Topic how to find the area and perimeter: Embark on a mathematical journey as we delve into "How to Find the Area and Perimeter," your essential guide to understanding these fundamental geometric concepts. Perfect for learners and enthusiasts alike!
Table of Content
- Understanding Area and Perimeter: Definitions and Importance
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeter for Different Shapes
- Methods to Find Area: Formulas for Common Geometric Shapes
- Practical Examples: Applying Area and Perimeter in Real Life
- YOUTUBE: Finding Perimeter and Area of a Composite Shape - L-Shaped Example - Geometry - Math with Mr. J
- Interactive Tools and Resources for Learning Area and Perimeter
- Tips for Remembering Formulas and Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Advanced Concepts: Area and Perimeter in Irregular Shapes
- How Technology Can Aid in Understanding and Calculating Area and Perimeter
- Connecting the Dots: Area and Perimeter in Everyday Contexts
- Further Learning: Books, Courses, and Online Resources
Understanding Area and Perimeter: Definitions and Importance
The concepts of area and perimeter are fundamental in geometry, each representing distinct but related measurements of shapes. Perimeter is the distance around the outside of a shape. It\"s like taking a walk along the edge of a playground – you\"re tracing its boundary. This measurement is crucial in situations like fencing a yard or framing a picture. The perimeter is calculated differently for various shapes, for instance, by adding all sides of a polygon or using specific formulas for circles and other complex shapes.
On the other hand, area describes the amount of space a shape covers. It\"s akin to determining how much paint you need to cover a wall. Calculating the area depends on the shape in question - for a rectangle, it involves multiplying the length by the width, whereas for a triangle, it\"s half the product of its base and height. Complex shapes, such as circles, trapezoids, and ellipses, have their unique formulas. Area is particularly important in real-life scenarios like carpeting a room or buying land.
Both area and perimeter have diverse applications in everyday life and various fields such as architecture, engineering, and interior design. Understanding these concepts enhances practical problem-solving skills and fosters a deeper appreciation for the geometry around us.
