Topic perimeter of the square calculator: Discover the simplicity of calculating the perimeter of a square with our easy-to-use Perimeter of the Square Calculator. Whether you're a student, teacher, or DIY enthusiast, our tool provides accurate results instantly. Learn the formula, explore examples, and avoid common mistakes to ensure precise calculations every time.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of the Square Calculator
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
- Understanding the Perimeter Formula
- Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
- Using a Perimeter Calculator
- Manual Calculation Examples
- Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculation
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Additional Resources and Tools
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Máy tính diện tích và chu vi cho hình vuông giúp bạn dễ dàng tính toán một cách nhanh chóng và chính xác. Thích hợp cho học sinh và giáo viên.
Perimeter of the Square Calculator
Welcome to our Perimeter of the Square Calculator. This tool helps you calculate the perimeter of a square quickly and easily. Simply enter the side length of your square, and the calculator will do the rest!
Formula
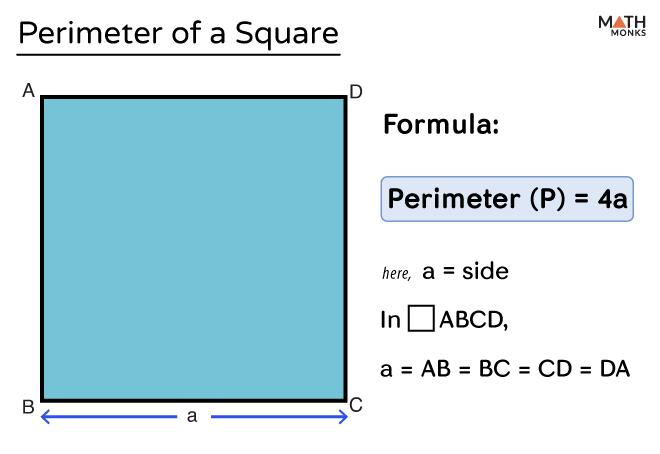
The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a square is:
\[ P = 4s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side of the square.
Calculator
Use the form below to calculate the perimeter:
Examples
- If the side length is 5 units, the perimeter is \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units.
- If the side length is 7.5 units, the perimeter is \( 4 \times 7.5 = 30 \) units.
- If the side length is 10 units, the perimeter is \( 4 \times 10 = 40 \) units.
Steps to Calculate Manually
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4.
- The result is the perimeter of the square.
Perimeter Calculation Table
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 2 | 8 |
| 4.5 | 18 |
| 6 | 24 |
| 8.2 | 32.8 |
| 11 | 44 |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all four sides of the square. It is an important measurement in geometry and is often used in various practical applications, such as construction, design, and everyday problem-solving. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square is fundamental for students and professionals alike.
To calculate the perimeter of a square, you can use the following formula:
\[ P = 4s \]
where \( P \) represents the perimeter and \( s \) represents the length of one side of the square.
Here is a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter of a square:
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4 to find the perimeter.
For example, if the length of one side of a square is 5 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[ P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units} \]
Knowing how to calculate the perimeter is useful in various contexts:
- Construction: Determining the amount of material needed for framing.
- Interior Design: Measuring the boundary of a space for furniture arrangement.
- Landscaping: Planning the layout of a garden or yard.
Understanding the concept of the perimeter and its calculation not only enhances your geometric skills but also prepares you for practical tasks in everyday life.
Understanding the Perimeter Formula
The formula for calculating the perimeter of a square is straightforward and essential for solving various geometric problems. The perimeter represents the total distance around the square and is calculated using the length of one of its sides. The formula is expressed as:
\[ P = 4s \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s \) is the length of one side of the square.
Let's break down the formula and understand its components:
- Identify the Side Length (s): The side length is the measurement of one of the four equal sides of the square.
- Multiply by 4: Since a square has four equal sides, multiplying the side length by 4 gives the total perimeter.
For example, if the side length of a square is 6 units, the calculation for the perimeter would be:
\[ P = 4 \times 6 = 24 \text{ units} \]
This formula works for any size of the square, making it a versatile tool for various applications. Here are some key points to remember:
- The side length must be the same for all four sides of the square.
- The unit of measurement for the perimeter is the same as that of the side length.
- Understanding this formula helps in accurately determining the perimeter for practical uses such as construction, art, and design.
