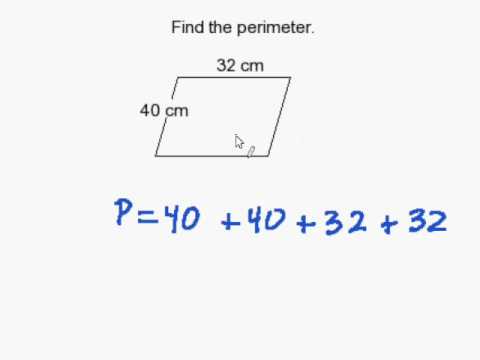
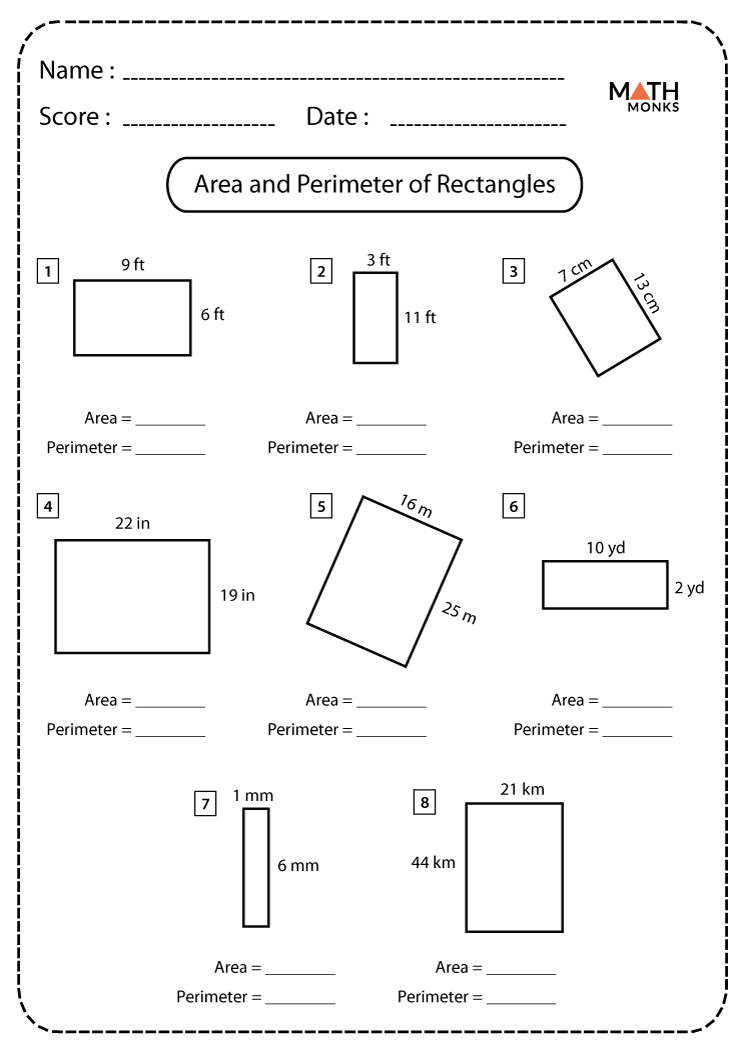
Topic area and perimeter of rectangle worksheet: Unlock the secrets of geometry with our comprehensive guide on area and perimeter of rectangle worksheets. Designed to engage and challenge students, these worksheets provide a variety of problems and exercises to enhance mathematical skills and understanding. Perfect for classroom use or home practice, our worksheets are the ultimate resource for mastering these fundamental concepts.
Table of Content
Area and Perimeter of Rectangles Worksheets
These worksheets are designed to help students practice calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles. Each worksheet includes a variety of problems that challenge students to apply their knowledge in different contexts.
Understanding the Concepts
To find the perimeter of a rectangle, use the formula:
\[ P = 2(l + w) \]
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
To find the area of a rectangle, use the formula:
\[ A = l \times w \]
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
Worksheet Examples
Calculate the perimeter and area of a rectangle with length 8 cm and width 5 cm.