- Formulas for calculating the perimeter and area vary based on the shape.
- Real-life applications of these measurements are extensive and varied.
- Grasping these concepts is essential for practical and academic purposes.

Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeter for Different Shapes
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its boundary. This section will guide you through calculating the perimeter for various shapes.
- Rectangle: To find the perimeter of a rectangle, add the lengths of all its four sides. Alternatively, use the formula P = 2l + 2w, where l is the length and w is the width.
- Square: Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is 4 times the length of one side, expressed as P = 4a.
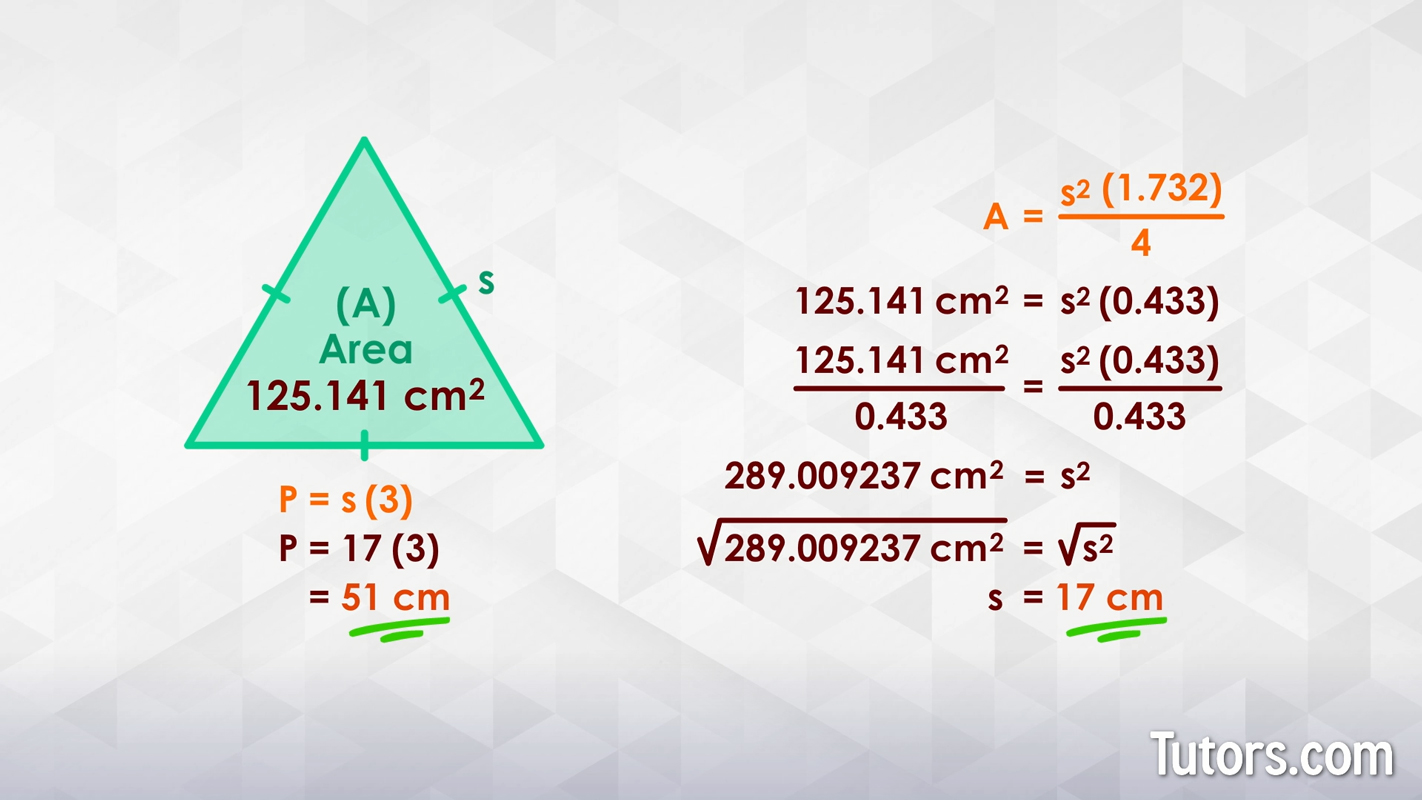
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides, denoted as P = a + b + c.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using the formula P = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
- Trapezoid: For trapezoids, add the lengths of all four sides, represented by P = a + b + c + d.
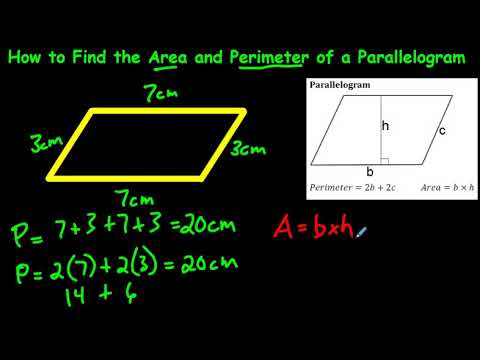
- Parallelogram: A parallelogram’s perimeter can be found by adding the lengths of its opposite sides, formulated as P = 2a + 2b.
- Ellipse: The perimeter of an ellipse is more complex to calculate and often involves an approximation like the Ramanujan approximation. One such formula is P = π×(3(a+b)−sqrt((3a+b)×(a+3b))), where a and b are the ellipse\"s semi-major and semi-minor axes, respectively.
Understanding these formulas and applying them correctly will enable you to accurately calculate the perimeter of various shapes, a skill crucial in geometry and many practical applications.

Methods to Find Area: Formulas for Common Geometric Shapes
Calculating the area of various shapes is a fundamental aspect of geometry. Here\"s a guide to the formulas for common geometric shapes.
- Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length (l) by its width (w). The formula is A = l × w.
- Square: Since all sides of a square are equal, its area is calculated by squaring the length of one side (a). Thus, A = a².
- Triangle: The area of a triangle can be calculated by multiplying its base (b) by its height (h) and then dividing by 2. The formula is A = 1/2 × b × h.
