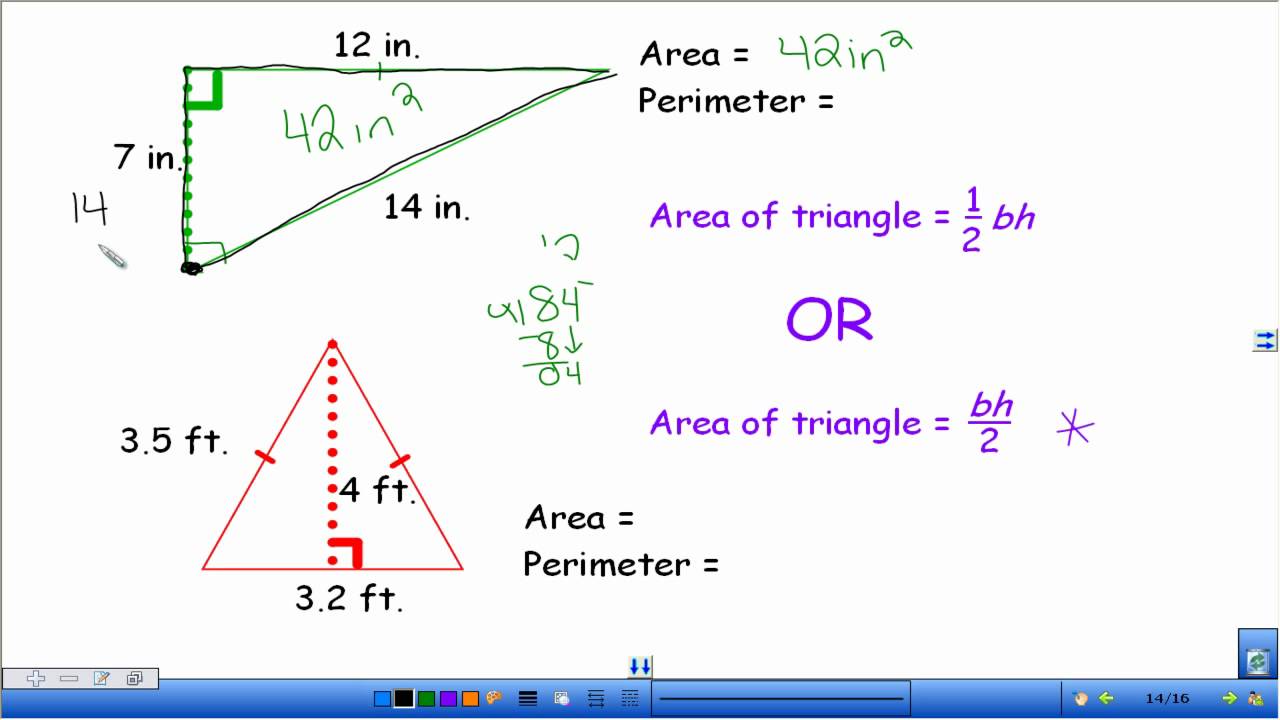
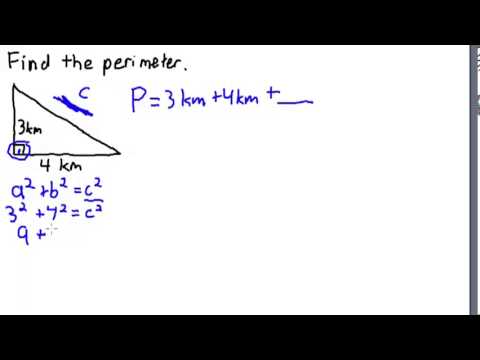
Topic area and perimeter 4th grade: Discover a fun and engaging way for 4th graders to master area and perimeter with our comprehensive guide. Packed with easy-to-understand explanations, interactive exercises, and exciting practice problems, this article will help students build confidence and excel in geometry. Start learning today and watch your math skills soar!
