Topic multiplying square roots calculator: The multiplying square roots calculator is an essential tool for anyone needing to quickly and accurately multiply square roots. This easy-to-use calculator simplifies complex operations, making it perfect for students, educators, and professionals. Discover how it can streamline your mathematical tasks and improve efficiency in problem-solving.
Table of Content
Multiplying Square Roots Calculator
This page provides detailed instructions on using a calculator to multiply square roots, along with several examples and a step-by-step guide.
How to Use the Multiplying Square Roots Calculator
- Enter the two numbers in the input fields.
- Click the "Submit" button to get the result.
- The calculator will display the solution and the steps involved.
Examples of Multiplying Square Roots
Below are examples demonstrating the multiplication of square roots:
- Example 1: \( \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{3} \)
Solution: \( \sqrt{2 \times 3} = \sqrt{6} \)
- Example 2: \( 2\sqrt{5} \times 3\sqrt{7} \)
Solution: \( (2 \times 3) \sqrt{5 \times 7} = 6\sqrt{35} \)
Step-by-Step Guide to Multiply Square Roots
Follow these steps to multiply square roots:
- Multiply the coefficients: If there are coefficients, multiply them first.
- Multiply the radicands: Multiply the numbers inside the square roots.
- Simplify if possible: If the resulting radicand is a product of a perfect square, simplify the expression.
Practice Problems
Try solving the following problems:
- \( \sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{12} \)
- \( 4\sqrt{2} \times 5\sqrt{8} \)
Using the Calculator
- Input: Enter the numbers in the calculator's input fields.
- Output: The result and explanation will be displayed below the calculator.
Additional Features
The calculator also allows:
- Clearing the input fields for new calculations.
- Generating random inputs to practice different problems.
- Copying and downloading the solution for future reference.
| Operation | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Multiplication | \( \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{9} \) | \( \sqrt{36} = 6 \) |
| Simplification | \( \sqrt{50} \) | \( \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2} \) |
Understanding the Multiplication Property of Square Roots
The multiplication property of square roots states that for any positive numbers \(a\) and \(b\), the product of the square roots is the square root of the product:
\( \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{ab} \)
Conclusion
The Multiplying Square Roots Calculator is a useful tool for quickly solving problems involving the multiplication of square roots. With step-by-step solutions and practice problems, it is designed to help users understand and apply the concepts effectively.
READ MORE:
Introduction
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on multiplying square roots using our specialized calculator. Multiplying square roots is a fundamental mathematical operation that can often appear in various contexts, from basic algebra to advanced scientific calculations. This guide will walk you through the process of multiplying square roots, explain the mathematical principles behind it, and show you how to utilize our online calculator to simplify your calculations.
Square roots are mathematical expressions that represent the value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 25 is 5, since \(5 \times 5 = 25\). When multiplying square roots, the process is straightforward: you multiply the radicands (the numbers inside the square root symbols) together, and then simplify if possible.
Here’s a step-by-step approach to multiplying square roots:
- Identify the square roots you need to multiply. For example, consider \(\sqrt{a}\) and \(\sqrt{b}\).
- Multiply the radicands: \(a \times b\).
- Simplify the resulting expression, if possible. For example, if the product of the radicands is a perfect square, you can simplify it further.
Using our online calculator, you can easily perform these steps without manual calculations. Simply enter the values of the radicands, and the calculator will display the result instantly, along with detailed steps to help you understand the process. This tool is particularly useful for students, educators, and professionals who need quick and accurate results.
Let’s look at an example to illustrate this process:
- Example: Multiply \(\sqrt{25}\) and \(\sqrt{36}\).
- Step 1: Multiply the radicands: \(25 \times 36 = 900\).
- Step 2: Simplify the resulting expression: \(\sqrt{900} = 30\).
By using our calculator, you can also explore more complex problems, generate random examples for practice, and even download or copy the solution for future reference. This comprehensive guide aims to enhance your understanding and make multiplying square roots an effortless task.
How to Multiply Square Roots
Multiplying square roots can be simplified using basic mathematical properties. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you understand and perform these calculations effectively.
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Identify the square roots to be multiplied. For example, consider \( \sqrt{a} \) and \( \sqrt{b} \).