- Circle: The area of a circle is found using the radius (r) with the formula A = π × r², where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- Parallelogram: Similar to a rectangle, the area of a parallelogram is calculated by multiplying its base (b) by its height (h), A = b × h.
- Trapezoid: The area of a trapezoid is found by adding the lengths of the two parallel sides (a and b), multiplying by the height (h), and then dividing by 2. The formula is A = 1/2 × (a + b) × h.
These formulas provide a basis for calculating the area of these shapes and are essential tools in both academic and practical applications of geometry.

Practical Examples: Applying Area and Perimeter in Real Life
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is not just academic; they are used in various real-life applications. Here are some practical examples where knowing how to calculate area and perimeter is essential.
Home Decoration and Renovation
- When painting a room, calculating the area of the walls helps in buying the right amount of paint.
- Flooring installation requires the area measurement of the floor to determine how much material (like tiles or carpet) is needed.
Gardening and Landscaping
- Calculating the perimeter of a garden bed helps in purchasing the correct length of border materials like fencing or edging.
- The area of a lawn is important for determining how much seed or fertilizer is required for even coverage.
Construction and Architecture
- Architects use area and perimeter calculations to design buildings and rooms, ensuring proper space utilization.
- In construction, knowing the perimeter helps in estimating the amount of materials needed for foundations, fences, and framing.
Sports and Recreation
- The area of sports fields (like soccer fields or tennis courts) must be calculated to adhere to regulation sizes.
- Track and field events use perimeter measurements to set accurate distances for races.
Education and Learning Activities
- Teachers often use real-life scenarios involving area and perimeter in teaching mathematics to provide practical context.
- Students engage in activities like measuring their classroom or playground to understand these concepts better.
Everyday Life
- Arranging furniture in a room requires understanding the area to ensure everything fits comfortably.
- When buying a plot of land, the perimeter and area measurements are crucial for planning and legal purposes.
These examples illustrate the importance of area and perimeter in various aspects of life, highlighting their practical value beyond the classroom.

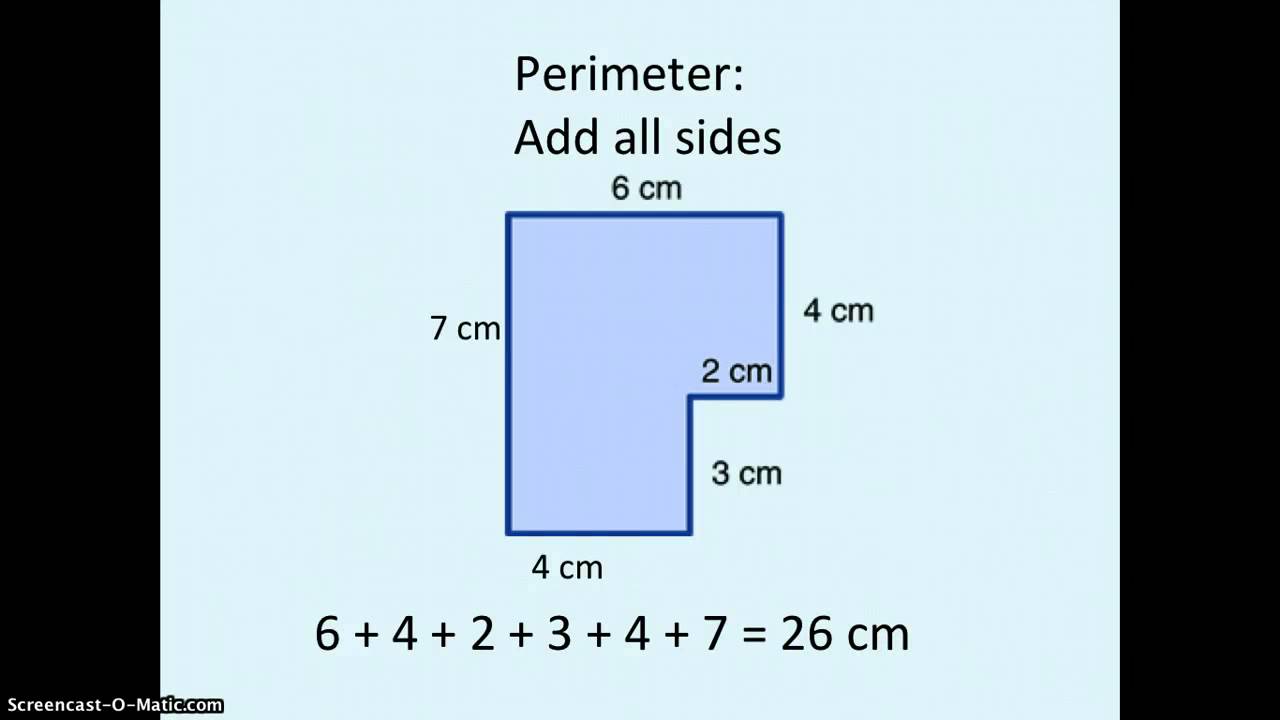
Finding Perimeter and Area of a Composite Shape - L-Shaped Example - Geometry - Math with Mr. J
Discover the endless possibilities of composite shapes in our captivating video! Explore how combining different geometrical figures can create unique and intriguing patterns. Join us to unravel the beauty and complexity of these fascinating shapes!
How to Find Area and Perimeter