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter Practice Problems for 4th Grade
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Key Concepts and Definitions
- Formulas for Area and Perimeter
- Understanding Units of Measurement
- Step-by-Step Problem Solving
- Visual Aids and Diagrams
- Interactive Exercises and Activities
- Practice Problems with Solutions
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Tips and Tricks for Students
- Games and Fun Activities for Learning
- Resources for Teachers and Parents
- Conclusion and Next Steps
- YOUTUBE:
Area and Perimeter Practice Problems for 4th Grade
Welcome to our collection of fun and engaging practice problems designed for 4th graders to master the concepts of area and perimeter. These exercises will help students build a solid foundation in geometry, making learning both enjoyable and effective.
Understanding Area and Perimeter
The area of a shape is the amount of space inside it, while the perimeter is the distance around the outside. Here are some key points to remember:
- Area: Measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square inches).
- Perimeter: Measured in linear units (e.g., meters, inches).
Formulas to Remember
For a rectangle:
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
For a square:
- Area: \( \text{Area} = \text{side} \times \text{side} \) or \( \text{side}^2 \)
- Perimeter: \( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \)
Practice Problems
-
A rectangle has a length of 8 units and a width of 3 units. Find the area and perimeter.
- Area: \( 8 \times 3 = 24 \, \text{square units} \)
- Perimeter: \( 2 \times (8 + 3) = 22 \, \text{units} \)
-
A square has a side length of 5 units. Calculate the area and perimeter.
- Area: \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \, \text{square units} \)
- Perimeter: \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{units} \)
-
A rectangle has a length of 10 units and a width of 7 units. Determine the area and perimeter.
- Area: \( 10 \times 7 = 70 \, \text{square units} \)
- Perimeter: \( 2 \times (10 + 7) = 34 \, \text{units} \)
-
A square has a side length of 9 units. What is the area and perimeter?
- Area: \( 9^2 = 81 \, \text{square units} \)
- Perimeter: \( 4 \times 9 = 36 \, \text{units} \)
Tips for Success
Here are some tips to help students excel in solving area and perimeter problems:
- Always double-check your measurements.
- Use the correct units for area and perimeter.
- Practice regularly to improve your skills.
Keep practicing, and soon you will become a pro at calculating area and perimeter!

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry that help us measure and understand the space occupied by shapes.
Area refers to the amount of space inside a shape, often measured in square units such as square inches or square meters. It tells us how much surface the shape covers.
Perimeter, on the other hand, is the total length around the outside of a shape. It is measured in linear units like inches or meters. Perimeter helps us understand the boundary or outline of a shape.
Understanding area and perimeter is crucial for various real-life applications, such as calculating the amount of fencing needed for a garden or determining the size of a room for flooring.
In this guide, we will explore the key concepts, formulas, and practical applications of area and perimeter, providing you with the tools to solve problems and understand geometric measurements effectively.
Key Concepts and Definitions
1. Area: The measure of the space inside a shape.
2. Perimeter: The total length around the outside of a shape.
3. Units of Measurement: Area is measured in square units (e.g., square inches, square meters), while perimeter is measured in linear units (e.g., inches, meters).
4. Formulas:
- Area: For basic shapes like squares and rectangles, area = length × width. For triangles, area = 0.5 × base × height. For circles, area = π × radius2.
- Perimeter: Perimeter = sum of all sides of the shape.
5. Practical Applications: Understanding area and perimeter helps in real-life scenarios such as landscaping, construction, and everyday measurements.
Formulas for Area and Perimeter
1. Area Formulas:
- Square: Area = side length × side length
- Rectangle: Area = length × width
- Triangle: Area = 0.5 × base × height
- Circle: Area = π × radius2
2. Perimeter Formulas:
- Square: Perimeter = 4 × side length
- Rectangle: Perimeter = 2 × (length + width)
- Triangle: Perimeter = sum of all three sides
- Circle: Perimeter = 2 × π × radius
3. Key Points:
- These formulas help calculate the area and perimeter of different geometric shapes.
- Understanding these formulas is essential for solving problems involving area and perimeter.
- Practice using these formulas with various examples to master geometric measurements.
Understanding Units of Measurement
1. Area Units: Area is measured in square units, such as square inches (in2), square feet (ft2), square meters (m2), etc.
2. Perimeter Units: Perimeter is measured in linear units, such as inches (in), feet (ft), meters (m), etc.
3. Importance of Units:
- Using the correct units is crucial for accurately measuring and communicating the size of shapes.
