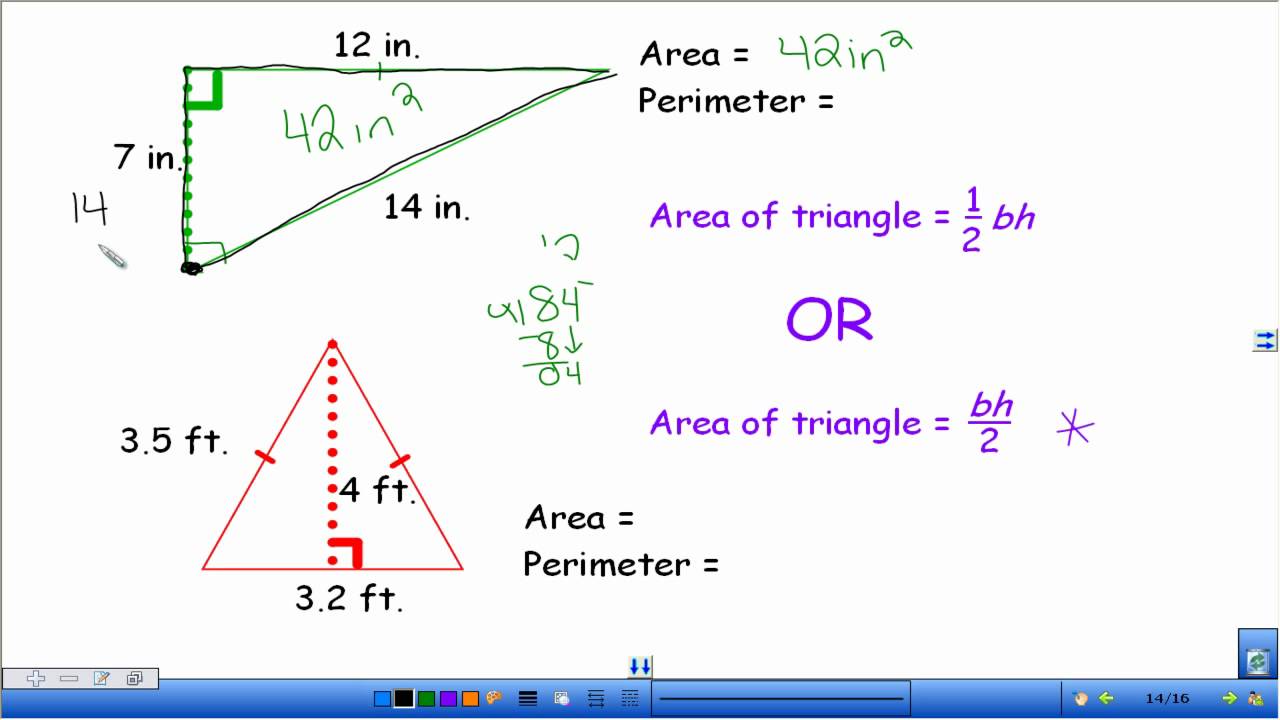
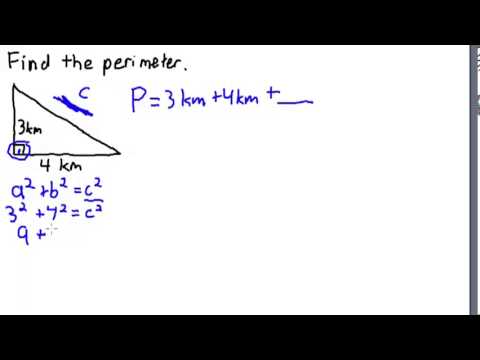
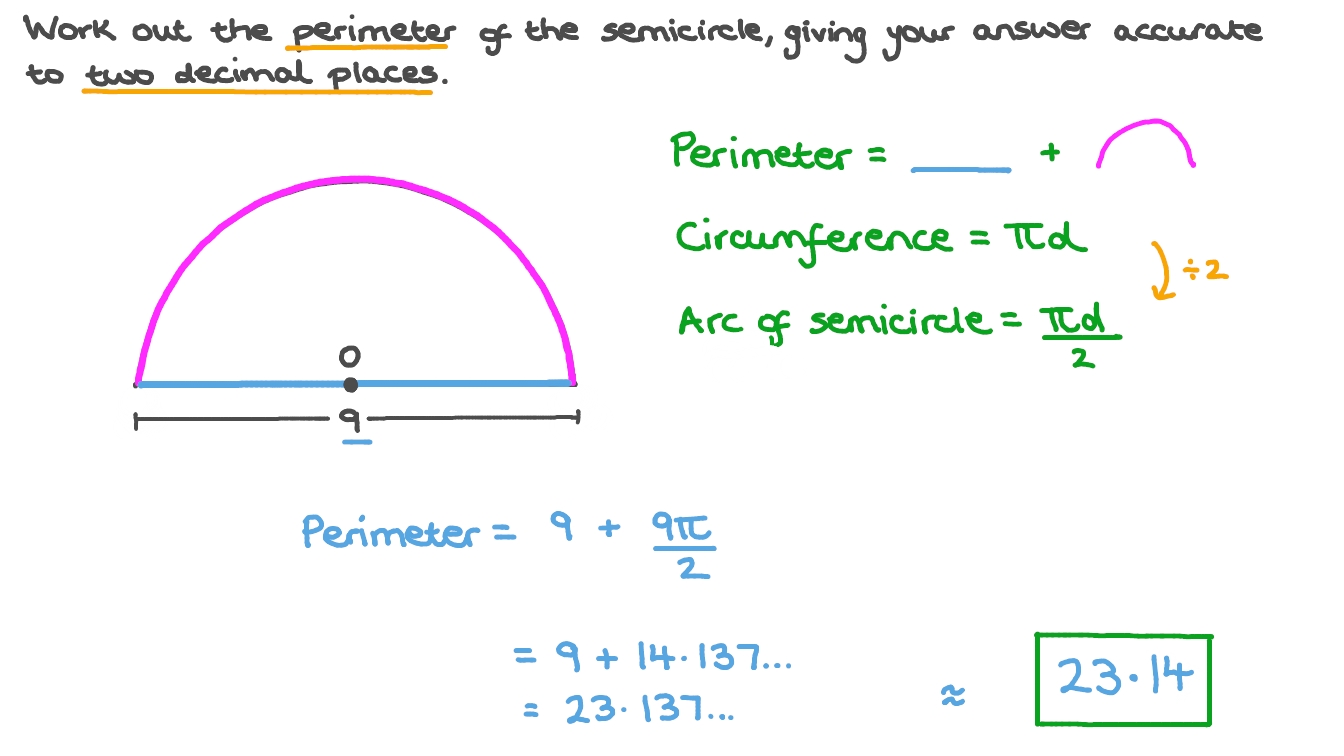
Topic area and perimeter of irregular shapes worksheet: Explore our comprehensive guide on the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. Our worksheets provide step-by-step instructions and practice problems to enhance your geometry skills. Perfect for students and educators looking to improve understanding and application of these key concepts.
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter of Irregular Shapes Worksheet
- Introduction to Irregular Shapes
- Understanding Area and Perimeter
- Basic Concepts and Formulas
- Grade-Specific Worksheets
- Worksheets for Elementary Grades
- Worksheets for Middle School Grades
- Complex Problems and Advanced Worksheets
- Interactive Learning Tools
- Visual Aids and Coordinate Grids
- Practical Applications
- Real-World Examples
- Problem-Solving Strategies
- Common Core Alignment
- Free Downloadable PDFs
- Online Resources and Tutorials
- Teacher and Parent Guides
- Additional Practice Problems
- Assessment and Evaluation
- YOUTUBE: Video này cung cấp rất nhiều ví dụ về cách tính diện tích và chu vi của các hình dạng không đều, giúp học sinh nắm vững kiến thức toán học quan trọng này.
Area and Perimeter of Irregular Shapes Worksheet
Understanding how to calculate the area and perimeter of irregular shapes is a crucial skill in geometry. These worksheets will guide you through various exercises designed to enhance your proficiency in these calculations.
Key Concepts
- Decomposing irregular shapes into familiar geometric figures
- Applying area formulas for standard shapes like rectangles, triangles, and circles
- Summing up the areas of decomposed shapes to find the total area
- Calculating the perimeter by adding the lengths of all sides
Worksheets
Counting Squares
Enhance your skills by counting unit squares within irregular shapes. This is suitable for students in grades 2 and 3.
Area of Compound Shapes
Practice finding the area of compound shapes by dividing them into simpler shapes. This includes exercises on using coordinate grid points for accurate measurements.
Independent Practice
Basic Skills: Find the area of various irregular shapes using provided diagrams and measurements.
Intermediate Skills: Break down complex shapes into segments to calculate the area.