Dive into the fascinating world of area and perimeter with our engaging video. Learn how to calculate the size and boundaries of various shapes, from rectangles and triangles to more complex figures. Unleash your mathematical prowess and join us on this exciting exploration!
Interactive Tools and Resources for Learning Area and Perimeter
There are numerous interactive tools and resources available online for learning and practicing area and perimeter calculations. These tools are designed to make learning engaging and effective for students of various ages. Below is a list of some notable resources.
Online Simulations and Games
- PhET Interactive Simulations offers an \"Area Builder\" game, where students can create shapes using colorful blocks to explore the relationship between perimeter and area. This tool also features a challenge mode to build shapes or find the area of complex figures.
- Interactive Maths provides various activities and exercises for practicing area and perimeter calculations, suitable for different learning levels.
- The \"Area Perimeter Explorer\" on Toy Theater allows students to create rectangles or irregular shapes on a grid, automatically showing the totals of perimeter and area, with options to toggle these features on and off.
- Math Playground\"s \"Geoboard Area and Perimeter\" tool enables students to create shapes using bands on a board, experimenting with different configurations to understand area and perimeter concepts.
- \"Area Blocks\" from Math Playground is a game where students create shapes on a 12x12 grid, focusing on solving problems involving perimeters of polygons and applying area and perimeter formulas for rectangles.
Interactive Activities and Educational Content
- Math Mammoth\"s \"Area and Perimeter Builder\" provides an activity and game designed for 2nd to 4th graders, allowing exploration and comparison of area and perimeter in various shapes.
- SplashLearn offers \"Area Shapes Games\" where students can learn about areas of composite figures and practice finding area with unit squares and side lengths.
- CameraMath\"s \"Perimeter & Area Calculator\" helps in understanding the basic concepts of perimeter and area, offering a straightforward method for calculation.
- Topmarks provides a variety of teaching tools demonstrating area and perimeter, ideal for interactive whiteboard use.
- Math-Center.Org features a range of area and perimeter worksheets and resources, helping students understand these concepts through interactive sheets.
These interactive tools and games make learning area and perimeter fun and engaging, helping students to better grasp these essential mathematical concepts.

_HOOK_
Tips for Remembering Formulas and Avoiding Common Mistakes
Mastering the formulas for area and perimeter is crucial for students, but it can be challenging. Here are some effective strategies to help students remember these formulas and avoid common mistakes:
1. Visualization and Mnemonics
- Use visualization techniques, such as associating the word \"peRIMeter\" with the outside ‘rim’ of a shape. This helps students remember that perimeter is the measure around the outside of a shape.