- Units help us understand the scale and relative size of different measurements.
- For example, knowing the area in square meters versus square feet can impact calculations for construction or land measurement.

Step-by-Step Problem Solving
1. Identify the Shape: Determine whether the problem involves a square, rectangle, triangle, or circle.
2. Gather Given Information: Note down the dimensions provided, such as side lengths, base, height, or radius.
3. Choose the Correct Formula: Depending on the shape, select the appropriate formula for area or perimeter.
4. Calculate Area:
- Apply the formula for area based on the shape's dimensions.
- Perform the necessary multiplication or division to find the area in square units.
5. Calculate Perimeter:
- Apply the formula for perimeter based on the shape's dimensions.
- Add up all the side lengths to find the perimeter in linear units.
6. Check and Verify: Review your calculations to ensure accuracy and double-check units of measurement.
7. Write the Solution: Present your answers clearly, including units, to complete the problem-solving process.
Visual Aids and Diagrams
1. Importance of Visual Aids:
- Visual aids such as diagrams and charts help illustrate geometric concepts clearly.
- They provide a visual representation of shapes, dimensions, and calculations.
- Visuals aid in understanding how area and perimeter are calculated and how shapes are measured.
2. Types of Visual Aids:
- Diagrams: Clear diagrams showing shapes like squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles with labeled dimensions.
- Charts: Comparison charts illustrating different areas and perimeters of common shapes.
- Interactive Tools: Online tools or apps that allow students to manipulate shapes and see how changes affect area and perimeter.
3. Benefits of Visual Learning:
- Visual aids engage students and make learning about geometry more interactive and memorable.
- They cater to different learning styles and help students grasp abstract concepts more effectively.
- Using visual aids encourages hands-on learning and exploration of geometric properties.
Interactive Exercises and Activities
1. Online Quizzes: Interactive quizzes that test understanding of area and perimeter concepts with multiple-choice or interactive questions.
2. Virtual Manipulatives: Digital tools that allow students to drag and resize shapes to explore how changes affect area and perimeter.
3. Game-Based Learning: Educational games where students solve puzzles or complete challenges involving area and perimeter calculations.
4. Hands-On Activities:
- Physical activities where students measure and compare areas and perimeters of objects in the classroom or outdoors.
- Group activities where students collaborate to solve real-world problems involving area and perimeter.
5. Interactive Worksheets: Worksheets with interactive elements like drag-and-drop or fill-in-the-blank to reinforce area and perimeter skills.
Practice Problems with Solutions
1. Problem 1: Calculate the area and perimeter of a rectangle with length 8 inches and width 5 inches.
| Solution: |
Area = length × width = 8 in × 5 in = 40 square inches Perimeter = 2 × (length + width) = 2 × (8 in + 5 in) = 26 inches |
2. Problem 2: Find the area and perimeter of a square with each side measuring 6 centimeters.
| Solution: |
Area = side length × side length = 6 cm × 6 cm = 36 square centimeters Perimeter = 4 × side length = 4 × 6 cm = 24 centimeters |
3. Problem 3: Determine the area and perimeter of a triangle with a base of 10 meters and a height of 4 meters.
| Solution: |
Area = 0.5 × base × height = 0.5 × 10 m × 4 m = 20 square meters Perimeter = sum of all three sides (if given) or calculate with provided side lengths. |
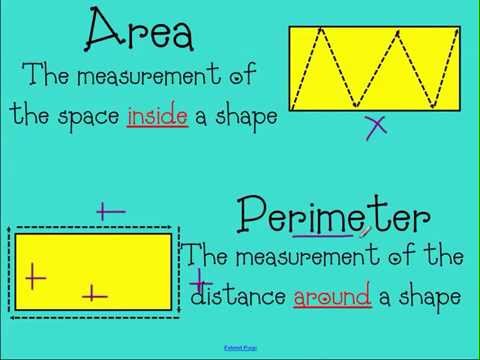
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Learning to calculate area and perimeter can be tricky for 4th graders. Here are some common mistakes students make and tips to avoid them:
-
Mistake 1: Confusing Area and Perimeter
Students often mix up the concepts of area and perimeter. The area is the space inside a shape, while the perimeter is the distance around the shape.