A rectangular garden has a width of 10 feet and a length of 15 feet. Find the area and perimeter.
The width of a rectangular deck is 5 feet and its length is 4 times its width. What is the deck’s area and perimeter?
A poster is 3 times as long as it is wide. If the width of the poster is 2 feet, what is the perimeter of the poster?
Katie cut out a piece of wrapping paper that was 2 times as long and 3 times as wide as the box that she was wrapping. The box was 5 inches long and 4 inches wide. What is the perimeter of the wrapping paper that Katie cut?
Practice Problems
Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 12 meters and a width of 7 meters.
A rectangular field has a length of 20 yards and a width of 10 yards. Calculate its area.
The length of a rectangle is twice its width. If the width is 6 inches, find the area and perimeter of the rectangle.
A swimming pool is 25 meters long and 10 meters wide. What is the perimeter and area of the pool?
The perimeter of a rectangular park is 60 meters. If the length is 20 meters, what is the width and area of the park?
Additional Resources
For more practice, you can download and print additional worksheets that cover a range of problems involving the area and perimeter of rectangles. These worksheets are suitable for students from elementary to middle school and include answer keys for easy grading.
| Worksheet | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic Rectangles | Simple problems involving the calculation of area and perimeter for rectangles with given dimensions. |
| Word Problems | Application problems that require the use of area and perimeter formulas in real-world contexts. |
| Mixed Problems | A combination of basic and word problems to challenge students’ understanding of the concepts. |
| Advanced Problems | More complex problems that involve multiple steps and critical thinking. |

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the area and perimeter of rectangles is a fundamental aspect of geometry that helps students build a solid foundation in mathematics. Rectangles are everywhere around us, from books and screens to rooms and fields. This section introduces the key concepts, formulas, and practical applications for calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles, providing a comprehensive overview to help students grasp these essential skills.
Calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles involves using simple mathematical formulas. The area of a rectangle is determined by multiplying its length by its width, while the perimeter is calculated by adding together twice the length and twice the width. These formulas are straightforward, but applying them correctly requires practice and understanding of measurement units and conversion between them.
Worksheets on the area and perimeter of rectangles are designed to offer a variety of exercises that cater to different learning levels. These worksheets include problems involving integers, decimals, and fractions, as well as unit conversions. They also incorporate real-world scenarios to help students relate mathematical concepts to everyday life.
Whether it's finding the area of a bedroom, calculating the perimeter of a garden, or solving complex word problems, mastering the area and perimeter of rectangles equips students with the skills needed for more advanced topics in geometry and beyond. Let's delve into the detailed worksheets and start practicing these essential math skills step by step.
Basic Concepts
Understanding the area and perimeter of a rectangle is fundamental in geometry. This section will provide a detailed explanation of these concepts, including their definitions and formulas.
Area of a Rectangle
The area of a rectangle is the amount of space it occupies. The formula to calculate the area is:
$$\text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width}$$
Where length is the longer side of the rectangle, and width is the shorter side. For example, if a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units, the area is:
$$\text{Area} = 5 \times 3 = 15 \, \text{square units}$$
Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around its edges. The formula to calculate the perimeter is:
$$\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width})$$
Using the same example, if the length is 5 units and the width is 3 units, the perimeter is:
$$\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16 \, \text{units}$$
These basic formulas are essential for solving various problems involving rectangles, from simple calculations to more complex applications in different fields of study.
Formulas for Area and Perimeter
The formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of a rectangle are fundamental in geometry. These formulas are based on the dimensions of the rectangle, namely the length and the width.
Area of a Rectangle
The area of a rectangle is the amount of space enclosed within its boundaries. The formula to calculate the area is:
\[ \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \]
Where:
- Length is the longer side of the rectangle.
- Width (or breadth) is the shorter side of the rectangle.
Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around the outside of the rectangle. The formula to calculate the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
Where:
- Length is the longer side of the rectangle.
