Topic area and perimeter of composite figures worksheet: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the area and perimeter of composite figures! This worksheet is designed to help students master essential geometry skills through engaging exercises and detailed explanations. Perfect for both classroom use and self-study, our resources will make learning these concepts both fun and effective.
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter of Composite Figures
- Introduction to Composite Figures
- Finding the Area of Composite Figures
- Finding the Perimeter of Composite Figures
- Decomposing Composite Figures
- Calculating Area Using Addition and Subtraction
- Common Geometric Shapes in Composite Figures
- Word Problems Involving Composite Figures
- Practice Worksheets and Exercises
- Interactive and Printable Worksheets
- Answers and Explanations
- Additional Resources and Tips
- Downloadable PDF Worksheets
- YOUTUBE:
Area and Perimeter of Composite Figures
Composite figures are shapes that are made up of two or more simple geometric shapes. Calculating the area and perimeter of these figures involves breaking them down into their simpler components, calculating each area and perimeter separately, and then combining these results appropriately.
Steps to Find the Area of Composite Figures
- Identify the simple shapes that make up the composite figure (e.g., rectangles, triangles, circles).
- Calculate the area of each simple shape using appropriate formulas:
- Rectangle: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Triangle: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Circle: \( \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
- Sum the areas of all the simple shapes to find the total area of the composite figure.
Steps to Find the Perimeter of Composite Figures
- Identify the outer boundary of the composite figure.
- Measure the lengths of all the sides that make up the perimeter.
- Sum the lengths to find the total perimeter.
Example Worksheet Problems
Below are example problems that can help students practice finding the area and perimeter of composite figures:
| Problem | Description |
|---|---|
| Problem 1 |
A composite figure made of a rectangle and a semicircle. The rectangle has a length of 10 units and a width of 4 units, and the semicircle has a diameter of 4 units.
|
| Problem 2 |
A composite figure made of a triangle and a rectangle. The triangle has a base of 5 units and a height of 3 units, and the rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 2 units.
|
Additional Resources
READ MORE:
Introduction to Composite Figures
Composite figures are shapes that are made up of two or more simple geometric shapes, such as rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles. Understanding how to calculate the area and perimeter of these figures involves breaking them down into their simpler components, calculating each part, and then summing the results.
- A composite figure may be composed of any combination of the basic shapes.
- To find the area of a composite figure, calculate the area of each individual shape and then add them together. This is known as the Area Addition Postulate.
- Similarly, to find the perimeter, sum the outer sides of all the shapes that form the composite figure.
Let's explore a step-by-step approach:
- Decompose the Composite Figure: Identify and separate the individual shapes that make up the composite figure.
- Calculate Individual Areas: Use the appropriate formulas to find the area of each shape.
- Add the Areas Together: Sum the areas of the individual shapes to find the total area.
- Calculate the Perimeter: For perimeter, add the lengths of the outer sides of the shapes that form the composite figure.
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \(A = l \times w\) | \(P = 2(l + w)\) |
| Triangle | \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\) | \(P = a + b + c\) |
| Circle | \(A = \pi r^2\) | \(C = 2 \pi r\) |
Finding the Area of Composite Figures
Finding the area of composite figures involves breaking down the figure into simpler shapes whose areas can be calculated easily. The process can be summarized in the following steps:
- Identify the simpler shapes within the composite figure (e.g., rectangles, triangles, circles).
- Calculate the area of each simple shape using appropriate formulas:
- Rectangle: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Triangle: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Circle: \( \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
- Add the areas of all the simple shapes to find the total area of the composite figure. If there are overlapping parts, subtract the overlapping area.
For example, consider a composite figure consisting of a rectangle and a semicircle:
| Shape | Dimensions | Formula | Calculation |
| Rectangle | Length = 8 units, Width = 4 units | \( 8 \times 4 \) | 32 square units |
| Semicircle | Radius = 2 units | \( \frac{1}{2} \times \pi \times 2^2 \) | \( 2\pi \) square units |
| Total Area | \( 32 + 2\pi \) square units | ||
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the area of any composite figure.
Finding the Perimeter of Composite Figures
Finding the perimeter of composite figures involves calculating the total distance around the figure. Follow these steps to accurately determine the perimeter:
- Identify the simpler shapes within the composite figure. This may include rectangles, triangles, circles, etc.