- For area, encourage students to visualize filling the inside of a shape and associating it with the word ‘AREA’. This can be enhanced by coloring the inside of the shapes in their journals.
2. Differentiating Area and Perimeter
- Teach area and perimeter as distinct concepts. For instance, use different computational methods: addition for perimeter and multiplication for area.
- Provide real-world context in problems to help students understand when to use each formula. This can include sorting exercises to distinguish between area and perimeter-related problems.
3. Practice and Reinforcement
- Regular practice with a variety of shapes reinforces the understanding of these concepts. Use task cards, quizzes, and interactive activities for continual engagement.
- Error analysis activities, where students identify and correct mistakes in perimeter and area calculations, can deepen their understanding and ability to apply these concepts correctly.
4. Learning through Songs and Rhymes
- Songs and rhymes about geometry can be a fun and effective way to remember formulas. For example, creating a song that differentiates between the formulas for perimeter and area.
5. Relatable Examples
- Using relatable, everyday examples, such as measuring rooms or objects, helps in solidifying these concepts. This approach also makes learning more engaging and practical.
By incorporating these strategies, students can develop a stronger grasp of area and perimeter, enabling them to apply these concepts accurately in various contexts.
Advanced Concepts: Area and Perimeter in Irregular Shapes
Mastering the formulas for area and perimeter is crucial for students, but it can be challenging. Here are some effective strategies to help students remember these formulas and avoid common mistakes:
1. Visualization and Mnemonics
- Use visualization techniques, such as associating the word \"peRIMeter\" with the outside ‘rim’ of a shape. This helps students remember that perimeter is the measure around the outside of a shape.
- For area, encourage students to visualize filling the inside of a shape and associating it with the word ‘AREA’. This can be enhanced by coloring the inside of the shapes in their journals.
2. Differentiating Area and Perimeter
- Teach area and perimeter as distinct concepts. For instance, use different computational methods: addition for perimeter and multiplication for area.
- Provide real-world context in problems to help students understand when to use each formula. This can include sorting exercises to distinguish between area and perimeter-related problems.
3. Practice and Reinforcement
- Regular practice with a variety of shapes reinforces the understanding of these concepts. Use task cards, quizzes, and interactive activities for continual engagement.
- Error analysis activities, where students identify and correct mistakes in perimeter and area calculations, can deepen their understanding and ability to apply these concepts correctly.
4. Learning through Songs and Rhymes
- Songs and rhymes about geometry can be a fun and effective way to remember formulas. For example, creating a song that differentiates between the formulas for perimeter and area.
5. Relatable Examples
- Using relatable, everyday examples, such as measuring rooms or objects, helps in solidifying these concepts. This approach also makes learning more engaging and practical.
By incorporating these strategies, students can develop a stronger grasp of area and perimeter, enabling them to apply these concepts accurately in various contexts.

How Technology Can Aid in Understanding and Calculating Area and Perimeter
Mastering the formulas for area and perimeter is crucial for students, but it can be challenging. Here are some effective strategies to help students remember these formulas and avoid common mistakes:
1. Visualization and Mnemonics
- Use visualization techniques, such as associating the word \"peRIMeter\" with the outside ‘rim’ of a shape. This helps students remember that perimeter is the measure around the outside of a shape.
- For area, encourage students to visualize filling the inside of a shape and associating it with the word ‘AREA’. This can be enhanced by coloring the inside of the shapes in their journals.
2. Differentiating Area and Perimeter
- Teach area and perimeter as distinct concepts. For instance, use different computational methods: addition for perimeter and multiplication for area.
- Provide real-world context in problems to help students understand when to use each formula. This can include sorting exercises to distinguish between area and perimeter-related problems.
3. Practice and Reinforcement
- Regular practice with a variety of shapes reinforces the understanding of these concepts. Use task cards, quizzes, and interactive activities for continual engagement.
- Error analysis activities, where students identify and correct mistakes in perimeter and area calculations, can deepen their understanding and ability to apply these concepts correctly.
