle |
By mastering this calculation, you'll be better equipped to handle a variety of geometric problems and real-world scenarios involving half circles.
Understanding the Concept of a Half Circle
A half circle, also known as a semicircle, is a geometric shape that represents half of a full circle. It consists of a curved boundary that forms a half-circle and a straight boundary, which is the diameter of the original circle.
To visualize a half circle, imagine slicing a full circle exactly through its center, creating two equal halves. Each half is a semicircle. Here are the key components and properties of a half circle:
- Radius (\( r \)): The distance from the center of the original full circle to any point on the curved boundary of the half circle.
- Diameter (\( 2r \)): The straight line across the half circle, passing through its center. This line is also the flat boundary of the half circle.
- Curved Boundary: The arc that makes up half of the full circle's circumference.
- Center: The point where the radius meets the diameter. It is the midpoint of the flat boundary of the half circle.
The shape of a half circle has several interesting properties:
- Symmetry: A half circle is symmetrical about its diameter. This means the shape on one side of the diameter is a mirror image of the shape on the other side.
- Area: The area of a half circle can be calculated using the formula: \[ A = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \] where \( A \) represents the area and \( r \) is the radius.
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a half circle, as discussed earlier, includes the arc length plus the diameter: \[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
To further understand the half circle, consider the following table that summarizes its essential properties:
| Property | Formula | Description |
| Radius | \( r \) | Distance from the center to the curved boundary |
| Diameter | \( 2r \) | Length of the straight boundary |
| Area | \( \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \) | Area covered by the half circle |
| Perimeter | \( \pi r + 2r \) | Total length around the half circle |
Understanding these aspects of a half circle is essential for solving various geometric problems and applying these principles in real-world scenarios, such as in architecture and engineering.
Mathematical Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
Calculating the perimeter (or circumference) of a half circle involves understanding both the curved edge and the straight edge (diameter) of the half circle. The formula for the perimeter of a half circle is derived from the formula for the circumference of a full circle.
The formula for the circumference of a full circle is:
\( C = 2 \pi r \)
where C is the circumference and r is the radius of the circle.
Since a half circle is half of a full circle, we need to take half of the circumference and add the diameter (which is the straight edge of the half circle). The formula becomes:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
where P is the perimeter of the half circle.
Breaking this down step-by-step:
- Calculate the curved part of the half circle, which is half the circumference of a full circle:
\( \text{Curved Part} = \pi r \)
- Add the diameter to the curved part to get the total perimeter:
\( \text{Diameter} = 2r \)
- Combine both parts to get the perimeter of the half circle:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
Therefore, the complete formula for the perimeter of a half circle is:
\( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
Where:
- P = Perimeter of the half circle
- r = Radius of the half circle
- \(\pi\) = Pi, approximately 3.14159
This formula accounts for both the curved and straight edges of the half circle, providing an accurate measure of its perimeter.
Step-by-Step Calculation of the Perimeter
The perimeter of a half circle (or semicircle) is calculated by adding the length of the curved part of the semicircle to the length of the diameter. Here's a step-by-step guide:
-
Identify the radius (r) of the semicircle:
The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its boundary.
-
Calculate the circumference of the full circle:
The formula for the circumference of a full circle is given by:
\[ \text{Circumference} = 2 \pi r \]
-
Determine half the circumference:
Since a semicircle is half of a circle, we take half of the full circumference:
\[ \text{Half Circumference} = \pi r \]
-
Calculate the length of the diameter:
The diameter (d) is twice the radius:
\[ d = 2r \]
-
Add the half circumference to the diameter:
The perimeter (P) of the semicircle is the sum of the half circumference and the diameter:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
This can be factored as:
\[ P = r (\pi + 2) \]
By following these steps, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any semicircle if you know its radius.
Let's consider an example:
-
If the radius of a semicircle is 7 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Substituting \( r = 7 \):
\[ P = \pi \cdot 7 + 2 \cdot 7 \]
\[ P = 22 + 14 \]
\[ P = 36 \text{ units} \]
This approach ensures accurate and efficient calculation of the semicircle's perimeter.

Using the Radius to Find the Perimeter
The perimeter of a half circle, also known as a semicircle, can be determined using the radius of the circle. The radius, denoted as \( r \), is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge.
To find the perimeter (or the total boundary length) of a semicircle, you need to consider two components: the curved part (half of the circumference of a full circle) and the straight line (the diameter) that forms the base of the semicircle.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle is:
Where:
- \( P \) is the perimeter of the semicircle.
- \( π \) (Pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Measure the Radius: Determine the radius of the semicircle. Let's denote this radius as \( r \).
Apply the Formula: Use the formula \( P = πr + 2r \).
Substitute the Radius: Insert the value of the radius into the formula. For instance, if the radius is 5 cm, the formula becomes:
Calculate the Curved Part: Multiply \( π \) by the radius to get the length of the curved part of the perimeter.