- Calculate the perimeter of each simpler shape individually.
- Add the lengths of all the outer sides of the composite figure. For shared sides between shapes, ensure you count them only once.
Here are a few examples to help illustrate:
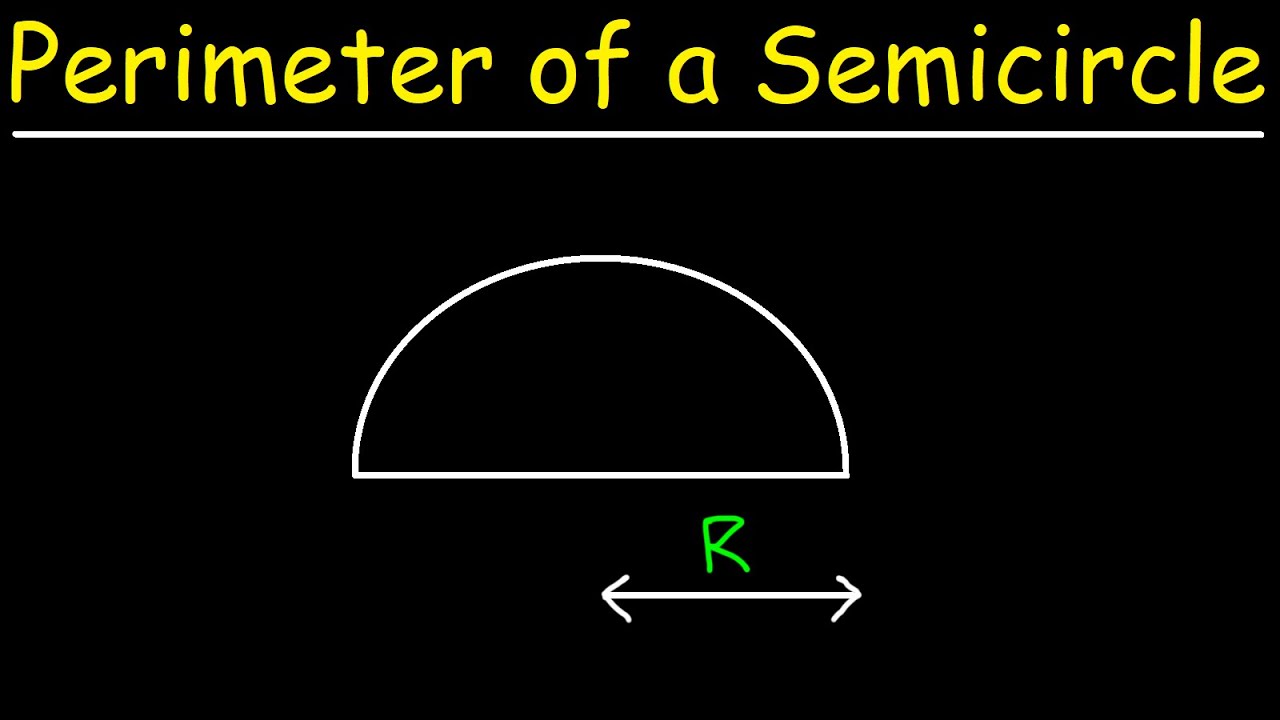
- If the composite figure consists of a rectangle and a semicircle, calculate the perimeter of the rectangle and add it to the perimeter of the semicircle (excluding the diameter).
- For a figure composed of multiple rectangles, sum the lengths of all the outer sides while ensuring not to double-count shared sides.
Consider an example:
If you have a composite figure with a rectangle of length 8 units and width 5 units attached to a semicircle of radius 2.5 units:
- Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle: \(2 \times (8 + 5) = 26 \) units.
- Calculate the perimeter of the semicircle: \( \pi \times 2.5 \) units (circumference of full circle is \(2\pi r\), so half is \( \pi r\)), which gives \( \pi \times 2.5 \approx 7.85 \) units.
- Since the semicircle is attached along the diameter, exclude the diameter from the perimeter calculation of the composite figure.
- Add the lengths: \(26 + 7.85 - 5 = 28.85 \) units (since 5 units is the length of the diameter).
The total perimeter of the composite figure is approximately 28.85 units.