Advanced Skills: Identify regular shapes within irregular figures and sum their areas to find the total area.
Application
Use these worksheets for a variety of applications, including warm-up exercises, formal assessments, and homework assignments. They cater to different skill levels, from basic to advanced, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the concepts.
Examples
| Shape | Area Calculation | Perimeter Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Irregular Polygon | \( \text{Area} = \sum \text{(Area of each segment)} \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = \sum \text{(Length of all sides)} \) |
| Compound Shape | \( \text{Area} = \text{Area}_1 + \text{Area}_2 + \text{Area}_3 \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = \text{Sum of all external sides} \) |
Practice Problems
- Calculate the area and perimeter of a shape that is a combination of a rectangle and a triangle.
- Find the total area of an irregular shape by dividing it into a rectangle and two triangles.
- Determine the perimeter of a polygon by adding the lengths of its irregular sides.
Conclusion
By working through these worksheets, students will develop a strong understanding of how to approach and solve problems involving the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. These skills are foundational for more advanced studies in geometry and practical applications in various fields.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Irregular Shapes
Understanding irregular shapes is crucial in geometry as they often appear in real-life scenarios. Unlike regular shapes, irregular shapes do not have equal sides or angles, making their area and perimeter calculations more complex. This section will introduce you to the concept of irregular shapes, their properties, and the methods used to calculate their area and perimeter step by step.
- Definition of Irregular Shapes
- Examples of Irregular Shapes in Real Life
- Methods to Calculate Area
- Methods to Calculate Perimeter
- Importance of Irregular Shapes in Geometry
To begin with, an irregular shape can be defined as any polygon that does not have equal sides and angles. These shapes can be found everywhere, from the layout of a garden to the design of a unique piece of art. The complexity of these shapes requires a deeper understanding of geometry principles, particularly in calculating areas and perimeters.
One common method to find the area of an irregular shape is by breaking it down into smaller, regular shapes like rectangles and triangles. By calculating the area of each smaller shape and then summing them up, you can determine the total area of the irregular shape.
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular shape involves adding the lengths of all its sides. This can sometimes require precise measurement, especially if the shape has many sides or intricate angles.
Understanding how to work with irregular shapes not only enhances your geometry skills but also prepares you for practical applications in fields like architecture, engineering, and various design disciplines.
Understanding Area and Perimeter
The concepts of area and perimeter are fundamental in geometry, allowing us to measure the size and boundary of shapes. When dealing with irregular shapes, calculating these measurements can be more challenging but equally rewarding. Let's delve into the basics of understanding area and perimeter, especially for irregular shapes.
- Area: The area of a shape is the amount of space it occupies. For regular shapes, this is calculated using specific formulas. However, for irregular shapes, we often need to break the shape down into smaller, regular shapes and sum their areas.
- Perimeter: The perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of a shape. For irregular shapes, this involves measuring each side's length and adding them together.
To understand these concepts better, let's break down the steps for calculating the area and perimeter of irregular shapes:
- Identify the shape: Look at the irregular shape and try to identify any regular shapes within it, such as rectangles, triangles, or circles.
- Divide the shape: Divide the irregular shape into smaller, regular shapes. This can be done by drawing lines within the shape to create easily calculable sections.
- Calculate individual areas: Use the appropriate formulas to calculate the area of each smaller shape. For example, use \( \text{Area of a rectangle} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \) or \( \text{Area of a triangle} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
- Sum the areas: Add up the areas of all the smaller shapes to get the total area of the irregular shape.
- Measure and sum perimeters: Measure each side of the irregular shape and add these lengths together to find the perimeter.
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the area and perimeter of any irregular shape. This method not only simplifies the process but also enhances your understanding of geometric principles.
Basic Concepts and Formulas
Understanding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes is crucial for solving many geometry problems. Here, we outline the basic concepts and formulas needed to calculate these measurements accurately.
For irregular shapes, we often break them down into smaller, regular shapes, such as rectangles, triangles, or circles, and then sum their areas or perimeters.
- Area of Irregular Shapes:
- Divide the shape into smaller, regular shapes.
- Calculate the area of each smaller shape using appropriate formulas.
- Sum the areas of the smaller shapes to find the total area.
- Perimeter of Irregular Shapes:
- Measure the length of each side of the shape.
- Add the lengths of all sides to find the total perimeter.