Calculate the Diameter: Multiply 2 by the radius to get the length of the straight part (diameter).
Add the Two Parts: Add the results of the curved part and the diameter to get the total perimeter.
Therefore, the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 5 cm is approximately 25.71 cm.
Applications of the Half Circle Perimeter in Real Life
The perimeter of a half circle, also known as a semicircle, has various practical applications in everyday life and different fields. Here are some key examples:
- Architecture and Construction:
In the construction of buildings, bridges, and roads, understanding the perimeter of semicircular structures is crucial for accurate measurements and material estimation. For example, when designing arches or curved pathways, knowing the semicircle's perimeter helps in calculating the amount of materials needed and ensuring structural integrity.
- Landscaping and Garden Design:
Semicircular designs are often used in landscaping to create aesthetically pleasing garden beds, pathways, and water features. The perimeter calculation assists in planning the layout and determining the quantity of edging materials required.
- Art and Fashion:
In the art world, semicircular shapes are used in various designs and patterns. Fashion designers also use semicircle calculations to create unique garment patterns and accessories, ensuring precision in the design and fitting process.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Design:
In manufacturing, particularly in the production of pipes and mechanical parts, semicircular components are common. Calculating the perimeter is essential for cutting materials to the correct dimensions and ensuring proper assembly.
- Urban Planning:
Urban planners use semicircular designs in parks, plazas, and public spaces. Accurate perimeter measurements help in designing seating arrangements, walkways, and decorative elements that fit well within the designated area.
- Sports and Recreation:
In sports facilities, semicircular perimeters are found in tracks and fields, such as the curved sections of running tracks. Precise perimeter calculations are necessary for constructing these areas to standard dimensions.
- Astronomy:
Astronomers and space scientists use the concept of semicircles to measure planetary orbits and motions. Understanding the perimeter helps in calculating distances and paths taken by celestial bodies.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a half circle, there are several common mistakes that people often make. Being aware of these mistakes can help you avoid them and ensure your calculations are accurate.
- Confusing Perimeter with Circumference
One of the most frequent errors is using the terms "perimeter" and "circumference" interchangeably. The perimeter of a half circle includes the straight edge (diameter) as well as the curved edge (half the circumference). Ensure you use the correct formula: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Forgetting to Include the Diameter
When calculating the perimeter, don't forget to add the length of the diameter. Many people only calculate the curved edge, which results in an incomplete measurement. Remember, the formula is \( P = \pi r + 2r \), which accounts for both the curved part and the straight edge.
- Incorrect Value of Pi
Using an incorrect value for π (pi) can lead to significant errors. While 3.14 is a common approximation, for more accurate results, use 3.14159 or the π button on your calculator.
- Measurement Unit Errors
Ensure that all measurements are in the same units before performing calculations. Mixing units (e.g., using centimeters for the radius and meters for the diameter) will result in incorrect calculations.
- Rounding Errors
Be cautious with rounding intermediate values too early in your calculations. This can lead to cumulative errors. Instead, perform calculations with full precision and round the final result if necessary.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking care to avoid them, you can ensure that your calculations of the perimeter of a half circle are accurate and reliable.
Practical Examples and Problem Solving
Understanding the perimeter of a half circle can be enhanced through practical examples and problem solving. Here are some detailed examples:
Example 1: Basic Perimeter Calculation
Given a half circle with a diameter of 10 cm, find the perimeter.
- Calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \, \text{cm} \).
- Use the perimeter formula for a half circle: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Substitute the radius into the formula: \( P = \pi \times 5 + 2 \times 5 \).
- Simplify: \( P = 5\pi + 10 \).
- Assuming \( \pi \approx 3.14 \), calculate the approximate value: \( P \approx 5 \times 3.14 + 10 = 15.7 + 10 = 25.7 \, \text{cm} \).
Example 2: Real-Life Application
A semi-circular garden has a radius of 4 meters. Calculate the length of the fencing required to surround the garden.
- Given radius \( r = 4 \, \text{m} \).
- Apply the perimeter formula: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Substitute the radius: \( P = \pi \times 4 + 2 \times 4 \).
- Simplify: \( P = 4\pi + 8 \).
- Using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P \approx 4 \times 3.14 + 8 = 12.56 + 8 = 20.56 \, \text{m} \).
Example 3: Composite Shape
A playground is in the shape of a rectangle combined with a half circle on one end. The rectangle is 20 meters long and 10 meters wide. Calculate the total perimeter of the playground.
- First, calculate the perimeter of the rectangle (excluding the semi-circular part): \( P_{\text{rect}} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) - \text{width} \) because one width is part of the semicircle.
- Substitute the values: \( P_{\text{rect}} = 2 \times (20 + 10) - 10 = 2 \times 30 - 10 = 60 - 10 = 50 \, \text{m} \).