- Use the product rule for square roots, which states: \[ \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{a \times b} \]
- Multiply the numbers inside the square roots. For instance, if you have \( \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{9} \), this becomes: \[ \sqrt{4 \times 9} = \sqrt{36} \]
- Simplify the resulting square root, if possible. In the example above: \[ \sqrt{36} = 6 \]
Examples
- Example 1: Multiply \( \sqrt{25} \) and \( \sqrt{36} \)
- Calculate inside the square roots: \[ \sqrt{25} = 5 \] \[ \sqrt{36} = 6 \]
- Multiply the simplified values: \[ 5 \times 6 = 30 \]
- Result: \( \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{36} = 30 \)
- Example 2: Multiply \( \sqrt{40} \) and \( \sqrt{49} \)
- Prime factorize and simplify: \[ \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{4 \times 10} = 2\sqrt{10} \] \[ \sqrt{49} = \sqrt{7 \times 7} = 7 \]
- Multiply the simplified values: \[ 2\sqrt{10} \times 7 = 14\sqrt{10} \]
- Result: \( \sqrt{40} \times \sqrt{49} = 14\sqrt{10} \approx 44.27 \)
Important Properties
- Product Rule: \( \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{a \times b} \)
- Multiplicative Property: When a square root is multiplied by itself, the result is the original number: \[ \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{a} = a \]
Using these steps and properties, you can easily multiply square roots and simplify the results. For more complex calculations, consider using an online calculator to verify your answers.
Step-by-Step Examples
Here are some step-by-step examples of multiplying square roots:
-
Example 1: Multiply \( \sqrt{2} \) by \( \sqrt{3} \).
Step 1: Write the square roots as a single radical: \( \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{3} = \sqrt{2 \cdot 3} \). Step 2: Calculate the product inside the radical: \( \sqrt{2 \cdot 3} = \sqrt{6} \). Therefore, \( \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{3} = \sqrt{6} \).
-
Example 2: Multiply \( 2\sqrt{5} \) by \( 3\sqrt{5} \).
Step 1: Multiply the coefficients: \( 2 \times 3 = 6 \). Step 2: Multiply the square roots: \( \sqrt{5} \times \sqrt{5} = \sqrt{25} \). Step 3: Simplify the result: \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \). Therefore, \( 2\sqrt{5} \times 3\sqrt{5} = 6 \times 5 = 30 \).
-
Example 3: Multiply \( (2 + \sqrt{3})(3 - \sqrt{3}) \).
Step 1: Apply the distributive property: \( (2 + \sqrt{3})(3 - \sqrt{3}) = 2 \cdot 3 + 2 \cdot (-\sqrt{3}) + \sqrt{3} \cdot 3 + \sqrt{3} \cdot (-\sqrt{3}) \). Step 2: Calculate each term: \( 6 - 2\sqrt{3} + 3\sqrt{3} - \sqrt{9} \). Step 3: Simplify the radicals: \( 6 + \sqrt{3} \). Therefore, \( (2 + \sqrt{3})(3 - \sqrt{3}) = 6 + \sqrt{3} \).
Benefits of Using a Calculator
Using a multiplying square roots calculator offers several advantages:
- Accuracy: Ensures precise calculations without manual errors.
- Efficiency: Saves time by quickly computing complex expressions.
- Convenience: Provides instant results, especially useful in exams or time-sensitive tasks.
- Learning Aid: Helps users understand the steps involved in multiplying square roots.
- Versatility: Can handle various forms of square root expressions and simplify radical results.
- Practical Applications: Useful in fields like engineering, physics, and finance where exact calculations are crucial.

Common Mathematical Properties
Understanding the mathematical properties related to multiplying square roots is essential:
- Product Rule: \( \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{a \cdot b} \)
- Multiplicative Property: \( \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{a} = a \)
- Cancellation Property: \( \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{\frac{1}{a}} = 1 \)
- Distributive Property: \( (a + b)\sqrt{c} = a\sqrt{c} + b\sqrt{c} \)
- Rationalizing Denominators: \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}} \times \frac{\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{b}}{\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a} - \sqrt{b}}{a - b} \)
- Simplifying Radical Expressions: \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \)
Applications
Multiplying square roots finds application in various fields:
- Geometry: Calculating distances, areas, and volumes involving square roots.
- Algebraic Equations: Solving equations and simplifying expressions.
- Engineering and Physics: Calculating forces, energy, and dimensions.
- Financial Mathematics: Calculating interest rates, investments, and financial models.
- Signal Processing: Analyzing signals and waveforms in electronics and communications.
- Computer Graphics: Generating and manipulating graphical elements.
Using Online Calculators
Online multiplying square roots calculators provide a user-friendly way to perform calculations:
- Input Flexibility: Enter square root expressions directly or use predefined templates.
