Topic negative square root of 100: The negative square root of 100 involves imaginary numbers, represented as ±10i. This concept is fundamental in advanced mathematics, particularly in complex number theory. Understanding this topic opens doors to various applications in engineering and physics.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Negative Square Root of 100
- Introduction
- Square Root Basics
- Understanding Negative Square Roots
- Mathematical Definition
- Examples of Square Roots
- Calculators and Tools
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá căn bậc hai của -100 và ứng dụng của nó trong toán học. Video này sẽ giải thích chi tiết về căn bậc hai âm và số phức.
Understanding the Negative Square Root of 100
The concept of square roots extends beyond positive numbers, especially when we consider negative numbers. The square root of a negative number involves imaginary numbers, which are crucial in various fields of mathematics and engineering.
Definition
A square root of a number x is a number y such that y2 = x. For negative numbers, the square root involves imaginary units. The imaginary unit i is defined as √-1.
Square Root of -100
To find the square root of -100, we use the concept of imaginary numbers:
Details and Examples
- The square roots of 100 are 10 and -10 because
- The square roots of -100 are because
Applications and Further Reading
Understanding the square root of negative numbers is fundamental in complex number theory, which has applications in electrical engineering, fluid dynamics, quantum physics, and more. For a detailed exploration, you can check out resources on , , and .

READ MORE:
Introduction
The negative square root of 100 is an intriguing mathematical concept that delves into the realm of complex numbers. While the square root of 100 is commonly known to be ±10, the negative square root introduces the imaginary unit 'i', resulting in ±10i. This concept is essential in advanced mathematics and engineering, providing solutions to equations that have no real number solutions.
Square Root Basics
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 100 is 10 because \(10 \times 10 = 100\). However, there is also a negative square root because \((-10) \times (-10) = 100\). Therefore, the square roots of 100 are both 10 and -10.
Square roots are represented using the radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \). For any positive number \(a\), the principal square root is denoted as \( \sqrt{a} \) and is always nonnegative. For instance, \( \sqrt{100} = 10 \).
When dealing with negative numbers, the square root involves imaginary numbers. The square root of -100 is represented as \( \sqrt{-100} = 10i \), where \( i \) is the imaginary unit and \( i = \sqrt{-1} \).
Here are some key points to understand about square roots:
- Every positive real number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
- The principal square root is the nonnegative root.
- Negative numbers have imaginary square roots.
Square roots are used in various mathematical calculations and are fundamental in algebra, geometry, and many other fields. Understanding how to find and use square roots is essential for solving equations and working with complex numbers.
Understanding Negative Square Roots
The concept of the negative square root can be perplexing at first, but it is a fundamental part of understanding complex numbers. In mathematics, the square root of a negative number is not a real number but a complex number.
For example, the square root of -100 is expressed as:
$$ \sqrt{-100} = \sqrt{100} \times \sqrt{-1} = 10i $$
Here, \( i \) is the imaginary unit, which is defined as \( i = \sqrt{-1} \). Therefore, \( i^2 = -1 \), and this property is crucial in dealing with the square roots of negative numbers.
To break it down step-by-step:
- Identify the positive counterpart of the negative number. In this case, it is 100.
- Calculate the square root of this positive number: \( \sqrt{100} = 10 \).
- Multiply this result by \( i \), the imaginary unit: \( 10 \times i = 10i \).
Therefore, the square root of -100 is \( 10i \). This approach applies to any negative number, transforming our understanding and allowing us to work within the realm of complex numbers.
Mathematical Definition
The square root of a number \( x \) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number \( x \). Mathematically, this is expressed as \( \sqrt{x} \). For example, the square root of 100 is denoted as \( \sqrt{100} \) and equals 10 because \( 10^2 = 100 \).
When dealing with negative numbers, such as the square root of -100, we enter the realm of complex numbers. The square root of -100 is expressed as \( \sqrt{-100} \) and equals \( 10i \) because \( (10i)^2 = -100 \), where \( i \) is the imaginary unit defined as \( \sqrt{-1} \).
- \( \sqrt{100} = 10 \) because \( 10 \times 10 = 100 \).
- \( \sqrt{-100} = 10i \) because \( (10i) \times (10i) = -100 \).
Thus, the mathematical definition and understanding of square roots extend beyond positive numbers into the domain of complex numbers when negative values are involved.