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
| Rectangle | \( \text{Area} = l \times w \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = 2(l + w) \) |
| Triangle | \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = \text{sum of all sides} \) |
| Circle | \( \text{Area} = \pi r^2 \) | \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \pi r \) (Circumference) |
These formulas provide a foundation for calculating the area and perimeter of more complex irregular shapes by breaking them into manageable parts.
Grade-Specific Worksheets
Our collection of grade-specific worksheets on the area and perimeter of irregular shapes is designed to cater to different educational levels. These worksheets provide a step-by-step approach to understanding and solving problems related to irregular shapes, ensuring students grasp the fundamental concepts and applications. Below, we outline the resources available for various grade levels.
Grade 2
- Introduction to basic shapes and their properties
- Counting squares to find area
- Simple perimeter calculations
Grade 3
- Finding the area of irregular shapes using grid counting
- Understanding and calculating the perimeter of basic shapes
Grade 4
- Advanced counting methods for finding area
- Perimeter calculations involving compound shapes
Grade 5
- Breaking down complex shapes into simpler ones for area calculation
- Using formulas to find the perimeter of irregular shapes
Grade 6
- Applying area and perimeter formulas to compound shapes
- Problem-solving with real-world applications
Grade 7
- Introduction to algebraic methods in finding area and perimeter
- Advanced problem sets involving irregular shapes
Grade 8
- Comprehensive review of all area and perimeter concepts
- Challenging worksheets designed to test mastery
High School
- Integration of geometry with algebra for complex problem solving
- Real-world applications and projects
These worksheets are meticulously crafted to build a strong foundation in geometry, ensuring students are well-prepared for advanced studies. Download the appropriate worksheets for your grade level and start mastering the concepts of area and perimeter of irregular shapes today.
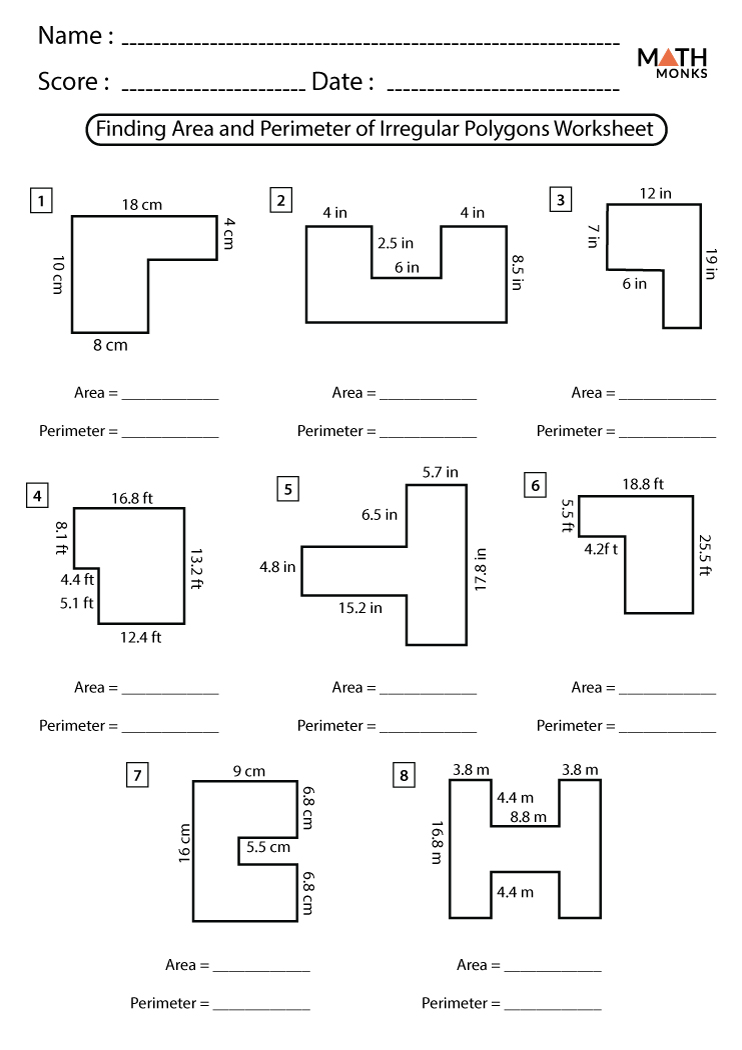
Worksheets for Elementary Grades
Here are some engaging worksheets designed to help elementary students master the concepts of area and perimeter for irregular shapes:
- Worksheet 1: Area of Irregular Shapes
This worksheet introduces students to calculating the area of irregular polygons by breaking them down into simpler shapes and using basic formulas. - Worksheet 2: Perimeter of Irregular Shapes
Students practice finding the perimeter of irregular shapes by identifying and adding up all sides, including any curved segments. - Worksheet 3: Mixed Problems
This worksheet challenges students with a variety of problems that combine both area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes, encouraging critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
These worksheets are accompanied by clear instructions and examples to guide students through each step of the problem-solving process. They are designed to be interactive and promote a deeper understanding of geometric concepts through practical application.