- Instant Results: Get accurate results instantly without manual computation errors.
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Some calculators offer detailed step-by-step solutions for better understanding.
- Accessibility: Accessible anytime, anywhere with an internet connection.
- Multiple Functions: Often include additional functions like simplification of radicals and handling complex expressions.
- Compatibility: Compatible across various devices including smartphones, tablets, and computers.
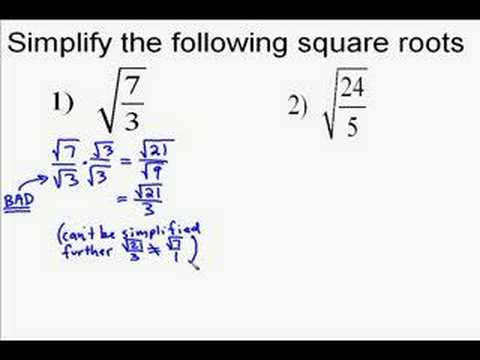
Xem video hướng dẫn cách nhân các biểu thức căn bậc hai và sau đó đơn giản hóa chúng.
Nhân Căn bậc Hai và Sau Đó Đơn giản hóa
READ MORE:
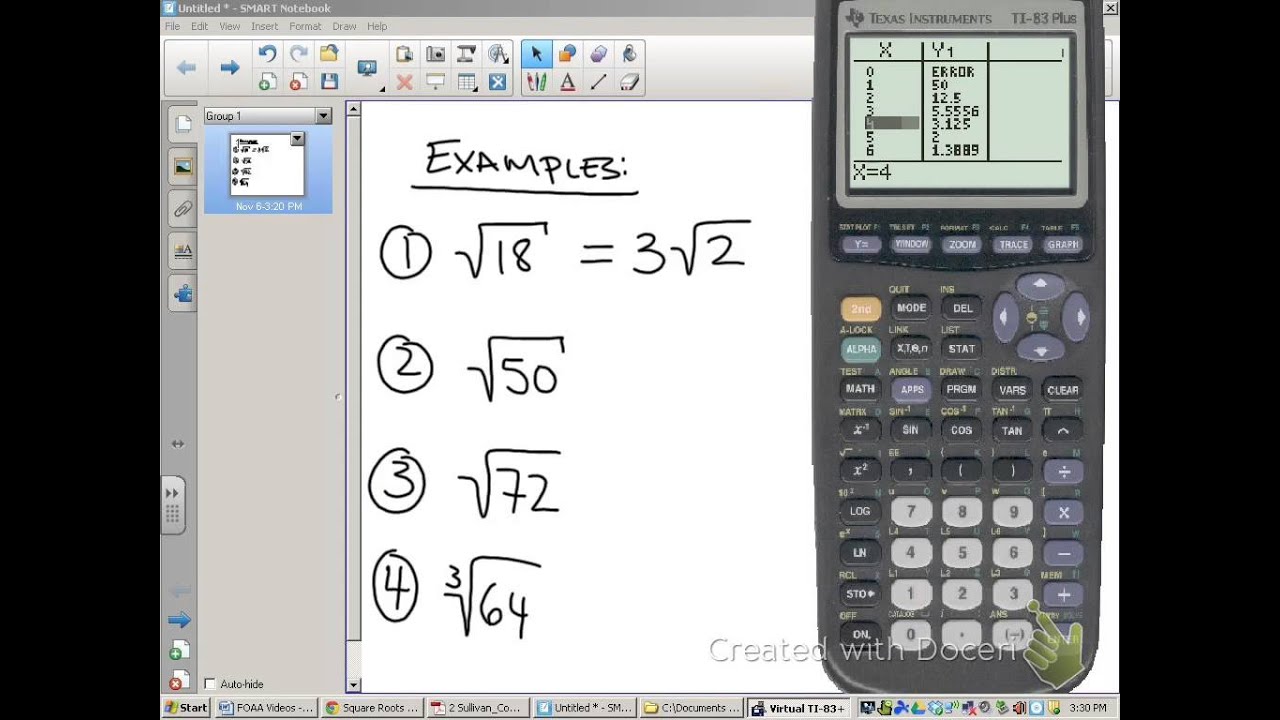
Xem video hướng dẫn cách nhân các biểu thức căn bậc hai bằng máy tính TI-84 Plus.
Nhân Căn bậc Hai bằng Máy tính (TI-84 Plus)