Decomposing Composite Figures
Decomposing composite figures involves breaking down a complex shape into simpler, familiar geometric shapes such as rectangles, triangles, and circles. This process makes it easier to calculate the area and perimeter of the entire figure.
Follow these steps to decompose a composite figure:
- Identify Simple Shapes: Look at the composite figure and identify the simple shapes that it can be divided into. Common shapes include rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles.
- Draw Lines to Separate Shapes: Use straight lines to separate the composite figure into these simpler shapes. Ensure that the lines you draw do not change the overall area of the figure.
- Label Each Shape: Assign a label to each of the simple shapes within the composite figure. This will help in keeping track of the different areas or perimeters you will calculate.
- Calculate the Area and Perimeter: Use the appropriate formulas to calculate the area and perimeter of each simple shape. For example:
- Rectangle: Area = \( \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Triangle: Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Circle: Area = \( \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
- Add the Areas: Sum up the areas of all the simple shapes to find the total area of the composite figure.
- Sum the Perimeters: To find the perimeter, carefully add the lengths of all the outer edges of the composite figure. Be mindful of the edges that are shared between shapes, as these should only be counted once.
Here's an example to illustrate:
| Shape | Formula | Calculation |
| Rectangle 1 | Area = \( l \times w \) | Area = \( 5 \, \text{cm} \times 3 \, \text{cm} = 15 \, \text{cm}^2 \) |
| Triangle | Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \) | Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times 4 \, \text{cm} \times 2 \, \text{cm} = 4 \, \text{cm}^2 \) |
| Total Area | Total Area = \( 15 \, \text{cm}^2 + 4 \, \text{cm}^2 = 19 \, \text{cm}^2 \) | |
By following these steps, you can simplify the process of finding the area and perimeter of complex composite figures.
Calculating Area Using Addition and Subtraction
Calculating the area of composite figures can be simplified by using the methods of addition and subtraction. Here's a step-by-step approach:
- Identify Simple Shapes: Break down the composite figure into simpler shapes such as rectangles, triangles, circles, etc.
- Calculate Individual Areas: Find the area of each simple shape using the respective area formulas.
- Rectangle: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Triangle: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Circle: \( \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
- Add Areas Together: Add the areas of all the simple shapes together if the composite figure is formed by adding these shapes.
\[ \text{Total Area} = \text{Area}_1 + \text{Area}_2 + \ldots + \text{Area}_n \]
- Subtract Overlapping Areas: If there are overlapping parts, calculate the area of the overlap and subtract it from the total area.
\[ \text{Total Area} = \text{Area}_1 + \text{Area}_2 - \text{Overlap Area} \]
Using these methods ensures accurate calculation of the area of any composite figure, making it easier to handle complex shapes in geometry problems.
Common Geometric Shapes in Composite Figures
Composite figures are made up of simple geometric shapes such as rectangles, squares, triangles, circles, and semicircles. Understanding these shapes is crucial for calculating the area and perimeter of composite figures.
- Rectangles and Squares: These shapes have opposite sides equal and can easily be calculated using length and width.
- Triangles: Often included in composite figures, triangles can vary in type, including equilateral, isosceles, and scalene. The area is found using \( \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
- Circles and Semicircles: Circular components add complexity. The area of a circle is \( \pi r^2 \), and for semicircles, it is \( \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \).
- Trapezoids: These shapes have a pair of parallel sides and an area calculated as \( \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \).
Recognizing these common shapes and knowing their area formulas are essential steps in breaking down composite figures for easier calculation.
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \( \text{length} \times \text{width} \) | \( 2(\text{length} + \text{width}) \) |
| Square | \( \text{side}^2 \) | \( 4 \times \text{side} \) |
| Triangle | \( \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \) | \( \text{sum of all sides} \) |
| Circle | \( \pi r^2 \) | \( 2 \pi r \) |
| Semicircle | \( \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \) | \( \pi r + 2r \) |
| Trapezoid | \( \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \) | \( \text{sum of all sides} \) |
By decomposing composite figures into these basic shapes, you can apply these formulas to find the total area and perimeter efficiently.
Word Problems Involving Composite Figures
Word problems involving composite figures can help students apply their understanding of area and perimeter in real-life contexts. These problems often require breaking down complex shapes into simpler geometric figures. Here’s how to approach them:
-
Read the Problem Carefully: Understand what is being asked. Identify the composite figure and the relevant dimensions.