- Width (or breadth) is the shorter side of the rectangle.
Examples
Here are a few examples to illustrate how these formulas are applied:
- If a rectangle has a length of 8 units and a width of 5 units:
- Area = 8 × 5 = 40 square units
- Perimeter = 2 × (8 + 5) = 2 × 13 = 26 units
- If a rectangle has a length of 10 meters and a width of 4 meters:
- Area = 10 × 4 = 40 square meters
- Perimeter = 2 × (10 + 4) = 2 × 14 = 28 meters
Interactive Calculation
Use the formulas above to calculate the area and perimeter for different rectangles. Practice by substituting various values for length and width.
Worked Examples
In this section, we will walk through some worked examples to help you understand how to calculate the area and perimeter of rectangles.
Example 1
Let's consider a rectangle with a length of 8 units and a width of 5 units.
- Calculate the Perimeter:
The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a rectangle is given by:
$$ P = 2 \times (l + w) $$
Substituting the given values:
$$ P = 2 \times (8 + 5) $$
$$ P = 2 \times 13 $$
$$ P = 26 \, \text{units} $$
- Calculate the Area:
The formula for the area \( A \) of a rectangle is:
$$ A = l \times w $$
Substituting the given values:
$$ A = 8 \times 5 $$
$$ A = 40 \, \text{square units} $$
Example 2
Consider another rectangle with a length of 12 units and a width of 7 units.
- Calculate the Perimeter:
Using the perimeter formula:
$$ P = 2 \times (l + w) $$
Substituting the values:
$$ P = 2 \times (12 + 7) $$
$$ P = 2 \times 19 $$
$$ P = 38 \, \text{units} $$
- Calculate the Area:
Using the area formula:
$$ A = l \times w $$
Substituting the values:
$$ A = 12 \times 7 $$
$$ A = 84 \, \text{square units} $$
Example 3
For a rectangle with a length of 15 units and a width of 10 units:
- Calculate the Perimeter:
Using the formula:
$$ P = 2 \times (l + w) $$
Substituting the values:
$$ P = 2 \times (15 + 10) $$
$$ P = 2 \times 25 $$
$$ P = 50 \, \text{units} $$
- Calculate the Area:
Using the formula:
$$ A = l \times w $$
Substituting the values:
$$ A = 15 \times 10 $$
$$ A = 150 \, \text{square units} $$
These examples illustrate the steps involved in calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles. By following these steps, you can solve similar problems easily.
Word Problems
Word problems help apply the concepts of area and perimeter in real-life scenarios. Below are some examples that illustrate how to solve such problems:
-
The projection screen in the school auditorium is 5 times as long and 5 times as wide as the screen in the library. The screen in the library is 4 feet long with a perimeter of 14 feet. What is the perimeter of the screen in the auditorium?
Solution:
- Library screen length = 4 feet
- Library screen perimeter = 14 feet
- Width of the library screen = \( \frac{14 - 2 \times 4}{2} = 3 \) feet
- Auditorium screen length = 5 × 4 = 20 feet
- Auditorium screen width = 5 × 3 = 15 feet
- Perimeter = 2 × (20 + 15) = 70 feet
-
The width of David’s tent is 5 feet. The length is twice the width. David’s rectangular air mattress measures 3 feet by 6 feet. If David puts the air mattress in the tent, how many square feet of floor space will be available for the rest of his things?
Solution:
- Width of the tent = 5 feet
- Length of the tent = 2 × 5 = 10 feet
- Area of the tent = 5 × 10 = 50 square feet
- Area of the air mattress = 3 × 6 = 18 square feet
- Available floor space = 50 - 18 = 32 square feet
-
Jackson’s bedroom has an area of 90 square feet. If the bedroom is 9 feet wide, what is its length?
Solution:
- Width = 9 feet
- Area = 90 square feet
- Length = \( \frac{90}{9} = 10 \) feet
-
The width of a rectangular deck is 5 feet and its length is 4 times its width. What is the deck’s area?
