Topic perimeter to area calculator: Discover the fascinating world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on "Perimeter to Area Calculator", a crucial tool for seamless mathematical transformations and real-world applications.
Table of Content
- Understanding Perimeter and Area
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Rectangle
- Calculating Perimeter and Area for Different Shapes
- Perimeter and Area of Uncommon Shapes
- Using Online Perimeter to Area Calculators
- Practical Applications of Perimeter and Area Calculations
- FAQs and Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Interactive Learning Tools and Resources
- Advanced Concepts in Perimeter and Area
Understanding Perimeter and Area
Perimeter and area are fundamental concepts in geometry, essential for understanding the properties of shapes. Perimeter refers to the total distance around a shape, like the boundary line of a playground, while area describes the size of the surface enclosed within this boundary. For instance, the perimeter of a playground is the distance one would walk around it, and the area would be the amount of space where children can play.
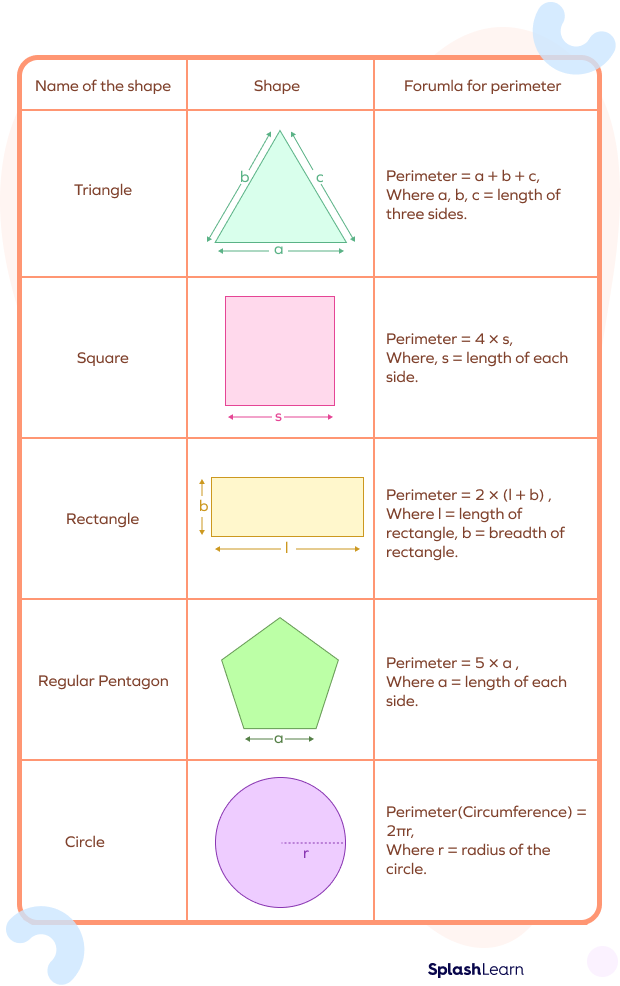
Calculating perimeter and area varies depending on the shape. For regular polygons like squares and rectangles, the perimeter is the sum of all sides, and the area is calculated by multiplying length by width. In the case of circles, the perimeter (also known as circumference) is calculated using the formula 2πr, and the area is πr². For other shapes like triangles, trapezoids, and ellipses, specific formulas are applied to calculate their perimeter and area.
- Perimeter of a Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is the sum of all its four sides. For a rectangle with length (l) and width (w), the perimeter is given by P = 2l + 2w.
- Area of a Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length by its width, A = l × w.