-
Decompose the Figure: Break the composite figure into simpler shapes (e.g., rectangles, triangles, circles).
- Label each part clearly.
- Note down the dimensions of each shape.
-
Calculate the Area:
- Find the area of each simple shape using appropriate formulas.
- Add or subtract the areas as needed to find the total area.
For example, if a composite figure consists of a rectangle and a semicircle:
- Area of rectangle \(= l \times w\)
- Area of semicircle \(= \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2\)
-
Calculate the Perimeter:
- Find the perimeter of each simple shape, then add them up.
- Adjust for any overlapping or shared sides.
For example, in the above composite figure:
- Perimeter of rectangle \(= 2(l + w)\)
- Circumference of semicircle \(= \pi r\)
- Combine these, adjusting for shared edges.
-
Check Your Work: Ensure all calculations are correct and all parts of the figure are accounted for.
Practicing these steps through various word problems enhances problem-solving skills and helps in understanding the practical applications of geometric concepts.
Practice Worksheets and Exercises
Enhance your understanding of composite figures with our comprehensive practice worksheets and exercises. These resources are designed to help you master the concepts of area and perimeter for composite shapes through a variety of problems and step-by-step solutions.
- Identify and decompose composite figures into simpler shapes.
- Apply formulas for area and perimeter to each component shape.
- Combine the areas or perimeters of individual shapes to find the total.
- Check your understanding with a variety of question formats, including multiple-choice, short answer, and word problems.
Our worksheets come with answer keys to help you verify your solutions and understand any mistakes. Practice consistently to improve your skills and confidence in solving composite figure problems.
| Worksheet | Description | Download |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Shapes | Practice identifying and calculating the area and perimeter of basic composite shapes. | |
| Intermediate Shapes | Work on more complex figures that require advanced decomposition techniques. | |
| Advanced Problems | Challenge yourself with intricate composite figures and word problems. |
These exercises are suitable for students from grade 3 to grade 8, aligning with common core standards. Keep practicing to excel in geometry!

Interactive and Printable Worksheets
Interactive and printable worksheets provide an excellent way for students to practice and master the concepts of area and perimeter of composite figures. These resources are designed to be engaging and flexible, catering to different learning styles and allowing for both online and offline practice.
- Interactive Worksheets:
Interactive worksheets often include dynamic features such as drag-and-drop exercises, immediate feedback, and adaptive learning paths. These tools help reinforce learning by making practice sessions more engaging and responsive to individual student needs.
- Printable Worksheets:
Printable worksheets offer the convenience of offline practice. They are perfect for homework assignments, in-class activities, or additional practice at home. These worksheets can be easily printed and distributed to students, providing a tangible resource for learning.
Benefits of Using Interactive and Printable Worksheets
- Enhances engagement and motivation through interactive elements.
- Allows for immediate feedback, helping students learn from their mistakes.
- Provides flexibility for both online and offline learning environments.
- Offers a wide range of problems to practice, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the topic.
- Facilitates personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs.
Examples of Interactive and Printable Worksheets
- Worksheets with problems on calculating the area and perimeter of various composite shapes.
- Exercises that require students to decompose complex figures into simpler shapes and find the total area.
- Word problems that apply the concepts of area and perimeter in real-life scenarios.
Utilizing both interactive and printable worksheets can greatly enhance the learning experience, making the study of composite figures' area and perimeter both effective and enjoyable.
Answers and Explanations
To effectively find the area and perimeter of composite figures, it's essential to break down the complex shapes into simpler ones. Here, we'll go through detailed steps and explanations for solving typical problems involving composite figures.
Example Problem 1: Area of Composite Figure
Consider a composite figure composed of a rectangle and a semicircle on one of its shorter sides. The rectangle has a length of 10 units and a width of 6 units, and the semicircle has a diameter equal to the width of the rectangle.