Solution:
- Width = 5 feet
- Length = 4 × 5 = 20 feet
- Area = 5 × 20 = 100 square feet
-
A poster is 3 times as long as it is wide. If the width of the poster is 2 feet, what is the perimeter of the poster?
Solution:
- Width = 2 feet
- Length = 3 × 2 = 6 feet
- Perimeter = 2 × (2 + 6) = 16 feet
-
Katie cut out a piece of wrapping paper that was 2 times as long and 3 times as wide as the box that she was wrapping. The box was 5 inches long and 4 inches wide. What is the perimeter of the wrapping paper that Katie cut?
Solution:
- Box length = 5 inches
- Box width = 4 inches
- Wrapping paper length = 2 × 5 = 10 inches
- Wrapping paper width = 3 × 4 = 12 inches
- Perimeter = 2 × (10 + 12) = 44 inches
-
Alexis has a piece of red paper that is 4 centimeters wide. Its length is twice its width. She glues a piece of blue paper on top of the red piece measuring 3 centimeters by 7 centimeters. How many square centimeters of red paper will be visible on top?
Solution:
- Red paper width = 4 centimeters
- Red paper length = 2 × 4 = 8 centimeters
- Area of red paper = 4 × 8 = 32 square centimeters
- Area of blue paper = 3 × 7 = 21 square centimeters
- Visible red paper area = 32 - 21 = 11 square centimeters
-
Brinn’s pantry has an area of 20 square feet. If the pantry is 4 feet wide, what is the length of the pantry?
Solution:
- Width = 4 feet
- Area = 20 square feet
- Length = \( \frac{20}{4} = 5 \) feet
-
The length of Marshall’s poster is 2 times its width. If the width is 5 inches, what is the area of the poster?
Solution:
- Width = 5 inches
- Length = 2 × 5 = 10 inches
- Area = 5 × 10 = 50 square inches
Real-World Applications
The concepts of area and perimeter are not confined to the pages of a textbook; they are vital in many real-world scenarios. Understanding these applications helps students see the practical relevance of mathematical principles and enhances their problem-solving skills.
- Measurement of Land or Fields: Farmers use perimeter to fence their fields and protect crops from animals. Real estate deals often involve calculating the area to determine the value of the land.
- Construction of Homes and Buildings: Architects and builders use area and perimeter to design floor plans, determine the amount of materials needed, and ensure structures are built to precise specifications.
- Construction of Roads and Bridges: Engineers calculate the area and perimeter during the planning and construction of roads and bridges to ensure proper materials are used and structures are safe.
- Interior Design: Interior designers use these concepts to determine the amount of paint, flooring, or tiles needed for a room. For example, to install tiles, the area of the floor must be calculated accurately.
- Art and Fashion: Artists and fashion designers use area and perimeter in their work, whether it’s planning the layout of a painting or designing a new clothing line. Precision in measurements ensures that their creations come out as intended.
- Sports Fields: The dimensions of sports fields, such as soccer fields or basketball courts, are calculated using area and perimeter to meet regulatory standards and ensure fair play.
- Technology and Computer Graphics: In the realm of computer graphics, area and perimeter calculations are used to render images and design interfaces accurately, contributing to the realism and functionality of digital products.
Below are a couple of practical examples:
- Example 1: A rectangular garden needs to be fenced. If the garden is 20 meters long and 10 meters wide, the perimeter is calculated as:
Perimeter = 2 × (length + width) = 2 × (20 m + 10 m) = 60 meters.
The area is calculated as:
Area = length × width = 20 m × 10 m = 200 square meters.
- Example 2: An artist wants to cover a rectangular canvas with paint. If the canvas is 5 feet long and 3 feet wide, the area is:
Area = length × width = 5 ft × 3 ft = 15 square feet.
Understanding these applications not only helps in academics but also equips students with skills to solve real-life problems efficiently.