Worksheets for Middle School Grades
Explore these comprehensive worksheets tailored for middle school students to enhance their understanding of area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes:
- Worksheet 1: Area and Perimeter Review
This worksheet provides a review of basic area and perimeter concepts for irregular polygons, reinforcing fundamental skills. - Worksheet 2: Advanced Area Problems
Students tackle more complex irregular shapes, applying formulas and strategies to calculate accurate area measurements. - Worksheet 3: Perimeter Challenges
Focuses on perimeter calculations for irregular shapes, including exercises with varied side lengths and angles to strengthen geometric reasoning. - Worksheet 4: Real-World Applications
Engages students with practical scenarios where they must apply their knowledge of area and perimeter to solve real-life problems involving irregular shapes.
Each worksheet includes detailed instructions, examples, and solutions to support middle schoolers in developing their problem-solving abilities and geometric comprehension effectively.
Complex Problems and Advanced Worksheets
Delve into these challenging worksheets designed to push advanced learners' understanding of area and perimeter calculations for intricate irregular shapes:
- Worksheet 1: Advanced Area Problems
This worksheet presents complex irregular shapes where students must employ advanced geometric methods to accurately calculate area. - Worksheet 2: Perimeter with Mixed Geometry
Focuses on irregular shapes with mixed geometry elements, such as curves and varying angles, challenging students to calculate precise perimeters. - Worksheet 3: Problem-Solving Challenges
Engages students with multi-step problems that integrate both area and perimeter calculations, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills. - Worksheet 4: Geometric Constructions
Involves constructing irregular shapes from given specifications and then calculating their area and perimeter, promoting hands-on learning and spatial reasoning.
These worksheets are designed to stretch students' abilities, providing comprehensive solutions and detailed explanations to support deeper exploration and mastery of geometric concepts.
Interactive Learning Tools
Explore these engaging interactive tools designed to enhance students' understanding of area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes:
- Tool 1: Virtual Geometric Manipulatives
Allows students to manipulate and explore irregular shapes virtually, aiding in visualizing and understanding how changes affect area and perimeter. - Tool 2: Interactive Area Calculators
Provides interactive calculators where students can input dimensions of irregular shapes to instantly calculate their area, reinforcing computational skills. - Tool 3: Perimeter Estimators
Interactive tools that help students estimate the perimeter of irregular shapes by dragging and placing virtual markers along their boundaries. - Tool 4: Problem-Solving Simulations
Engages students with interactive simulations where they solve real-world problems involving irregular shapes and apply their knowledge of area and perimeter.
These interactive tools are designed to promote active learning and facilitate deeper exploration of geometric concepts through hands-on engagement and immediate feedback.

Visual Aids and Coordinate Grids
Explore these visual aids and coordinate grid resources designed to enhance students' understanding of area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes:
- Visual Aid 1: Shape Templates
Provides printable templates of irregular shapes on coordinate grids, allowing students to practice plotting points and calculating area and perimeter. - Visual Aid 2: Interactive Coordinate Grids
Offers interactive grids where students can plot vertices of irregular shapes, reinforcing understanding of how coordinates relate to geometric measurements. - Visual Aid 3: Area Visualization Tools
Visualizes the process of calculating area by shading irregular shapes on grids, helping students grasp the concept of area as a measure of space. - Visual Aid 4: Perimeter Demonstration
Demonstrates how to calculate perimeter using coordinate points and straight-line distances on grids, facilitating hands-on learning of perimeter concepts.
These visual aids and coordinate grid tools aim to make abstract geometric concepts more tangible and accessible, promoting deeper understanding and proficiency in area and perimeter calculations.
Practical Applications
Explore practical applications of area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes with these real-world examples:
- Example 1: Garden Design
Calculate the area and perimeter of irregular-shaped garden beds to determine the amount of soil and fencing required. - Example 2: Landscaping Projects
Use area calculations to estimate the amount of turf or mulch needed and perimeter calculations for installing edging around irregular paths. - Example 3: Architecture and Building Design
Apply area and perimeter calculations to irregular floor plans and building facades to optimize space utilization and material requirements. - Example 4: Art and Design
Calculate the area of irregular-shaped canvases or materials for art projects and use perimeter measurements for framing irregular artworks.
