Topic what's the square root of 6: What's the square root of 6? This intriguing question opens up a world of mathematical wonder. In this article, we explore the properties, calculations, and real-life applications of the square root of 6. Join us on this mathematical journey to uncover the secrets of this unique number.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 6
- Introduction to Square Root of 6
- Decimal Approximation of Square Root of 6
- Properties of Square Root of 6
- Methods to Calculate Square Root of 6
- Prime Factorization Method
- Long Division Method
- Using a Calculator
- Mathematical Context and Explanation
- Applications of Square Root of 6 in Real Life
- Visualizing the Square Root of 6
- Common Questions About Square Root of 6
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video giới thiệu và giải thích về căn bậc hai của 6, cung cấp kiến thức cơ bản và ứng dụng thực tế.
Square Root of 6
The square root of 6, denoted as , is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.
Decimal Approximation
The approximate value of the square root of 6 is:
Properties
- Irrational Number: The square root of 6 cannot be exactly represented as a fraction.
- Non-Terminating, Non-Repeating Decimal: The decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.
Calculation Methods
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 6:
- Prime Factorization: Not very practical for 6 since it's not a perfect square.
- Long Division Method: A manual method to find the square root digit by digit.
- Using a Calculator: The most straightforward method to get a quick approximation.
Mathematical Context
In mathematical terms, the square root function is the inverse operation of squaring. For any positive number a, the square root is a number x such that:
Applying this to 6:

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 6
The square root of 6, represented as , is an important and interesting concept in mathematics. This number is irrational, meaning it cannot be precisely written as a fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
The approximate value of the square root of 6 is:
Understanding the square root of 6 involves several key concepts:
- Irrational Number: The square root of 6 cannot be expressed as an exact fraction, similar to the square roots of other non-perfect squares.
- Mathematical Calculation: Calculating the square root of 6 can be done using various methods, including long division and using a calculator for a quick approximation.
- Applications: The square root of 6 appears in various fields such as geometry, algebra, and physics, making it a significant number in both theoretical and applied mathematics.
In essence, the square root of 6 is a fascinating number that helps us delve deeper into the world of irrational numbers and their properties.
Decimal Approximation of Square Root of 6
The square root of 6, represented as , is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed exactly as a fraction. Its decimal approximation is an endless, non-repeating sequence.
The most commonly used decimal approximation for the square root of 6 is:
For practical purposes, we often round this value. Here are some common approximations:
- Rounded to 2 decimal places: 2.45
- Rounded to 3 decimal places: 2.449
- Rounded to 4 decimal places: 2.4495
To understand how this approximation is achieved, let's explore a step-by-step method using long division:
- Step 1: Start with an initial guess. For example, 2.4.
- Step 2: Square the guess to see how close it is to 6. .
- Step 3: Adjust the guess based on whether the square is less than or greater than 6. Try 2.45.
- Step 4: Square the new guess: .
- Step 5: Refine the guess and repeat the process to achieve greater accuracy.
Using a calculator is the quickest way to find this value, but understanding the method behind it gives insight into the nature of irrational numbers and their approximations.
Properties of Square Root of 6
The square root of 6, denoted as , possesses several interesting and significant properties in mathematics.
- Irrational Number: The square root of 6 is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
- Decimal Approximation: The value of the square root of 6 in decimal form is approximately 2.449489742783178. For practical purposes, it is often rounded to a few decimal places, such as 2.45 or 2.449.
- Algebraic Property: The square of the square root of 6 returns the original number 6, i.e., .
- Non-Rational Square: Since 6 is not a perfect square, its square root does not result in a whole number.
- Transcendence: While the square root of 6 is not a transcendental number, it is important to distinguish that it is still a non-algebraic number.
To explore the properties further, consider the implications in different mathematical contexts:
- Geometry: In geometry, the square root of 6 can represent the length of a diagonal in a cuboid with side lengths of 1, 2, and 3 units.
- Algebra: In algebraic equations, the square root of 6 can appear in solutions to quadratic equations or in expressions involving radicals.
- Number Theory: The irrationality of the square root of 6 demonstrates interesting aspects of number theory, particularly in understanding the distribution of prime numbers and their properties.
Overall, the properties of the square root of 6 illustrate its unique place in mathematics, highlighting the complexity and beauty of irrational numbers.