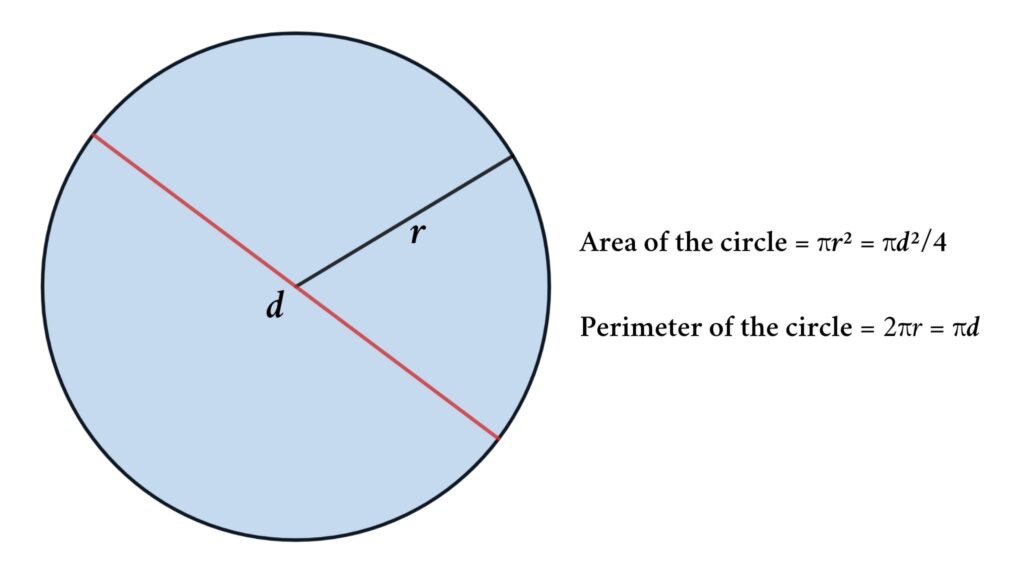
- Perimeter of a Circle: The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the formula P = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
- Area of a Circle: The area of a circle is given by A = πr², where r is the radius.
- Perimeter and Area of a Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides. The area, however, depends on the type of triangle and is generally 1/2 times the base times the height.
Understanding these concepts is crucial, not only in academic settings but also in various practical applications, such as in construction, art, design, and daily life calculations.

READ MORE:
Finding the Area and Perimeter of a Rectangle
calculator: Dive into the world of numbers and equations with our fascinating calculator video. Explore the endless possibilities of this powerful tool and discover how it can simplify your everyday calculations effortlessly. Watch and be amazed!
Explaining Perimeter, Area, and Volume in Mathematics
mathematics: Unlock the secrets of this captivating subject through our enlightening mathematics video. Join us on a journey of logic and problem-solving as we delve into the awe-inspiring world of equations, formulas, and geometric wonders. Prepare to be inspired and develop a whole new appreciation for the beauty of mathematics.
Calculating Perimeter and Area for Different Shapes
Calculating the perimeter and area of various shapes is a fundamental skill in geometry. The perimeter is the total distance around a shape, while the area is the size of the surface enclosed by the shape. Let\"s explore how to calculate these for common shapes.
- Square: For a square with side length \"a\", the perimeter is 4a, and the area is a².
- Rectangle: A rectangle with length \"a\" and width \"b\" has a perimeter of 2a + 2b, and an area of a × b.
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of its three sides, and the area can be calculated using various methods, depending on the type of triangle.
- Circle: For a circle with radius \"r\", the perimeter (circumference) is 2πr, and the area is πr².
- Ellipse: An ellipse with semi-major axis \"a\" and semi-minor axis \"b\" has an area of π × a × b. The perimeter of an ellipse is more complex and often involves approximation.
- Trapezoid: The area of a trapezoid with parallel sides \"a\" and \"b\", and height \"h\" is (a + b) × h / 2. Its perimeter is the sum of all four sides.
- Parallelogram: A parallelogram\"s area can be calculated as b × h, where \"b\" is the base and \"h\" is the height.
- Rhombus: For a rhombus, the area can be found if you know either the side and height or the diagonals.
These formulas provide a basis for calculating the perimeter and area of various geometric shapes, each with its unique properties and calculation methods.
Perimeter and Area of Uncommon Shapes
Calculating the perimeter and area of uncommon shapes requires specific formulas and approaches. Uncommon shapes can include ellipses, sectors, and trapezoids, each with their own unique characteristics.
- Ellipse: An ellipse has two axes: the semi-major axis \"a\" and the semi-minor axis \"b\". The area of an ellipse is calculated using the formula A = π × a × b. The perimeter of an ellipse is more complex and often involves approximation.
- Sector of a Circle: A sector is a portion of a circle. The area of a sector can be found with the formula A = r² × α / 2, where \"r\" is the radius and \"α\" is the central angle in radians. The perimeter of a sector includes the arc length plus the two radii.