These practical applications demonstrate the relevance of geometric concepts in everyday scenarios, encouraging students to apply their mathematical knowledge to solve real-life problems effectively.
Real-World Examples
Explore these real-world examples where understanding area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes is essential:
- Example 1: Parcel of Land
Calculate the area to determine the size of a irregular-shaped parcel of land for purchasing or development purposes. - Example 2: Room Flooring
Use area calculations to estimate flooring material needed for irregular-shaped rooms, considering waste and cost-efficiency. - Example 3: Playground Design
Calculate perimeter for fencing and area for playground equipment placement in irregular-shaped areas to ensure safety and functionality. - Example 4: Road Construction
Apply perimeter calculations to determine fencing needs and area calculations for land grading in irregular-shaped road projects.
These examples illustrate how area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes are applied in various practical contexts, emphasizing their importance in decision-making and problem-solving.
Problem-Solving Strategies
Explore effective problem-solving strategies for mastering area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes:
- Strategy 1: Decomposition Method
Break down irregular shapes into simpler geometric figures (rectangles, triangles) to calculate their individual areas and perimeters. - Strategy 2: Approximation Techniques
Use approximation methods to estimate area and perimeter by dividing irregular shapes into smaller, more manageable sections. - Strategy 3: Coordinate Geometry
Utilize coordinate points to determine vertices and sides of irregular shapes, applying formulas for area and perimeter based on geometric coordinates. - Strategy 4: Visualization and Drawing
Visualize irregular shapes on grids or paper, drawing auxiliary lines or shapes to facilitate area and perimeter calculations through geometric visualization.
These strategies encourage critical thinking and problem-solving skills, enabling students to approach complex geometric problems with confidence and proficiency.
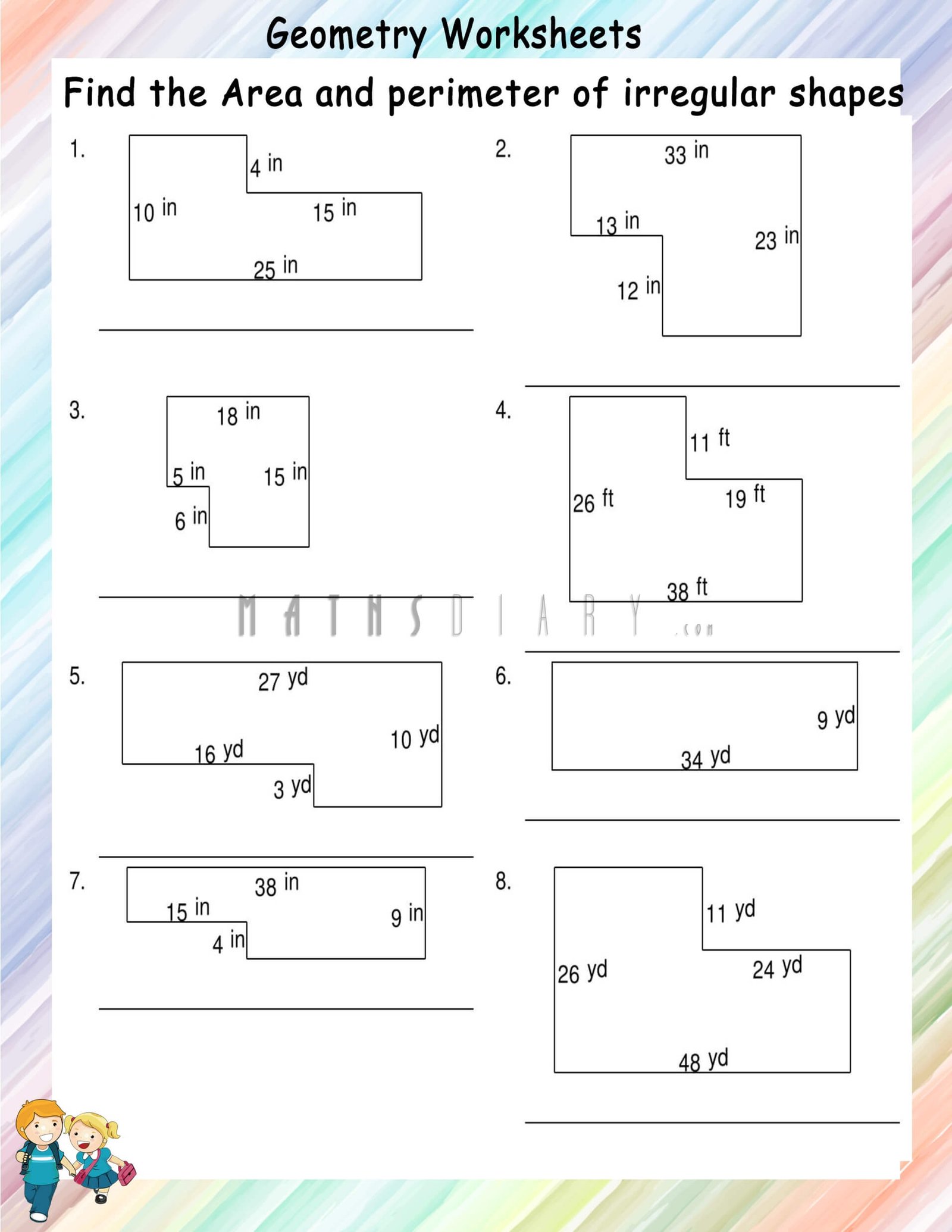
Common Core Alignment
Explore how area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes align with Common Core standards:
- Standard 1: Measurement and Data
Apply geometric measurement concepts and formulas to solve problems involving irregular shapes, aligning with Common Core standards for measurement. - Standard 2: Mathematical Practices
Use critical thinking and problem-solving skills to analyze and solve real-world problems using area and perimeter calculations for irregular shapes. - Standard 3: Integration of Knowledge
Integrate knowledge of geometric properties, including area and perimeter, with other mathematical concepts and real-world applications, fostering interdisciplinary connections. - Standard 4: Rigor and Depth of Understanding
Demonstrate proficiency in calculating area and perimeter of irregular shapes through rigorous application of mathematical concepts and procedures.