Methods to Calculate Square Root of 6
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 6, each varying in complexity and accuracy. Below, we explore some of the most common techniques.
- Using a Calculator
The quickest and most straightforward method to find the square root of 6 is by using a calculator. Most scientific calculators have a square root function that provides an immediate approximation. For instance, using a calculator, you get:
- Long Division Method
The long division method is a manual approach to finding the square root of a number, providing a step-by-step approximation. Here’s how it works:
- Step 1: Start by grouping the digits of 6 in pairs from the decimal point. Since 6 is a single digit, we consider it as 6.00, pairing 6 and 00.
- Step 2: Find the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to 6. This is 2, since .
- Step 3: Subtract 4 from 6 to get 2. Bring down the next pair of zeros to make it 200.
- Step 4: Double the number obtained in step 2 (which is 2) to get 4. Now, find a digit X such that is less than or equal to 200. In this case, X is 4, since = 176.
- Step 5: Subtract 176 from 200 to get 24. Bring down the next pair of zeros to get 2400 and repeat the process.
Continuing this method yields increasingly accurate digits of the square root of 6.
- Prime Factorization
Prime factorization involves expressing the number as a product of its prime factors and then simplifying. However, since 6 is not a perfect square and its prime factors are 2 and 3, this method is less straightforward for finding an exact square root. The prime factorization of 6 is:
Thus, , which can be approximated using the known values of and .
Each method provides a different level of insight and accuracy, with calculators offering the quickest results and manual methods like long division providing a deeper understanding of the process behind finding square roots.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method involves breaking down a number into its prime factors and using these to find the square root. Although 6 is not a perfect square, understanding its prime factors can offer insights into its square root. Here’s how you can use this method for the square root of 6:
- Identify Prime Factors:
First, express 6 as a product of its prime factors:
- Express as a Product of Square Roots:
Next, use the property of square roots that states:
Apply this to the prime factors of 6:
- Approximate Square Roots of Prime Factors:
We know the approximate values for the square roots of 2 and 3:
- Multiply the Approximations:
Finally, multiply these approximations to get the square root of 6:
This method shows the relationship between the square root of a composite number and the square roots of its prime factors. While it involves approximations for irrational numbers, it helps in understanding the calculation process.
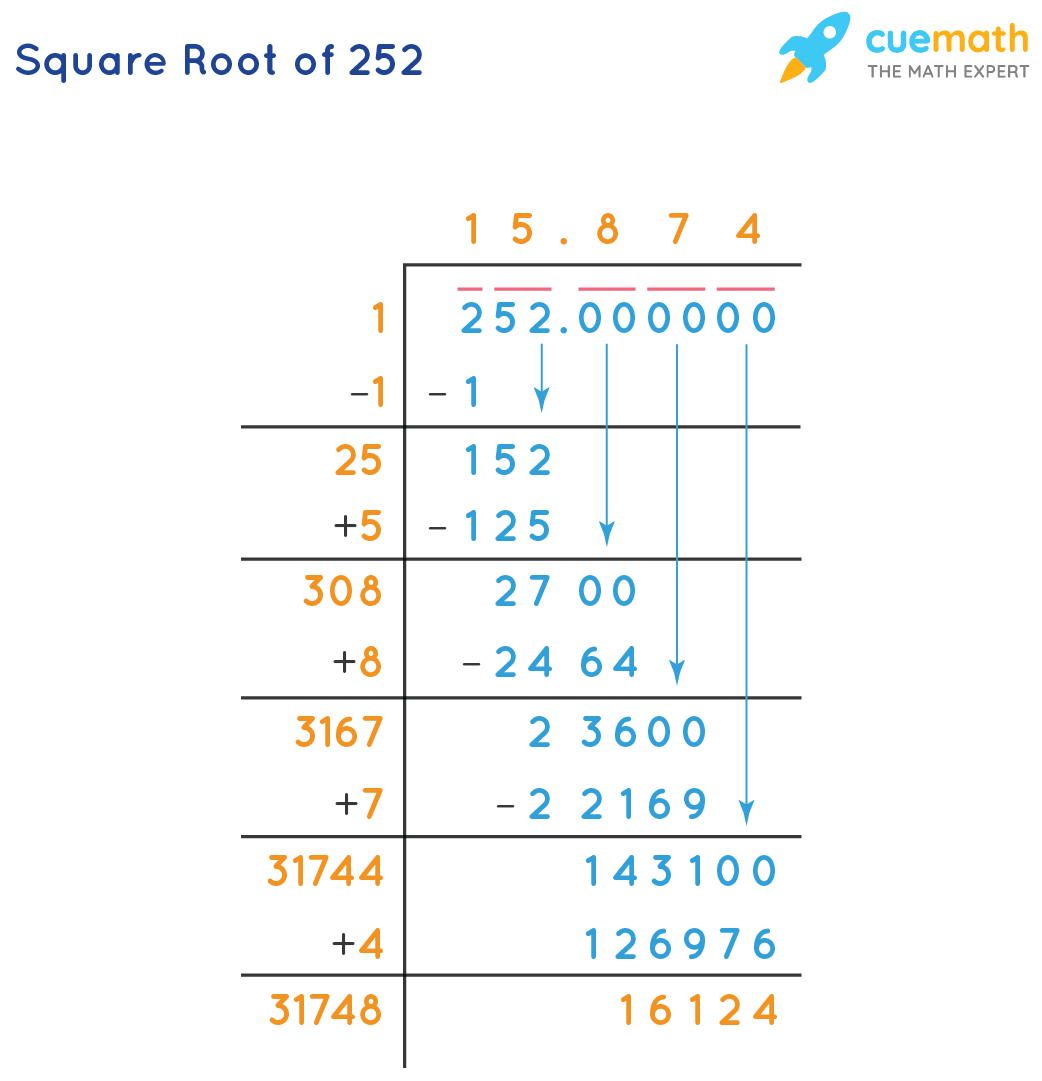
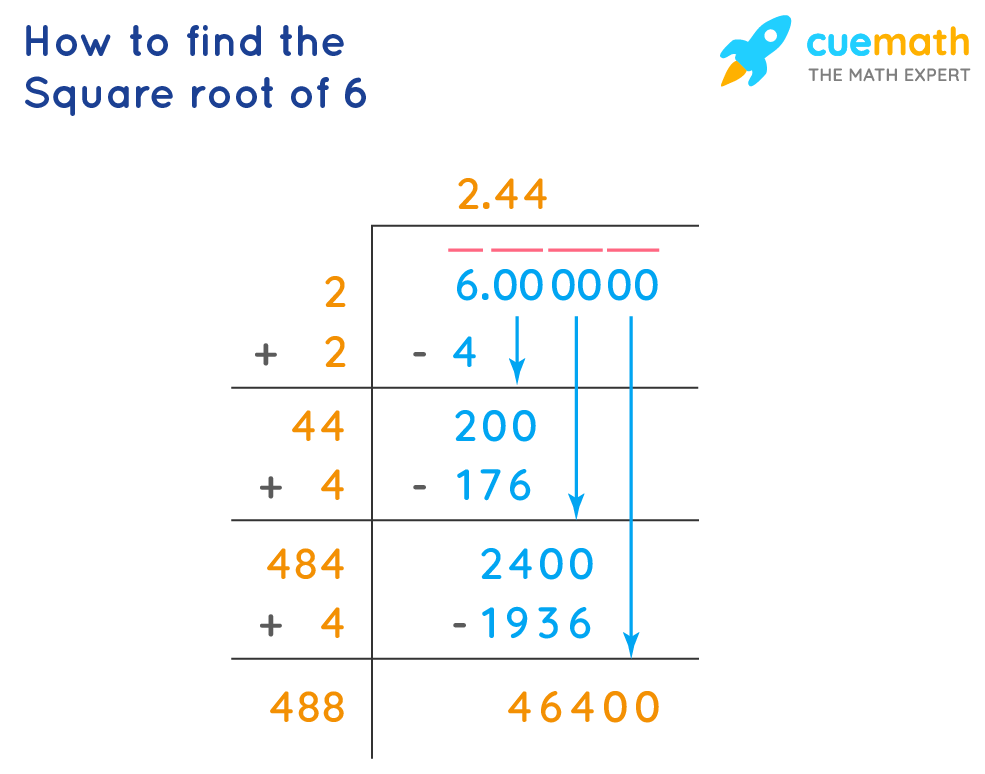
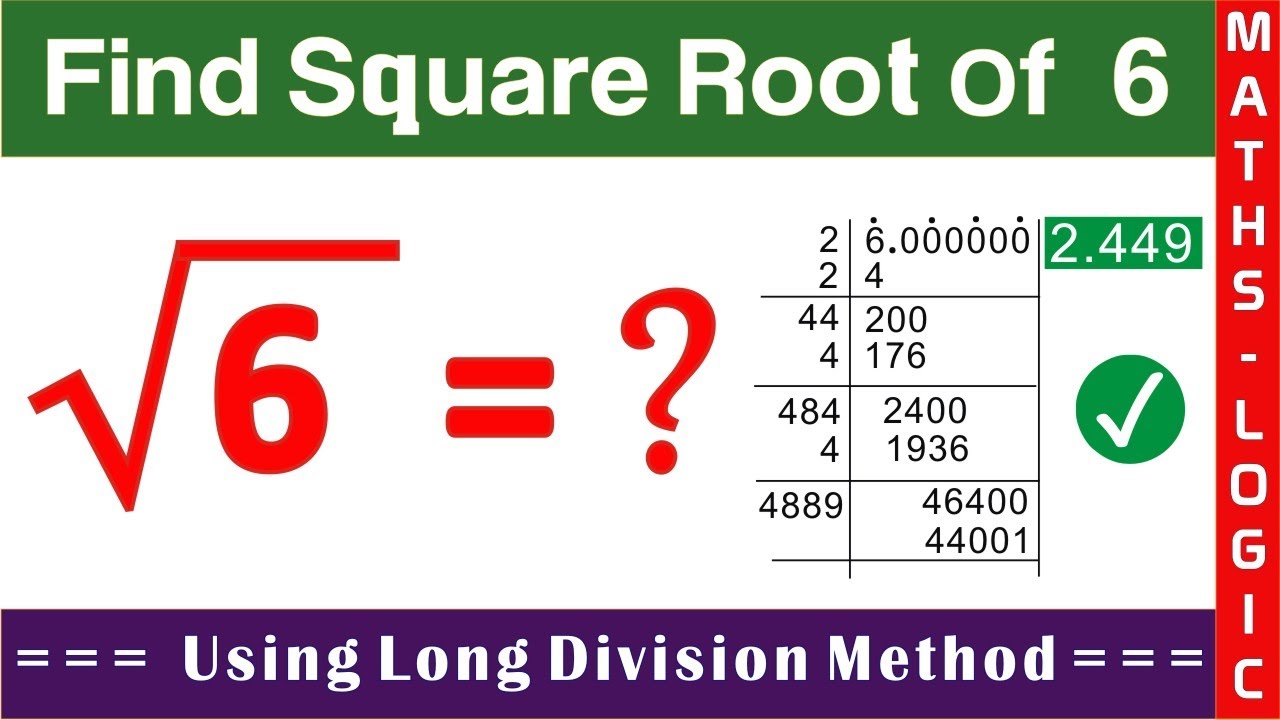