How to Avoid: Emphasize the difference by using visual aids. For example, show that perimeter involves adding up all the sides, while area involves multiplying the length and width for rectangles.
-
Mistake 2: Incorrect Use of Units
Another common mistake is using the wrong units or mixing up units when calculating area and perimeter.
How to Avoid: Teach students to always include units in their answers. For area, the units are squared (e.g., cm²), and for perimeter, the units are linear (e.g., cm). Practice converting between different units to build confidence.
-
Mistake 3: Miscounting the Lengths of Sides
Students sometimes miscount the lengths of sides, especially in irregular shapes.
How to Avoid: Encourage students to double-check their measurements and use tools like rulers and grid paper to ensure accuracy. Teach them to break down complex shapes into smaller, more manageable parts.
-
Mistake 4: Forgetting to Add All Sides for Perimeter
When calculating the perimeter, students might forget to add all the sides, especially if a shape has many sides.
How to Avoid: Use systematic approaches such as starting at one point and moving around the shape to ensure all sides are included. Practice with different shapes to reinforce the concept.
-
Mistake 5: Incorrect Multiplication for Area
For area calculations, students sometimes multiply incorrectly or forget to multiply both dimensions.
How to Avoid: Reinforce multiplication skills and practice with area-specific problems. Use visual aids like arrays and grids to help students understand the multiplication process.
By being aware of these common mistakes and practicing regularly, students can improve their skills in calculating area and perimeter.
Tips and Tricks for Students
Learning about area and perimeter can be fun and easy with the right strategies. Here are some helpful tips and tricks for mastering these concepts:
-
Understand the Difference:
Remember that perimeter is the distance around the outside of a shape, while area is the amount of space inside the shape. A simple way to remember this is that perimeter is like a fence around a yard, and area is like the grass inside the yard.
-
Use Formulas:
Make sure to memorize and use the correct formulas:
- For rectangles and squares:
- Perimeter: \(P = 2 \times (length + width)\) or \(P = 4 \times side\) (for squares)
- Area: \(A = length \times width\) or \(A = side^2\) (for squares)
- For triangles:
- Perimeter: \(P = a + b + c\) (sum of all sides)
- Area: \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height\)
- For rectangles and squares:
-
Draw and Label:Always draw the shapes and label the sides with their measurements. This visual aid can help you keep track of the dimensions and apply the formulas correctly.
-
Check Your Units:
Ensure you are using the same units for all measurements. If the length is in meters and the width is in centimeters, convert them to the same unit before calculating.
-
Practice with Real-Life Objects:
Find objects around you like books, doors, or tables and measure their dimensions to calculate the area and perimeter. This practical application helps reinforce the concepts.
-
Use Graph Paper:
Graph paper can help you draw shapes to scale and understand the concept of area better. Count the squares inside the shape to find the area.
-
Break Down Complex Shapes:
If you encounter a complex shape, break it down into smaller, more manageable shapes (like rectangles and triangles), find the area or perimeter of each, and then add them together.
-
Double-Check Your Work:
Always review your calculations to make sure you didn't miss any sides for the perimeter or any dimensions for the area. A quick recheck can prevent simple mistakes.
Games and Fun Activities for Learning
Learning about area and perimeter can be exciting and engaging through interactive games and fun activities. Here are some creative ways to help students understand and enjoy these concepts:
-
Area and Perimeter Builder
In this online activity, students can create their own shapes using colorful blocks and explore the relationship between area and perimeter. They can compare the area and perimeter of different shapes and build figures with specific dimensions.
-
Block Letter Names
Students trace their names on graph paper, then calculate the area and perimeter of each letter. This activity combines creativity with math practice and helps reinforce the concept of measuring space.
-
Tape Shapes on the Floor
Using masking or painter's tape, create squares or rectangles on the floor. Students measure the sides to determine the area and perimeter. This hands-on activity is great for visual and kinesthetic learners.
-
Design a Dream House
Have students use graph paper to design a dream house, zoo, carnival, or any other place. They calculate the area and perimeter of each section, combining art and math in a meaningful way.