These alignments ensure that students develop a deep understanding of geometric measurement and its application, preparing them for higher-level mathematics and real-world problem-solving.
Free Downloadable PDFs
Enhance your understanding of the area and perimeter of irregular shapes with our collection of free downloadable PDF worksheets. These resources are designed to cater to students from elementary to middle school, providing a variety of exercises to solidify your grasp of these essential geometric concepts.
Available Worksheets
These worksheets are meticulously crafted to cover a broad spectrum of irregular shapes, from simple to complex, ensuring that students can build confidence in calculating areas and perimeters through progressive challenges.
Features of the Worksheets
- Exercises range from basic counting of unit squares to advanced problems involving complex shapes.
- Visual aids and geometric illustrations to help students better understand the shapes and their properties.
- Step-by-step solutions provided to enhance learning and problem-solving skills.
By regularly practicing with these worksheets, students can improve their accuracy and speed in solving problems related to the area and perimeter of irregular shapes. These resources are free to download, making them easily accessible for both classroom and home use.
Start practicing today and master the art of calculating the area and perimeter of irregular shapes!
Online Resources and Tutorials
Explore a wealth of online resources and tutorials designed to help you master the concepts of area and perimeter for irregular shapes. These tools are perfect for students, teachers, and parents looking to enhance their learning experience.
Interactive Worksheets and Tutorials
These interactive worksheets allow students to engage with problems in a dynamic way, reinforcing their understanding through practice and immediate feedback. Each worksheet is designed to cater to different learning levels, ensuring a step-by-step approach to mastering the calculations.
Video Tutorials and Lessons
Video tutorials provide a visual and auditory learning experience, making complex concepts easier to grasp. These resources include step-by-step explanations and examples, helping students to understand and apply their knowledge effectively.
Interactive Games and Activities
Interactive games and activities are a fun way to reinforce learning. These games are designed to make math practice engaging, helping students to develop their skills in a playful environment.
By utilizing these online resources and tutorials, students can significantly improve their understanding of the area and perimeter of irregular shapes, making learning both effective and enjoyable.
Teacher and Parent Guides
Teaching and guiding children in understanding the area and perimeter of irregular shapes can be challenging, but there are numerous resources available to assist both teachers and parents. Below is a comprehensive guide to help you get started:
Understanding Basic Concepts
- Introduction to Irregular Shapes: Begin by explaining what makes a shape irregular and how it differs from regular shapes. Use simple examples like combining rectangles or triangles to form an irregular shape.