Long Division Method
The long division method is a manual technique for finding the square root of a number, offering a precise step-by-step process. Here’s how you can use this method to calculate the square root of 6:
- Pair the Digits:
Begin by pairing the digits of 6 from the decimal point. Since 6 is a single digit, we consider it as 6.00, pairing 6 and 00.
- Initial Guess:
Find the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to 6. This number is 2, since .
Write 2 as the first digit of the square root. Subtract 4 from 6 to get the remainder 2. Bring down the next pair of zeros to make it 200.
- Calculate Next Digit:
Double the current quotient (2), giving 4. Determine the next digit (X) such that is less than or equal to 200. The value of X is 4, since = 176.
Write 4 next to 2, making the quotient 2.4. Subtract 176 from 200 to get 24. Bring down the next pair of zeros to get 2400.
- Repeat the Process:
Continue this process by finding the next digit. Double the current quotient (24) to get 48. Find X such that is less than or equal to 2400. The value of X is 4 again, since = 1936.
Write 4 next to 2.44, making the quotient 2.44. Subtract 1936 from 2400 to get 464. Bring down the next pair of zeros to get 46400.
By continuing this process, you will get a more accurate approximation of the square root of 6. The result converges to:
The long division method, although labor-intensive, provides a clear understanding of how square roots can be calculated manually.