4. Learning through Songs and Rhymes
- Songs and rhymes about geometry can be a fun and effective way to remember formulas. For example, creating a song that differentiates between the formulas for perimeter and area.
5. Relatable Examples
- Using relatable, everyday examples, such as measuring rooms or objects, helps in solidifying these concepts. This approach also makes learning more engaging and practical.
By incorporating these strategies, students can develop a stronger grasp of area and perimeter, enabling them to apply these concepts accurately in various contexts.
Connecting the Dots: Area and Perimeter in Everyday Contexts
Understanding area and perimeter is not just a mathematical skill; it’s a practical tool we use in everyday life. From planning a new garden to deciding the quantity of paint needed for a room, these concepts are widely applicable. Let’s explore some common scenarios where area and perimeter calculations become useful.
- Home Decorating and Renovation: Calculating the area of walls or floors is essential when you\"re painting, tiling, or carpeting. For instance, to determine the amount of paint required for a room, measure the area of each wall and sum them up.
- Gardening and Landscaping: Knowing the perimeter and area of your garden helps in planning the layout and buying the right amount of plants and materials. For a flower bed, the perimeter gives the length of the border, while the area helps in estimating soil and mulch requirements.
- Event Planning: Setting up an event space requires knowledge of area and perimeter to ensure that there’s enough room for guests and activities. Whether it\"s a wedding or a corporate event, understanding the space\"s dimensions helps in organizing seating, activities, and decorations efficiently.
- Sports and Recreation: Many sports require a specific field size, which is defined by its perimeter. The area of a sports field affects how many people can be accommodated, either as participants or spectators.
- Construction Projects: For any construction work, from a small shed to a large building, knowing the area and perimeter is crucial for material estimation, space planning, and compliance with building regulations.
- Education and Learning Tools: Real-world examples like measuring rooms or creating a garden layout can be excellent projects for students learning about area and perimeter, making the concepts more tangible and understandable.
In conclusion, area and perimeter are not just abstract mathematical concepts, but are key to solving numerous practical problems. Their applications extend from simple home projects to complex architectural designs, proving their significance in everyday life.

Further Learning: Books, Courses, and Online Resources
For those eager to deepen their understanding of area and perimeter, a wealth of resources is available. From comprehensive online courses to insightful books, here’s a curated list to guide your journey in mastering these fundamental concepts of geometry.
- Online Courses:
- Khan Academy offers extensive lessons and practice problems on various geometric shapes, their area, and perimeter. Their interactive platform includes topics like area of triangles, rectangles, trapezoids, and circles, along with quizzes and real-life application examples.
- CalcWorkshop provides a detailed guide on finding area and perimeter with practical examples and surefire methods to grasp these concepts.
- MathPlanet’s Pre-Algebra course covers calculating area and perimeter, among other basic mathematical concepts, ideal for beginners.
- Books:
- \"The Joy of Mathematics\" by Theoni Pappas - This book explores various mathematical concepts including area and perimeter, making them accessible and enjoyable to a wide audience.
- \"How to Solve It\" by George Pólya - Although not exclusively about area and perimeter, this classic book offers strategies for solving mathematical problems, which can be applied to geometry as well.
- Interactive Tools:
- CameraMath offers an Area & Perimeter Calculator, which allows students to input dimensions and automatically calculate the area and perimeter of different shapes.
- BYJU’S Learning App provides interactive learning modules with formulas and examples for calculating the area and perimeter of various shapes.
- Additional Online Resources:
- SplashLearn offers fun facts, practice problems, and quizzes on area and perimeter, tailored for a younger audience.
- BYJU\"S website has a comprehensive section on area and perimeter formulas, definitions, and examples for different geometric figures.
Through these resources, learners of all ages can explore and master the concepts of area and perimeter, laying a strong foundation for further mathematical learning.
Embark on an enlightening journey to master area and perimeter, essential skills for practical and academic success. Explore our comprehensive resources and embrace the joy of learning these fundamental geometric concepts in a fun, engaging manner.
_HOOK_