- Calculating Area and Perimeter: Teach students to break down complex shapes into simpler ones, calculate the area or perimeter of each part, and then combine the results. Use diagrams and step-by-step instructions to illustrate these processes.
Worksheets and Practice
Utilize a variety of worksheets designed to reinforce these concepts:
- : Offers a range of worksheets that guide students through calculating the area of irregular shapes by breaking them down into rectangles. Ideal for grades 3-5.
- : Provides practice problems for finding the area of irregular shapes, with step-by-step solutions and review sheets for reinforcement.
- : Features revision resources with diagrams and explanatory notes, helping students solve area and perimeter problems of irregular shapes.
Interactive Tools and Visual Aids
- Interactive Learning: Use online tools and apps that allow students to manipulate shapes and see how changing dimensions affects the area and perimeter.
- Visual Aids: Incorporate charts, grids, and visual examples to help students better understand the concepts. Twinkl and other educational websites offer excellent visual resources.
Strategies for Effective Teaching
- Use Real-World Examples: Show how the concepts of area and perimeter apply to everyday objects and scenarios, such as gardening or room decoration.
- Encourage Group Work: Have students work in groups to solve problems, fostering collaboration and deeper understanding through discussion.
- Regular Assessments: Use quizzes and practice worksheets to regularly assess student progress and identify areas needing more focus.
Additional Resources
For more detailed guides and additional practice problems, consider these resources:
- : A variety of worksheets and teaching resources for both basic and advanced students.
- : Offers downloadable PDF worksheets that focus on the area of irregular shapes, complete with solutions.
These guides and resources will equip you with the necessary tools to effectively teach and guide students in mastering the area and perimeter of irregular shapes.

Additional Practice Problems
To further enhance students' understanding of area and perimeter of irregular shapes, we offer a variety of practice problems that range from basic to advanced levels. These problems are designed to challenge students and help them apply their knowledge in practical scenarios.
- Basic Level Practice Problems:
Find the area of irregular shapes by decomposing them into smaller rectangles. Sum the areas of these rectangles to get the total area.
Determine the perimeter of irregular shapes by summing the lengths of all the sides.
- Intermediate Level Practice Problems:
Calculate the area of irregular shapes that include circles and triangles. Use appropriate formulas for each segment and add the areas together.
Use coordinates to find the perimeter of shapes plotted on a grid. Calculate the distance between points to find the lengths of sides.
- Advanced Level Practice Problems:
Solve complex problems involving irregular shapes with mixed figures such as trapezoids and polygons. Apply advanced geometric formulas to find areas and perimeters.
Engage in critical thinking problems that require the use of area and perimeter concepts in real-world contexts.
These practice problems not only reinforce theoretical knowledge but also encourage practical application and problem-solving skills.
For a comprehensive set of worksheets and problems, visit our downloadable resources:
Assessment and Evaluation
Assessing and evaluating students' understanding of the area and perimeter of irregular shapes is crucial for tracking their progress and identifying areas that need improvement. Here are some effective strategies for assessment and evaluation:
- Formative Assessments:
Use quick quizzes and in-class worksheets to gauge students' grasp of basic concepts.
Incorporate peer-review sessions where students check each other's work and provide feedback.
- Summative Assessments:
Design comprehensive tests that include a variety of problems, from simple calculations to complex, multi-step challenges.
Include real-world application problems that require students to apply their knowledge in practical contexts.
- Project-Based Assessments:
Assign projects where students create their own irregular shapes and calculate the area and perimeter. This promotes creativity and deeper understanding.
Use presentations and reports to allow students to explain their methods and reasoning.
- Interactive Assessments:
Leverage digital tools and interactive platforms for assessments. These can provide instant feedback and adapt to individual student needs.
Incorporate gamified assessments to make learning more engaging and motivating.
Regularly reviewing assessment data helps teachers to tailor their instruction to meet the diverse needs of their students, ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to succeed.
Video này cung cấp rất nhiều ví dụ về cách tính diện tích và chu vi của các hình dạng không đều, giúp học sinh nắm vững kiến thức toán học quan trọng này.
Diện Tích và Chu Vi của Hình Dạng Không Đều - Rất Nhiều Ví Dụ!
READ MORE:
Video này cung cấp các ví dụ về cách tính diện tích và chu vi của các hình dạng không đều, giúp học sinh nắm vững kiến thức toán học quan trọng này.
Diện Tích và Chu Vi của Hình Dạng Không Đều