To further illustrate the use of the perimeter formula, consider the following table with different side lengths and their corresponding perimeters:
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 12 |
| 5 | 20 |
| 7.5 | 30 |
| 10 | 40 |
| 12.5 | 50 |
By mastering the perimeter formula, you can efficiently solve problems involving the perimeter of squares, enhancing your mathematical skills and practical knowledge.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
Calculating the perimeter of a square is a simple and straightforward process. Follow this step-by-step guide to ensure accurate and efficient calculations:
- Measure the Side Length: Begin by measuring the length of one side of the square. Ensure that the measurement is accurate and in the desired unit (e.g., meters, feet, inches).
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula for the perimeter of a square:
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s \) is the length of one side.
\[ P = 4s \] - Multiply by 4: Multiply the measured side length by 4 to get the total perimeter. This is because a square has four equal sides.
- Record the Result: Write down the calculated perimeter and ensure that the units are consistent with the side length measurement.
Let's go through an example to solidify the understanding:
Suppose the side length of a square is 8 units. To find the perimeter, we follow these steps:
- Measure the side length: 8 units
- Apply the formula: \( P = 4 \times 8 \)
- Multiply: \( P = 32 \) units
- Record the result: The perimeter is 32 units
This process ensures that the perimeter is calculated accurately every time. Below is a table showing various side lengths and their corresponding perimeters for additional practice:
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 2 | 8 |
| 4.5 | 18 |
| 6 | 24 |
| 9 | 36 |
| 11.2 | 44.8 |
By following this step-by-step guide, you can confidently calculate the perimeter of any square, whether for academic purposes or practical applications.
Using a Perimeter Calculator
A perimeter calculator simplifies the process of finding the perimeter of a square by automating the calculations. This tool is especially useful for quick and accurate results, saving time and minimizing errors. Follow these steps to use a perimeter calculator effectively:
- Find a Reliable Calculator: Search online for a perimeter calculator specifically designed for squares. Ensure the calculator is reputable and user-friendly.
- Input the Side Length: Enter the length of one side of the square into the designated input field. Make sure the value is accurate and in the desired unit of measurement (e.g., meters, feet, inches).
- Initiate the Calculation: Click the "Calculate" button to process the input. The calculator will automatically apply the formula:
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s \) is the side length.
\[ P = 4s \] - View the Result: The calculator will display the perimeter of the square. Record this value and ensure it is in the same unit as the side length.
Using a perimeter calculator offers several advantages:
- Speed: Instantly calculates the perimeter, saving time compared to manual calculations.
- Accuracy: Reduces the risk of errors, ensuring precise measurements every time.
- Convenience: Easily accessible online, allowing for quick calculations from any device.
Let's look at an example using a perimeter calculator:
Suppose you have a square with a side length of 7 units. Here's how you would use the calculator:
- Open the perimeter calculator in your web browser.
- Enter "7" in the input field for the side length.
- Click "Calculate."
- The calculator displays the perimeter as 28 units.
This example demonstrates the ease and efficiency of using a perimeter calculator. For additional practice, you can use the table below to verify the calculations:
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 12 |
| 5.5 | 22 |
| 8 | 32 |
| 10.1 | 40.4 |
| 15 | 60 |
By using a perimeter calculator, you can quickly and accurately determine the perimeter of any square, making it a valuable tool for both educational and practical purposes.

Manual Calculation Examples
Calculating the perimeter of a square manually is a simple process that involves basic multiplication. Here are some detailed examples to illustrate the steps:
Example 1
Suppose the side length of a square is 4 units. Follow these steps to calculate the perimeter:
- Measure the Side Length: The side length is given as 4 units.
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula for the perimeter of a square:
\[ P = 4s \] - Multiply: Substitute the side length into the formula:
\[ P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \text{ units} \] - Record the Result: The perimeter of the square is 16 units.
Example 2
Consider a square with a side length of 7.5 units:
- Measure the Side Length: The side length is given as 7.5 units.
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula for the perimeter:
\[ P = 4s \] - Multiply: Substitute the side length into the formula:
\[ P = 4 \times 7.5 = 30 \text{ units} \] - Record the Result: The perimeter of the square is 30 units.
Example 3
Let's calculate the perimeter for a square with a side length of 12 units:
- Measure the Side Length: The side length is given as 12 units.