Using a Calculator
Calculating the square root of 6 using a calculator is the simplest and quickest method. Modern calculators, including those on smartphones and computers, have built-in functions to compute square roots. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use a calculator for this purpose:
- Turn On the Calculator:
Ensure your calculator is turned on. If you are using a physical calculator, press the power button. For a digital calculator on a smartphone or computer, open the calculator application.
- Enter the Number:
Key in the number 6. You can do this by pressing the digit '6' on the calculator keypad.
- Access the Square Root Function:
Locate the square root function on your calculator. This is usually represented by the symbol or simply . On most calculators, you might need to press a function key like '2nd' or 'Shift' before pressing the square root button.
- Calculate the Square Root:
Press the square root button. The calculator will process the input and display the result. For the square root of 6, the display should show:
- Rounding the Result:
For practical purposes, you may need to round the result to a certain number of decimal places. Common rounding includes:
- To 2 decimal places: 2.45
- To 3 decimal places: 2.449
- To 4 decimal places: 2.4495
Using a calculator to find the square root of 6 is a fast and efficient method, ideal for quick calculations and verifying results obtained through manual methods.
Mathematical Context and Explanation
The square root of 6, denoted as √6, is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. To understand the mathematical context and implications of this value, we explore several key concepts:
- Decimal Approximation: The square root of 6 is approximately 2.44949. This can be obtained using a calculator or through numerical methods such as the long division method.
- Irrational Number: As an irrational number, √6 cannot be written as a ratio of two integers. Its decimal expansion goes on forever without repeating.
- Algebraic Properties:
(√6)^2 = 6√6 * √6 = 6√a * √b = √(a * b)(for any positive numbersaandb), so√6 = √(2 * 3)
- Geometric Interpretation: If you have a square with an area of 6 square units, the length of each side of the square is
√6units. - Prime Factorization: While prime factorization helps simplify square roots, √6 remains in its simplest radical form because 6 is the product of the primes 2 and 3, neither of which are squares.
To provide a deeper understanding, consider the methods used to calculate √6:
- Prime Factorization: While not directly simplifying √6, recognizing it as √(2 * 3) helps in understanding its components.
- Long Division Method: This iterative method provides a step-by-step approach to find the decimal approximation of √6 to any desired level of accuracy.
By using these methods, the exact value and properties of the square root of 6 can be comprehensively understood and applied in various mathematical contexts.
Applications of Square Root of 6 in Real Life
The square root of 6, denoted as √6, has various applications in real life, particularly in fields that require precise measurements, calculations, and geometric interpretations. Here are some notable examples:
- Engineering and Architecture:
- In designing structures, the square root of 6 is used in calculations involving areas and dimensions to ensure accuracy and stability.
- It is essential in calculations for materials, load distribution, and structural integrity.
- Physics:
- In physics, √6 can be involved in solving problems related to wave functions, quantum mechanics, and other areas where precise measurements are crucial.
- For example, certain constants or derived formulas may incorporate √6 in their calculations.
- Geometry:
- The square root of 6 is used to determine the length of the diagonal in a rectangular prism with dimensions 1, 2, and 3 units.
- It is also used in various geometric proofs and constructions.
- Mathematics Education:
- Students encounter √6 when learning about irrational numbers, simplifying radicals, and in exercises involving the Pythagorean theorem.
- It helps in understanding the nature of irrational numbers and their properties.
- Computer Science:
- Algorithms that require numerical methods, such as square root calculations, often involve √6 in testing and validation scenarios.
- It can be used in graphics programming and simulations requiring precise geometric calculations.
By recognizing these applications, the importance of understanding and accurately calculating the square root of 6 becomes evident in various practical and theoretical contexts.
Visualizing the Square Root of 6
Visualizing the square root of 6 (√6) can enhance understanding and provide a clearer sense of its magnitude and properties. Here are some ways to visualize √6:
Geometric Interpretation
One of the most straightforward ways to visualize √6 is through geometry:
- Square and Area: Imagine a square with an area of 6 square units. The side length of this square is
√6. Although it is challenging to draw this precisely, it provides a basic visual understanding. - Rectangular Prism: Consider a rectangular prism with dimensions 1, 2, and 3 units. The diagonal of this prism represents
√6. Using the Pythagorean theorem in three dimensions:\[
\sqrt{1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2} = \sqrt{1 + 4 + 9} = \sqrt{14}
\]
This shows the magnitude but requires simplification for√6.