- Find the area of the rectangle:
- Area of rectangle = length × width
- \( A_{\text{rectangle}} = 10 \times 6 = 60 \, \text{square units} \)
- Find the area of the semicircle:
- Radius of semicircle = diameter / 2
- \( r = 6 / 2 = 3 \, \text{units} \)
- Area of semicircle = \( \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \)
- \( A_{\text{semicircle}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi (3)^2 = \frac{9 \pi}{2} \, \text{square units} \approx 14.14 \, \text{square units} \)
- Find the total area of the composite figure:
- Total area = Area of rectangle + Area of semicircle
- \( A_{\text{total}} = 60 + 14.14 = 74.14 \, \text{square units} \)
Example Problem 2: Perimeter of Composite Figure
Consider the same composite figure: a rectangle and a semicircle.
- Find the perimeter of the rectangle (excluding the side where the semicircle is attached):
- Perimeter of three sides of the rectangle = length + 2 × width
- \( P_{\text{rectangle}} = 10 + 2 \times 6 = 22 \, \text{units} \)
- Find the circumference of the semicircle:
- Circumference of semicircle = \( \pi r \)
- \( C_{\text{semicircle}} = \pi \times 3 = 3 \pi \, \text{units} \approx 9.42 \, \text{units} \)
- Find the total perimeter of the composite figure:
- Total perimeter = Perimeter of three sides of the rectangle + Circumference of the semicircle
- \( P_{\text{total}} = 22 + 9.42 = 31.42 \, \text{units} \)
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to reinforce your understanding:
- Calculate the area and perimeter of a composite figure made up of a square and an equilateral triangle.
- Determine the area of a figure composed of two rectangles and a right triangle.
Remember to decompose the figures into simpler shapes, calculate their individual areas and perimeters, and then sum them up to get the total values.
Additional Resources and Tips
Enhancing your understanding and practice with composite figures involves exploring various resources and strategies. Below are some additional resources and tips to assist you:
- Interactive Learning Platforms: Websites like MathWorksheets4Kids and K12 LibreTexts offer a range of interactive worksheets and exercises specifically designed for composite figures. These resources often include step-by-step solutions and visual aids to reinforce learning.
- Printable Worksheets: Printable PDFs are available from several educational websites. These worksheets provide problems on finding the area and perimeter of composite shapes, often including both simple and complex figures. They are ideal for offline practice and homework assignments.
- Visual Aids: Use graph paper or geometry software to draw and visualize composite figures. Breaking down complex shapes into simpler ones, such as rectangles and triangles, can help in understanding how to calculate their area and perimeter.
- Step-by-Step Problem Solving: When tackling a composite figure, follow these steps:
- Identify and label all the simpler shapes within the composite figure.
- Calculate the area and perimeter of each simpler shape.
- Use addition or subtraction to combine these areas and perimeters as needed.
- Formula Review: Make sure to review and memorize key area and perimeter formulas for basic shapes like rectangles, triangles, circles, and trapezoids. This knowledge is crucial for solving composite figure problems efficiently.
- Online Tutorials: Websites like ThirdSpaceLearning provide detailed tutorials and examples on calculating the area and perimeter of composite shapes. These tutorials often include video explanations, which can be very helpful for visual learners.
- Practice with Real-World Problems: Apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios, such as calculating the area of a garden plot with irregular shapes or the perimeter of a composite-shaped fence. This practical application reinforces theoretical understanding.
These resources and tips can significantly enhance your proficiency in working with composite figures, making your learning experience more engaging and effective.
Downloadable PDF Worksheets
Here is a collection of downloadable PDF worksheets to help you practice finding the area and perimeter of composite figures. These worksheets cover various levels of difficulty and are suitable for different grade levels.
-
Area of Composite Figures Worksheet - Set 1
This set includes problems involving simple geometric shapes combined to form composite figures. It is perfect for beginners.
-
Area of Composite Figures Worksheet - Set 2
These worksheets increase in complexity and introduce additional geometric shapes, offering intermediate-level practice.
-
Area of Composite Figures Worksheet - Set 3
Advanced worksheets designed for students who are comfortable with a variety of geometric shapes and are ready for challenging problems.
-
Grade-Specific Worksheets
These resources are designed to help students build a solid understanding of how to calculate the area and perimeter of composite figures through practice and repetition.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Học cách tìm diện tích của hình ghép bao gồm các hình chữ nhật ghép lại. Video hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Tìm Diện Tích Hình Ghép | Diện Tích Hình Chữ Nhật Ghép