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula:
\[ P = 4s \] - Multiply: Substitute the side length:
\[ P = 4 \times 12 = 48 \text{ units} \] - Record the Result: The perimeter of the square is 48 units.
Example 4
For a square with a side length of 9.2 units, follow these steps:
- Measure the Side Length: The side length is 9.2 units.
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula:
\[ P = 4s \] - Multiply: Substitute the side length:
\[ P = 4 \times 9.2 = 36.8 \text{ units} \] - Record the Result: The perimeter of the square is 36.8 units.
Example 5
Finally, for a square with a side length of 15 units:
- Measure the Side Length: The side length is 15 units.
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula:
\[ P = 4s \] - Multiply: Substitute the side length:
\[ P = 4 \times 15 = 60 \text{ units} \] - Record the Result: The perimeter of the square is 60 units.
These examples demonstrate how easy it is to manually calculate the perimeter of a square using the basic formula. Practice with different side lengths to become proficient in these calculations.
Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of a square is not only a fundamental mathematical skill but also has numerous practical applications in various fields. Understanding how to determine the perimeter can aid in tasks ranging from construction projects to everyday problem-solving. Here are some key applications:
Construction and Architecture
In construction and architecture, knowing the perimeter of a square is essential for planning and material estimation. For example:
- Building Layouts: Determining the perimeter helps in planning the boundaries of rooms, gardens, and plots.
- Material Calculation: Estimating the amount of materials such as fencing, molding, or baseboards needed for a project.
- Blueprints: Creating accurate blueprints and ensuring precise measurements for construction projects.
Interior Design
Interior designers often use perimeter calculations to enhance spaces efficiently. Applications include:
- Furniture Arrangement: Measuring the perimeter of a room to plan the placement and fit of furniture.
- Decorative Elements: Calculating the length of decorative elements such as wallpaper borders and trim.
- Flooring: Estimating the amount of flooring material required for a specific area.
Landscaping and Gardening
In landscaping and gardening, perimeter calculations are crucial for designing and maintaining outdoor spaces:
- Garden Beds: Planning the layout and size of garden beds and borders.
- Pathways: Determining the length of walkways and driveways.
- Fencing: Calculating the amount of fencing material needed to enclose a garden or yard.
Sports and Recreation
In sports and recreational activities, knowing the perimeter can assist in designing and organizing spaces:
- Sports Fields: Measuring the perimeter of courts and fields for accurate markings and dimensions.
- Playgrounds: Planning the layout and safety boundaries of playgrounds and recreational areas.
- Track Design: Designing running tracks and ensuring they meet specific length requirements.
Everyday Uses
Perimeter calculations can also be applied in various everyday situations:
- Home Improvement: Estimating the amount of paint, wallpaper, or other materials needed for home projects.
- DIY Projects: Planning and executing do-it-yourself projects that require precise measurements.
- Event Planning: Organizing spaces for events and ensuring adequate space and materials.
Understanding the practical applications of perimeter calculation enhances your ability to tackle a wide range of tasks efficiently and accurately. Whether for professional purposes or personal projects, mastering this skill can lead to better planning and execution.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While calculating the perimeter of a square is straightforward, certain mistakes can lead to incorrect results. Here are common errors to watch out for and tips on how to avoid them:
1. Incorrectly Measuring the Side Length
One of the most frequent mistakes is measuring the side length inaccurately. Ensure that:
- You use a precise measuring tool.
- The measurement is taken from one end of the side to the other without any gaps or overlaps.
- Measurements are taken in the correct unit (e.g., meters, feet, inches).
2. Misapplying the Perimeter Formula
Another common error is using the wrong formula. The correct formula for the perimeter of a square is:
\[ P = 4s \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s \) is the side length. Ensure you multiply the side length by 4 and not by any other number.
3. Mixing Up Units of Measurement
Using inconsistent units can lead to incorrect results. To avoid this mistake:
- Make sure all measurements are in the same unit before performing the calculation.
- Convert units when necessary to maintain consistency.
4. Rounding Errors
Rounding off numbers too early in the calculation process can result in significant inaccuracies. To prevent this:
- Carry out the multiplication first before rounding off the final result.
- Use as many decimal places as possible during intermediate steps, rounding only the final result.