Number Line Representation
Plotting √6 on a number line helps visualize its approximate location:
- First, locate the integers 2 and 3, knowing
2 < √6 < 3. √6is approximately 2.44949, placing it between 2.4 and 2.5.
Graphical Method
Another effective method is to use graphs:
- Plot the function
y = x^2on a Cartesian plane. - Draw a horizontal line at
y = 6. The x-coordinate where this line intersects the curvey = x^2is√6. - To approximate, use the intersection of
y = 6andy = x^2to estimate√6as 2.44949.
Using a Right Triangle
A right triangle can also help visualize √6:
- Construct a right triangle where one leg is
√2and the other leg is2. Using the Pythagorean theorem, the hypotenuse is√( (√2)^2 + 2^2 ) = √6. - This triangle visually demonstrates how
√6relates to other square roots.
Graphical Software and Tools
Utilizing graphing calculators or software like GeoGebra can dynamically illustrate √6:
- Input the function and observe the exact point of intersection for a precise visual representation.
- These tools allow for zooming and detailed inspection of the value and its position on graphs.
By using these methods, one can gain a more intuitive and accurate understanding of the square root of 6.
Common Questions About Square Root of 6
The square root of 6, √6, often raises various questions among students and enthusiasts of mathematics. Here are some common questions and their detailed answers:
1. What is the value of the square root of 6?
The square root of 6 is an irrational number, which means its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. The approximate value of √6 is 2.44949.
2. Is the square root of 6 a rational number?
No, the square root of 6 is not a rational number. It cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. It is an irrational number because its decimal expansion goes on forever without repeating.
3. How can we calculate the square root of 6?
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 6:
- Using a Calculator: The most straightforward way to find the value of
√6is by using a scientific calculator. - Long Division Method: This method provides a step-by-step approach to manually calculate the square root to a desired level of accuracy.
- Approximation Methods: Iterative methods such as the Newton-Raphson method can be used to approximate the square root of 6.
4. What are the properties of the square root of 6?
√6is an irrational number.- The value of
√6is approximately 2.44949. (√6)^2 = 6.√6 * √6 = 6.- It can be expressed as
√(2 * 3)using the properties of square roots.
5. How is the square root of 6 used in real life?
The square root of 6 has various applications in different fields such as engineering, physics, architecture, and computer science. For instance, it is used in calculations involving areas, dimensions, and geometric interpretations.
6. Can the square root of 6 be simplified further?
No, √6 is already in its simplest radical form. It cannot be simplified further because 6 is not a perfect square and does not have any square factors other than 1.
Understanding the square root of 6 involves recognizing its properties, applications, and the methods used to calculate it. These common questions and answers provide a comprehensive overview of √6 and its significance in mathematics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the square root of 6, denoted as √6, is a significant mathematical concept with diverse applications across various fields. As an irrational number, √6 has a non-terminating and non-repeating decimal representation, approximately equal to 2.44949. This property highlights the complexity and beauty of irrational numbers.
Understanding √6 involves exploring its properties, such as:
(√6)^2 = 6√6 * √6 = 6- Its expression in simplest radical form as
√(2 * 3)
We have delved into various methods to calculate √6, including using calculators, long division, and approximation methods. Each method offers unique insights and levels of precision, catering to different needs and contexts.
The practical applications of √6 are vast, ranging from engineering and architecture to physics and computer science. Its role in accurate measurements, geometric interpretations, and complex calculations underscores its importance in real-world scenarios.
Visualizing √6 through geometric shapes, number lines, graphs, and right triangles helps in gaining a more intuitive understanding of its magnitude and significance. Utilizing graphical software further enhances this comprehension, providing dynamic and precise visual representations.
Common questions about √6 reflect a curiosity about its nature, calculation methods, properties, and applications. Addressing these questions reinforces the fundamental concepts and encourages deeper exploration into the fascinating world of irrational numbers.
Overall, the square root of 6 is not just a mathematical value but a gateway to understanding broader mathematical principles and their real-life implications. Embracing the complexity and utility of √6 enriches our appreciation of mathematics and its pervasive role in various domains.
Video giới thiệu và giải thích về căn bậc hai của 6, cung cấp kiến thức cơ bản và ứng dụng thực tế.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 6
READ MORE:
Video giới thiệu và giải thích về căn bậc hai của 6, cung cấp kiến thức cơ bản và ứng dụng thực tế.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 6