- Calculate the perimeter of the half circle: \( P_{\text{semi}} = \pi r + 2r \).
- Here, radius \( r = \frac{\text{width}}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \, \text{m} \).
- So, \( P_{\text{semi}} = \pi \times 5 + 2 \times 5 = 5\pi + 10 \).
- Using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \): \( P_{\text{semi}} \approx 5 \times 3.14 + 10 = 15.7 + 10 = 25.7 \, \text{m} \).
- Total perimeter: \( P_{\text{total}} = P_{\text{rect}} + P_{\text{semi}} = 50 + 25.7 = 75.7 \, \text{m} \).
Advanced Topics: Integrating with Full Circle and Sector Calculations
Understanding the perimeter of a half circle is essential for more advanced topics in geometry, including full circle and sector calculations. Here, we will explore how these concepts interrelate.
Full Circle Perimeter
The perimeter of a full circle, also known as the circumference, is given by the formula:
where C is the circumference and r is the radius of the circle.
Sector Calculations
A sector of a circle is a portion bounded by two radii and the arc between them. To find the perimeter of a sector, you need the radius and the central angle (θ in radians). The formula for the perimeter of a sector is:
Here, P is the perimeter, r is the radius, and θ is the central angle in radians.
Example Problem
Consider a sector with a radius of 5 units and a central angle of π/3 radians. To find the perimeter:
- Calculate the arc length:
- Sum the two radii and the arc length:
Therefore, the perimeter of the sector is \(10 + \frac{5\pi}{3}\) units.
Integrating with Half Circle Calculations
To integrate half circle calculations with full circle and sector calculations, note that the perimeter of a half circle is a special case of the sector with a 180° or π radians central angle. The formula simplifies accordingly, emphasizing the continuity in geometric principles across different circular shapes.
Tips for Efficient Calculations
Calculating the perimeter of a half circle can be made easier and more efficient with the following tips:
-
Understand the Formula:
The perimeter \( P \) of a half circle is given by the formula:
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\]
where \( r \) is the radius of the half circle. Knowing this formula by heart can speed up calculations. -
Use Accurate Values for π:
Using a more precise value for π, such as 3.14159, can make your calculations more accurate. For quick calculations, 3.14 is often sufficient.
-
Leverage Technology:
Use calculators or computational tools to handle the arithmetic, especially when dealing with large numbers or when you need to ensure high precision.
-
Simplify Before Calculating:
Simplify the expression as much as possible before plugging in numbers. For example, calculate the diameter \( D = 2r \) first to reduce the steps required.
-
Check Units Consistency:
Ensure that all measurements are in the same unit before performing any calculations. Convert units if necessary to avoid errors.
-
Double-Check Your Work:
Always review your calculations for any potential errors. Recompute the perimeter to verify your results if time permits.
-
Practice with Examples:
Regular practice with different problems can help you become more efficient. Familiarity with various scenarios enhances your ability to quickly and accurately compute the perimeter.
By incorporating these tips into your approach, you can efficiently and accurately calculate the perimeter of a half circle in various situations.
Conclusion: Importance of Understanding Perimeter in Geometry
Understanding the perimeter of geometric shapes, including the half circle, is fundamental in geometry. The concept of perimeter not only helps in solving mathematical problems but also has practical applications in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and everyday life.
Here are some key points highlighting the importance:
-
Foundation of Geometry:
Perimeter is one of the basic properties of geometric figures. Grasping this concept lays the groundwork for more complex topics such as area, volume, and surface area. This foundational knowledge is crucial for progressing in the study of mathematics.
-
Real-Life Applications:
Understanding perimeter is essential in real-world applications. For example, in construction, calculating the perimeter of a plot of land is necessary to determine the amount of fencing required. Similarly, in design, knowing the perimeter helps in creating accurate models and layouts.
-
Problem-Solving Skills:
Learning to calculate the perimeter enhances problem-solving skills. It involves logical thinking and the ability to apply mathematical formulas accurately. These skills are transferable to various problem-solving scenarios beyond geometry.
-
Integration with Other Concepts:
The concept of perimeter is interconnected with other geometric and algebraic principles. For instance, understanding the perimeter of a half circle aids in comprehending the properties of circles, sectors, and segments. This integration deepens overall mathematical understanding.
In conclusion, mastering the calculation and understanding of perimeters, including that of a half circle, is vital for academic success in geometry and practical competence in numerous real-world situations. This knowledge empowers individuals to tackle various challenges, making geometry both a valuable and applicable field of study.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Nửa Hình Tròn
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi của một hình bán nguyệt kết hợp với một hình vuông. Video này sẽ giúp bạn nắm vững các bước và công thức cần thiết để giải quyết bài toán này.
Tìm Chu Vi Của Một Hình Bán Nguyệt Và Hình Vuông Kết Hợp!