- Trapezoid: A trapezoid has a pair of parallel sides. Its area can be calculated with the formula A = (a + b) × h / 2, where \"a\" and \"b\" are the lengths of the parallel sides, and \"h\" is the height. The perimeter is the sum of all four sides.
These formulas provide the necessary tools to calculate the perimeter and area for these less common shapes, broadening our understanding of geometry and its applications.

Using Online Perimeter to Area Calculators
Online perimeter to area calculators are user-friendly tools that simplify complex geometric calculations. These calculators can compute the perimeter and area for a variety of shapes, including standard and irregular forms, making them indispensable for students, professionals, and hobbyists alike.
To use these calculators, follow these general steps:
- Select the type of shape for which you need to calculate the perimeter and area. Online calculators often have options for common shapes like squares, rectangles, circles, and more complex forms like ellipses and trapezoids.
- Enter the required dimensions of the shape, such as side lengths, radius, or diameters. It\"s important to use consistent units of measurement to ensure accurate results.
- Hit the calculate button. The calculator will automatically compute the perimeter and area based on the input values and the geometric properties of the selected shape.
- Review the results. Most calculators will display both the perimeter and area, sometimes even providing the steps or formulas used in the calculation.
These calculators not only provide quick answers but also help in understanding the relationships between different geometric properties. They\"re particularly useful in educational settings or in fields requiring quick and accurate geometric calculations.
Remember, while online calculators are convenient, it\"s also essential to understand the underlying mathematical concepts and formulas, as this knowledge is crucial for solving more complex problems and in situations where a calculator may not be available.
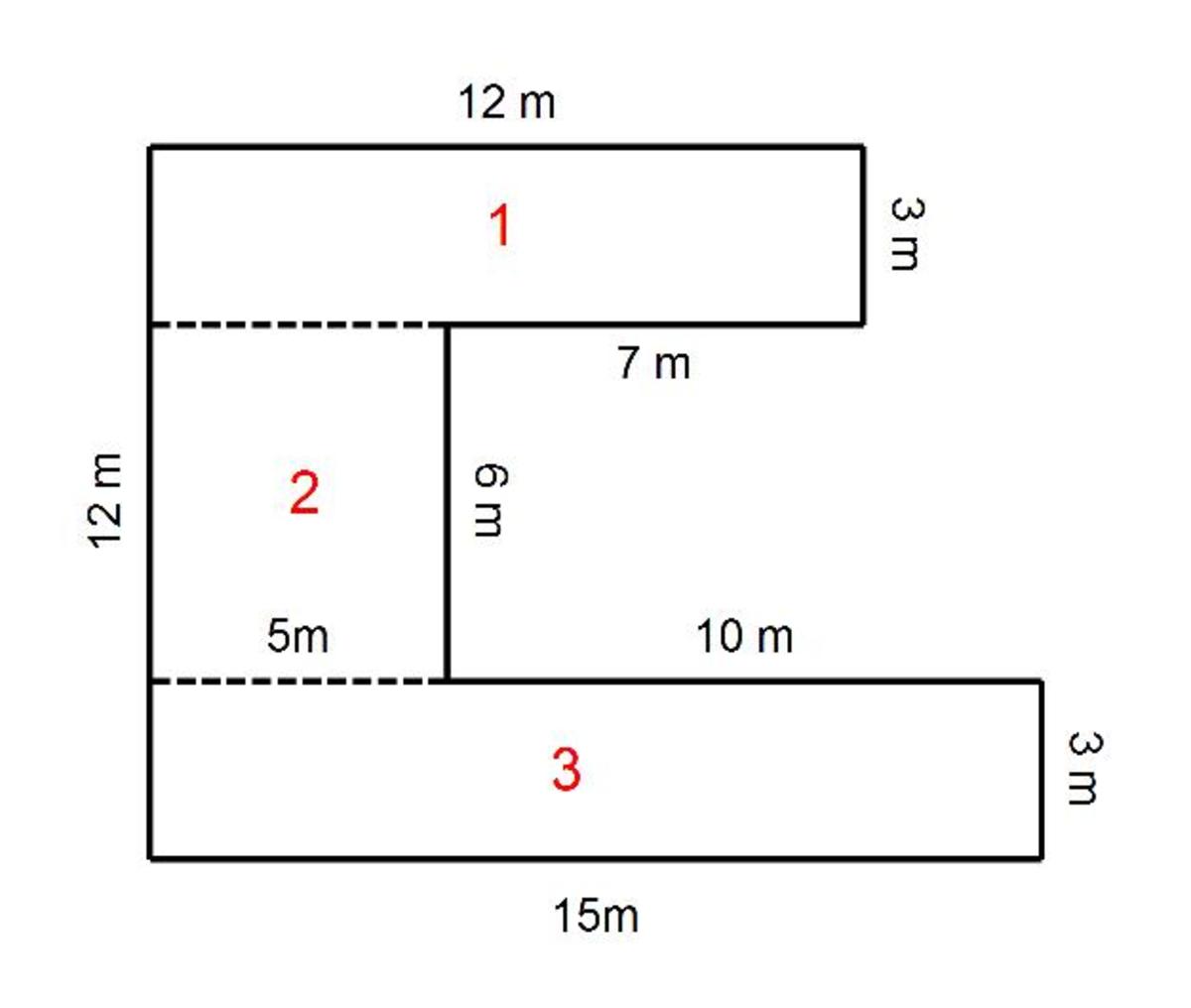
Practical Applications of Perimeter and Area Calculations
Understanding the concepts of perimeter and area is not just academically beneficial but also has numerous practical applications in everyday life. These concepts are widely used in various fields, offering solutions to real-world problems.
- Construction and Architecture: In construction, calculating the area and perimeter is crucial for designing buildings and rooms. It helps in estimating the amount of materials needed, like paint for walls or tiles for flooring.
- Agriculture and Gardening: Farmers and gardeners use area calculations to determine the amount of fertilizer required for a given land area or to plan crop rotations effectively.