-
Land Grab Game
In this game, students play in pairs with graph paper and dice. They roll the dice to determine the length and width of a rectangle, draw it on the graph paper, and calculate the area. The player with the most area at the end wins.
-
Table Arranging Challenge
Present students with a challenge to arrange tables for a certain number of people, ensuring everyone has a seat. They calculate the area and perimeter of different table arrangements to find the most efficient setup.
-
Farmer's Cropping Activity
Students help a farmer plant crops in a field by calculating the maximum area for planting and the perimeter for fencing. This activity connects math with real-world applications.
Resources for Teachers and Parents
Supporting students in learning about area and perimeter can be greatly enhanced with the right resources. Here are some valuable tools and ideas for teachers and parents to help 4th graders master these concepts:
-
Khan Academy:
Khan Academy offers a comprehensive unit on area and perimeter with video lessons, interactive exercises, and quizzes. This can be a great resource for both in-class activities and additional practice at home.
-
Printable Worksheets:
Websites like Education.com and DoodleMath provide printable worksheets that cover a variety of problems related to area and perimeter. These can be used for homework, extra practice, or assessment purposes.
-
Interactive Games:
Engaging students with interactive games can make learning fun and effective. Websites like We Are Teachers suggest activities such as using LEGO bricks, creating math mosaics, and playing area and perimeter games like "Island Conquer."
-
Hands-On Activities:
Incorporate hands-on activities such as building kites, creating floor tile designs, and designing tiny houses. These projects help students apply their knowledge in real-world contexts, making the learning experience more meaningful.
-
Classroom Projects:
Projects like building a city or becoming an interior designer allow students to work collaboratively while applying area and perimeter concepts. These activities can also integrate other subjects like art and social studies.
-
Math Songs and Videos:
Use catchy songs and educational videos to reinforce concepts. These tools can help students remember formulas and procedures for calculating area and perimeter.
-
Parental Involvement:
Encourage parents to engage with their children’s learning by providing them with access to educational apps and online resources. DoodleMath, for example, offers a platform where parents can track progress and find additional practice materials.
-
Professional Development:
Teachers can benefit from professional development resources that offer strategies and lesson plans for teaching area and perimeter. Online communities and educational websites often provide free resources and ideas for innovative teaching methods.
By utilizing these resources, teachers and parents can create a supportive and enriching learning environment that helps students succeed in understanding area and perimeter.

Conclusion and Next Steps
As we wrap up our comprehensive guide on area and perimeter for 4th graders, it's important to remember the key concepts we've covered and the skills we've developed. Understanding how to calculate the area and perimeter of different shapes is a fundamental aspect of geometry that will serve as a building block for more advanced math topics.
Here are the key takeaways from this guide:
- Key Concepts: We learned the definitions and differences between area and perimeter, and how to measure them using various units.
- Formulas: We explored the formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles, squares, and other polygons.
- Problem Solving: We practiced step-by-step problem-solving strategies, including working with word problems and real-world applications.
- Common Mistakes: We discussed common errors and how to avoid them, ensuring accurate calculations every time.
- Interactive Learning: Through games, activities, and interactive exercises, we made learning about area and perimeter fun and engaging.
Here are some next steps to continue your learning journey:
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice helps reinforce the concepts you've learned. Use the practice problems and interactive exercises provided in this guide.
- Explore Real-World Applications: Look for opportunities to apply your knowledge of area and perimeter in real-life situations, such as measuring rooms, furniture, or outdoor spaces.
- Seek Additional Resources: Utilize online resources, educational websites, and math apps to further enhance your understanding and skills.
- Ask for Help: Don't hesitate to ask teachers, parents, or peers for assistance if you're struggling with a particular concept or problem.
- Stay Curious: Keep exploring and asking questions about geometry and other math topics. A curious mind is key to ongoing learning and success in math.
Thank you for using this guide to learn about area and perimeter. We hope you found it helpful and enjoyable. Keep practicing and exploring, and you'll continue to improve your math skills!
Bài Hát Diện Tích và Chu Vi Cho Trẻ Em | Lớp 3 - 4
READ MORE:
Lớp 4 - Toán - Diện Tích và Chu Vi - Tổng Quan Chủ Đề