Interactive Activities
Interactive activities are a fantastic way to engage students in learning about the area and perimeter of rectangles. Here are some hands-on and digital activities to make the learning process fun and effective:
-
LEGO Bricks
Use LEGO bricks to explore the concepts of area and perimeter. Students can build various rectangular shapes and calculate their area and perimeter.
-
Math Mosaics
Have students create mosaics using square tiles. They can arrange the tiles to form different shapes and calculate the area and perimeter of their creations.
-
Interactive Worksheets
Utilize online interactive worksheets where students can drag and drop shapes to calculate their area and perimeter. offers a variety of these activities.
-
PhET Interactive Simulations
The PhET Interactive Simulations project at the University of Colorado provides an online tool where students can build shapes and understand the relationship between area and perimeter. to enhance their learning experience.
-
Floor Tile Shapes
Use floor tiles and painter’s tape to create various shapes on the classroom floor. Students can measure and calculate the area and perimeter of these shapes.
-
Building a Kite
Have students design and build their own kites. They can calculate the area and perimeter of their kites, then see how these measurements affect flight performance.
-
City Building Project
Engage students in building a miniature city. They can design buildings and calculate the area and perimeter of each structure, integrating volume for a more comprehensive understanding.
These activities not only make learning about area and perimeter enjoyable but also help students see the practical applications of these mathematical concepts in everyday life.
Printable Worksheets
Printable worksheets for calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles are a valuable resource for students and teachers. These worksheets help reinforce understanding through a variety of exercises and problems. Below are some types of printable worksheets available:
-
Basic Calculation Worksheets
These worksheets focus on the basic formulae for calculating area (Area = length × width) and perimeter (Perimeter = 2 × (length + width)) of rectangles. They include problems with integer, decimal, and fractional side lengths.
-
Counting Squares Worksheets
These worksheets are designed for younger students to introduce the concept of area by counting unit squares within rectangles. They are suitable for grades 2 to 4.
-
Mixed Practice Worksheets
These include a mix of problems where students must calculate either the area or perimeter of given rectangles, or sometimes both, enhancing their versatility in solving different types of problems.
-
Word Problem Worksheets
These worksheets present real-world scenarios where students must apply their knowledge of area and perimeter to solve problems. For example, they might determine the amount of material needed for a project or the fencing required for a garden.
-
Advanced Worksheets
For more advanced students, these worksheets involve more complex problems such as finding missing dimensions when given the area or perimeter, or dealing with composite shapes that can be broken down into rectangles.
Here are some example problems from these worksheets:
| Type | Example Problem |
|---|---|
| Basic Calculation | Calculate the area of a rectangle with length 5 cm and width 3 cm. |
| Counting Squares | Count the number of 1 cm squares within a 4 cm by 3 cm rectangle to find the area. |
| Mixed Practice | Find the perimeter of a rectangle with length 7.5 m and width 2.5 m. |
| Word Problem | A garden is 10 meters long and 4 meters wide. How much fencing is needed to enclose the garden? |
| Advanced | If the area of a rectangle is 56 square inches and the length is 7 inches, find the width. |
These worksheets can be easily downloaded and printed for classroom or home use. They often come with answer keys to help students check their work and understand any mistakes.

Answer Keys
Answer keys are essential tools for students and educators alike, providing a means to verify solutions and understand mistakes. Here are some common components found in answer keys for area and perimeter of rectangle worksheets:
-
Step-by-Step Solutions
These provide detailed steps to arrive at the correct answer, ensuring students can follow the logic and methodology used to solve each problem.
-
Final Answers
For quick reference, final answers are often listed in a straightforward manner, making it easy for students to check their work.
-
Common Errors
Some answer keys include explanations of common mistakes and how to avoid them, helping students learn from their errors.
-
Alternative Methods
Where applicable, different methods to solve the same problem might be provided, offering students various approaches to understand the concepts better.
Here are some example problems along with their solutions:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Calculate the area of a rectangle with length 8 cm and width 5 cm. |
|
| Find the perimeter of a rectangle with length 7 m and width 3 m. |
|
| A rectangle has an area of 54 square inches and a width of 6 inches. Find the length. |
|
Answer keys can be downloaded or printed along with worksheets, making them convenient for both classroom and home use. They are valuable for self-assessment and ensuring accurate learning.