- Interior Design: Area calculation is vital in interior design for choosing the right size of carpets, furniture layout, and optimizing the space utilization.
- Urban Planning: Perimeter calculations aid urban planners in defining the boundaries of buildings, parks, and designing city layouts.
- Art and Fashion: In art, understanding perimeter helps in framing and scaling artwork. In fashion, it\"s used for fabric measurements and designing clothing.
- Education: Educators use area and perimeter to enhance students\" problem-solving skills and practical understanding of geometry.
- Logistics and Packaging: These calculations are important in determining the right size of packaging material and for efficient space management in logistics.
- Technology and Graphics: In computer graphics, especially in gaming and animation, area and perimeter calculations ensure precision and realism in visual representations.
These examples illustrate how the theoretical concepts of area and perimeter are applied in various sectors, proving their significance beyond the classroom.
_HOOK_
FAQs and Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding the basics of perimeter and area calculations can sometimes lead to confusion. Here, we address some common questions and issues to help clarify these concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the difference between perimeter and area?
- The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. In contrast, the area is the amount of space inside the shape. Perimeter is measured in linear units, while area is measured in square units.
- How do I calculate the perimeter of irregular shapes?
- To calculate the perimeter of an irregular shape, measure the lengths of all its sides. If the shape includes circular arcs, measure the radius and the central angle to calculate the arc length. Add these measurements together for the total perimeter.
- Can the same shape have different perimeters?
- Shapes with the same area can have different perimeters. For example, a narrow rectangle and a near-square can have the same area but different perimeters due to their different shapes.
- What are some common mistakes in calculating area and perimeter?
- Common mistakes include confusing the formulas for area and perimeter, miscalculating units (e.g., using meters for one measurement and centimeters for another without conversion), and errors in measurement or arithmetic.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Inaccurate Measurements: Ensure all measurements are accurate and in the same units. Use precise tools for measuring lengths and angles.
- Mixing Units: Be consistent with units. Convert all measurements to the same unit before performing calculations.
- Formula Confusion: Double-check that you are using the correct formula for the shape you are calculating. Area and perimeter formulas differ significantly.