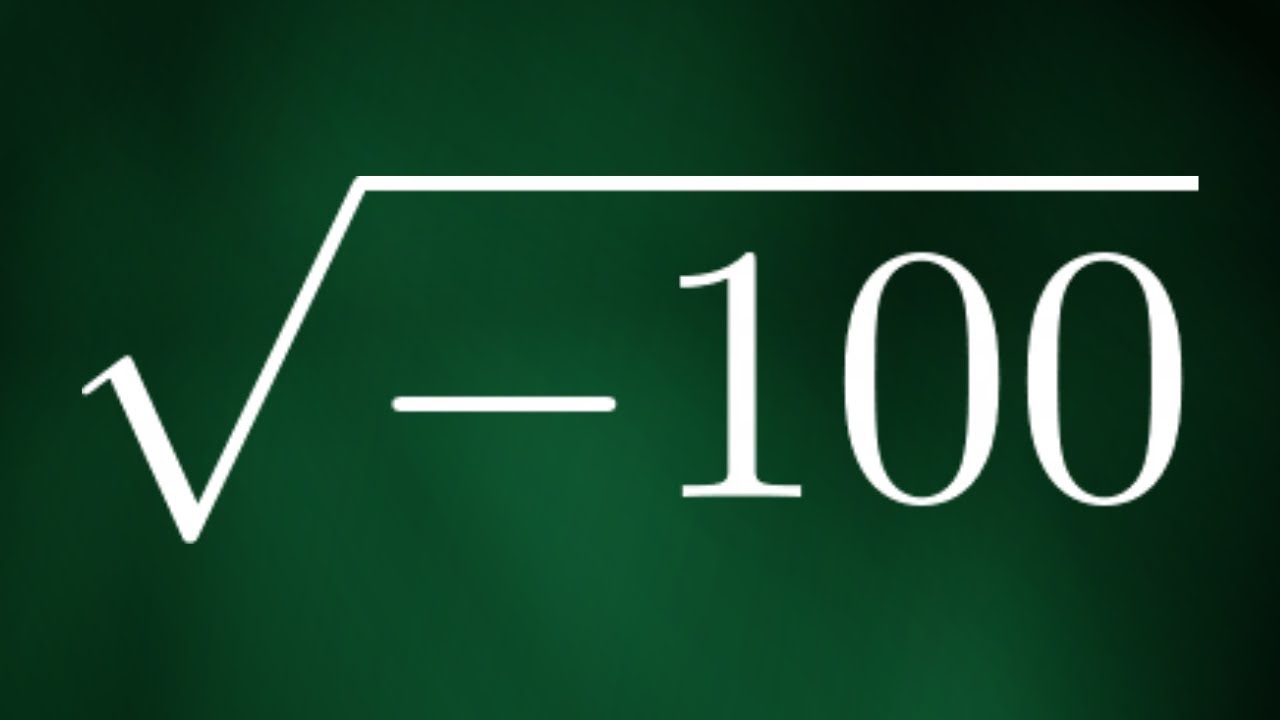
Examples of Square Roots
Understanding square roots involves looking at both positive and negative roots, especially when dealing with perfect squares and imaginary numbers. Here are some examples to illustrate:
- The square root of 100 is .
- The square root of -100 is an imaginary number: , where is the imaginary unit defined by
Let's explore some more examples to deepen our understanding:
| Number | Square Root | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | Perfect square | |
| 9 | Perfect square | |
| 25 | Perfect square | |
| -25 | Imaginary number | |
| 49 | Perfect square | |
| -49 | Imaginary number |
For non-perfect squares, the square roots are irrational numbers. For instance, the square root of 10 is approximately 3.162. This is because:
- 3.1 squared is 9.61
- 3.2 squared is 10.24
- Therefore, is between 3.1 and 3.2
In summary, the concept of square roots extends beyond just perfect squares to include negative numbers resulting in imaginary roots and non-perfect squares resulting in irrational roots.
Calculators and Tools
Several online calculators can help you find the square root of any real or complex number, providing detailed step-by-step solutions. Below are some popular tools:
-
Calculator Soup
This calculator can find the principal square root and the roots of real numbers, whether positive or negative. It also simplifies radicals and provides complex solutions for square roots of negative numbers.
- Website:
-
Symbolab
Symbolab's Square Root Calculator offers step-by-step solutions for square root calculations, including negative and imaginary numbers. It's a comprehensive tool for learning and solving complex math problems.
- Website:
-
Mathway
Mathway provides an intuitive interface to calculate the square roots of any number. It supports both exact form and decimal form for non-perfect squares, and it can handle complex numbers.
- Website:
-
Calculator.io
This calculator identifies both the principal square root and the opposite root. It can determine whether the input number is a perfect square and provide the corresponding roots.
- Website:
-
Swiftutors
Swiftutors offers a Negative Square Root Calculator that handles calculations involving imaginary numbers. It breaks down the process of finding the square roots of negative numbers.
- Website:
Conclusion
Understanding the negative square root of 100 involves grasping the concept of imaginary numbers, where the square root of a negative number is not real but complex. The square roots of -100 are ±10i, derived from the properties of imaginary numbers where \(i\) is the square root of -1.
This topic is fundamental in various fields of mathematics and engineering, helping solve equations that involve negative values under the square root. The principal square root of -100 is 10i, and the negative counterpart is -10i, both of which are essential in complex number theory.
Utilizing online calculators and tools can greatly aid in computing the square roots of both real and imaginary numbers. These resources provide detailed solutions and explanations, making it easier to understand and apply these concepts in different mathematical problems.
In conclusion, the exploration of negative square roots not only broadens one's mathematical knowledge but also enhances problem-solving skills in advanced mathematics and engineering disciplines. With the assistance of modern computational tools, learning and applying these concepts becomes more accessible and efficient.
Khám phá căn bậc hai của -100 và ứng dụng của nó trong toán học. Video này sẽ giải thích chi tiết về căn bậc hai âm và số phức.
Căn bậc hai của -100 || Căn(-100)
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số âm bằng cách sử dụng đơn vị tưởng tượng i. Bài tập 8 trong chuỗi bài giảng về số phức và căn bậc hai âm.
Hướng Dẫn - Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai Âm Sử Dụng Đơn Vị Tưởng Tượng i Bài Tập 8