Tips and Tricks for Solving Problems
Solving problems involving the area and perimeter of rectangles can be made easier with some helpful tips and tricks. Here are some strategies to keep in mind:
- Understand the Formulas: Make sure you know the basic formulas by heart:
- Area: \( A = l \times w \)
- Perimeter: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- Identify Given Values: Carefully read the problem to determine what values are given and what you need to find. Label the length (l) and width (w) clearly.
- Units Matter: Always pay attention to the units. Convert all measurements to the same unit before performing calculations.
- Double-Check Calculations: After computing the area or perimeter, revisit your calculations to ensure they are correct.
- Visualize the Problem: Draw a sketch of the rectangle, labeling all known dimensions. This helps in understanding the problem better.
- Break Down Complex Problems: If the problem is complex, break it down into smaller parts. Solve each part step-by-step and then combine the results.
- Use Estimation: Estimating the result before calculating can help catch errors. If your final answer is far from your estimate, re-check your work.
- Check for Special Conditions: Look out for clues that may simplify the problem, such as when the rectangle is a square (length equals width).
- Practice Word Problems: Practicing different types of word problems helps in understanding how to apply formulas in various scenarios.
- Interactive Tools: Utilize interactive online tools and apps that can provide instant feedback and step-by-step solutions to reinforce your understanding.
By applying these tips and tricks, solving problems related to the area and perimeter of rectangles will become more manageable and efficient.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with area and perimeter problems for rectangles, students often make common mistakes. Below is a list of tips to help avoid these errors:
- Confusing Area and Perimeter:
Ensure students understand that the area measures the space inside the rectangle (length × width) while the perimeter measures the distance around the rectangle (2 × (length + width)).
- Incorrect Units:
Always use the correct units for area (square units) and perimeter (linear units). For example, if length and width are in meters, the area should be in square meters (m²) and the perimeter in meters (m).
- Calculation Errors:
Double-check all calculations to avoid simple arithmetic mistakes. It's useful to have students redo the calculations or use a calculator for verification.
- Forgetting to Double the Length and Width for Perimeter:
When calculating the perimeter, remember to multiply the sum of the length and width by 2. The formula is .
- Misinterpreting Dimensions in Word Problems:
Read word problems carefully to identify which dimensions are length and width. Diagrams can help visualize the problem better.
- Incorrectly Applying the Formulas to Non-Rectangles:
Ensure that students only apply these formulas to rectangles and not to other shapes like squares or irregular quadrilaterals without verifying their dimensions.
By paying attention to these common mistakes and following these tips, students can improve their accuracy and understanding of calculating area and perimeter for rectangles.
Conclusion
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter of rectangles is fundamental to mastering geometry. This knowledge not only helps in solving mathematical problems but also has practical applications in various real-world scenarios. From designing a floor plan to determining the amount of fencing needed for a yard, these calculations are invaluable.
By working through the worksheets provided, students gain hands-on experience in applying formulas, interpreting diagrams, and solving word problems. These exercises build a strong foundation and enhance problem-solving skills.
In addition to practice problems, interactive activities, and real-world applications, students are also equipped with tips and tricks to simplify their calculations and avoid common mistakes. Answer keys and additional resources ensure that students can verify their work and seek further learning opportunities if needed.
Overall, this comprehensive set of materials aims to provide a well-rounded understanding of the area and perimeter of rectangles, making learning both effective and enjoyable. Keep practicing, stay curious, and continue to apply these mathematical concepts in everyday life.

Làm thế nào để tìm diện tích và chu vi của hình chữ nhật
READ MORE:
Học cách tìm chu vi của hình chữ nhật cùng thầy J. Video hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu, giúp học sinh nắm vững kiến thức cơ bản về hình học.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Hình Chữ Nhật | Toán với Thầy J