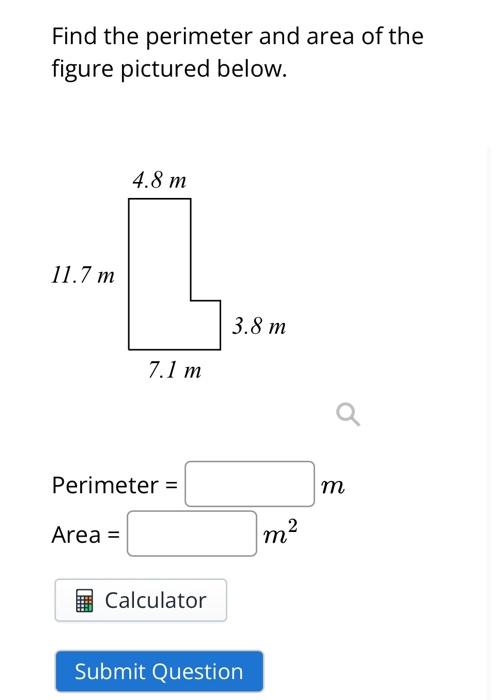
- Complex Shapes: For complex shapes, break them down into simpler shapes, calculate the area or perimeter of these simple shapes, and then sum them up.
Additional Tips
Using online calculators can be a great way to check your work. Remember, practice makes perfect. Regularly working on different types of problems will help you become more familiar with various shapes and formulas.

Interactive Learning Tools and Resources
Engaging with interactive tools and resources can significantly enhance the learning process, especially in understanding concepts like perimeter and area. Below is a curated list of interactive tools and resources that provide practical, hands-on experiences for learners of all ages.
Online Interactive Tools
- PhET Interactive Simulations: Offers a variety of interactive simulations to explore relationships between perimeter and area, including creating custom shapes and comparing them. Accessible in multiple languages for global learners.
- Geoboard by The Math Learning Center: A versatile app for forming line segments and polygons, exploring perimeter, area, angles, and more. Available on various platforms including web, iOS, and Chrome.
- Desmos: A comprehensive online calculator that allows exploration of mathematical concepts including area and perimeter calculations.
- Math Playground\"s Geoboard: This tool provides a virtual geoboard to create shapes and explore their properties including perimeter and area.
- Smashmaths: Features games and activities like \"Perimeter Shoot\" and \"Area Shape Shoot\", providing a fun way to learn and practice calculations.
Educational Websites with Interactive Content
- Khan Academy: Offers comprehensive lessons on area and perimeter, including quizzes and practice problems to test knowledge and understanding.
- Interactive Maths: Provides interactive resources to learn about the area and perimeter of various shapes, suitable for different learning levels.
Tips for Using Interactive Tools
- Experiment with different shapes and sizes to see how changes in dimensions affect perimeter and area.
- Utilize the various learning modes offered by these tools - from guided tutorials to challenge problems and quizzes.
- Integrate these tools into regular study sessions for a more dynamic and engaging learning experience.
These interactive tools and resources are designed to make the learning process both fun and educational, catering to various learning styles and preferences.
READ MORE:
Advanced Concepts in Perimeter and Area
In this section, we delve deeper into the advanced concepts of perimeter and area, exploring complex calculations and their practical applications. These concepts are fundamental in mathematics and provide a foundation for algebra, trigonometry, and calculus.
Understanding Perimeter
- Perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional shape. It can be calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides of a polygon.
- For rectangles, the formula for perimeter is ( P = 2l + 2w ), where ( l ) is the length and ( w ) is the width.
- In triangles, the perimeter is the sum of its three sides. For instance, for a triangle with sides of 6m, 8m, and 12m, the perimeter would be 26 meters.
Advanced Concepts in Area
- Area is measured in square units and represents the amount of space covered by a shape.
- For parallelograms, including rectangles, the area is calculated by ( A = b imes h ), where ( b ) is the base and ( h ) is the height.
- The area of a square is found using ( A = s^2 ), where ( s ) is the length of a side of the square.
- Triangles have a unique formula for area, ( A = frac{1}{2} b imes h ), where ( b ) is the base and ( h ) is the height perpendicular to the base.
Applications and Practical Use
Knowledge of area and perimeter is widely applied in fields such as architecture, engineering, and graphic design. It is essential for spatial reasoning, like determining the amount of paint needed for a room or calculating the fencing required for a garden.
Challenges and Exercises
To solidify your understanding of these concepts, try solving problems that require applying these formulas in real-world scenarios. This can include finding the area of irregular shapes or calculating the amount of material needed for a construction project.
Discover the fascinating world of geometry with our comprehensive guide on perimeter and area calculations. Perfect for learners and enthusiasts, this resource simplifies complex concepts, making understanding and applying these fundamental mathematical principles both enjoyable and accessible.