5. Forgetting to Double-Check Work
Skipping the review of calculations can lead to undetected errors. Always:
- Recheck each step of the calculation to ensure accuracy.
- Verify that the final result makes sense given the initial measurements.
6. Using the Wrong Geometric Shape Formula
Sometimes, the formula for another geometric shape is mistakenly used. Remember that the perimeter of a square specifically requires:
\[ P = 4s \]
Unlike rectangles or other polygons, a square has four equal sides, so ensure the correct formula is applied.
7. Not Using a Calculator When Needed
Manual calculations can sometimes lead to simple arithmetic errors. To avoid this:
- Use a calculator for more accurate results, especially for larger numbers or decimals.
- Verify manual calculations with a calculator when in doubt.
Example Error Correction
Let’s correct a common error where the wrong formula is used:
- Incorrect Calculation: Using the formula for a rectangle instead of a square:
for a square with side length 5 units might lead to incorrect use of different lengths.
\[ P = 2l + 2w \] - Correct Calculation: Applying the correct formula for a square:
\[ P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \text{ units} \]
By being aware of these common mistakes and knowing how to avoid them, you can ensure accurate perimeter calculations for any square.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a square?
The formula is \( P = 4 \times a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side of the square.
- What is the unit of measurement for the perimeter of a square?
The unit of measurement is the same as the unit of the side length, such as inches, feet, centimeters, etc.
- Can the perimeter of a square be zero?
No, a square cannot have a side length of zero, therefore, its perimeter cannot be zero.
- What happens to the perimeter if the side length of the square doubles?
If the side length doubles, the perimeter will also double.
- Is it possible to calculate the perimeter of a square without knowing the side length?
No, you must know the side length to calculate the perimeter.
- What tools can I use to measure the side length of a square?
Common tools include rulers, measuring tapes, and for larger squares, a GPS device.
- Why is the perimeter of a square four times the side length?
Because a square has four equal sides, so the total distance around the square (the perimeter) is four times the length of one side.
- Can I use the perimeter to find the area of a square?
Yes, if you know the perimeter, you can divide it by four to find the side length, then square the side length to find the area.
- What is the difference between the perimeter and area of a square?
The perimeter is the total distance around the square, while the area is the amount of space inside the square.
- What factors can affect the accuracy of a perimeter calculation?
The accuracy of the side length measurement and the straightness of the sides can affect the accuracy of a perimeter calculation.
Additional Resources and Tools
Here are some additional resources and tools that can help you understand and calculate the perimeter of a square:
-
This calculator allows you to enter the side length of a square and instantly get the perimeter. It also works in reverse, where you can input the perimeter to find the side length.
-
Use this tool to calculate the side length, diagonal, perimeter, or area of a square. Given any one of these variables, the calculator will compute the other three.
-
This site provides multiple methods to calculate the perimeter, including using side length, area, or diagonal.
Related Calculators
-
Find the area and diagonal of a square along with the perimeter.
-
Calculates the area given the side length, perimeter, or diagonal.
-
Calculate the area of a square using side length, perimeter, or diagonal.
Educational Resources
-
Video tutorials and exercises to help understand the concepts of perimeter and area of squares.
-
Interactive lessons and activities on squares, including perimeter and area calculations.
Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter of a square is essential for a variety of practical and theoretical applications. Whether you're calculating the perimeter for a school project, a DIY home improvement task, or a professional architectural plan, the formula P = 4a where a is the side length, remains a straightforward and reliable method.
Using the perimeter calculator simplifies this process, allowing you to input the side length, diagonal, or area of the square to quickly find the perimeter. This tool is especially useful for those who need accurate and swift results without manual calculations.
Remember, the accuracy of your perimeter calculation depends on the precision of your measurements. Always double-check your inputs to ensure the most accurate output. Additionally, familiarize yourself with various measurement methods to enhance your overall understanding and ability to handle different scenarios.
In conclusion, the perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept that, with the help of reliable calculators and proper measurement techniques, can be easily mastered and applied to a wide range of practical situations. Continue to explore and utilize these resources to enhance your mathematical proficiency and problem-solving skills.
READ MORE:
Máy tính diện tích và chu vi cho hình vuông giúp bạn dễ dàng tính toán một cách nhanh chóng và chính xác. Thích hợp cho học sinh và giáo viên.
Máy tính diện tích và chu vi (cho hình vuông)