Topic how to find perimeter of octagon: Discover the secrets of octagonal geometry with our comprehensive guide on finding the perimeter of an octagon. Whether regular or irregular, our step-by-step methods demystify calculations, making it easy and engaging for geometry enthusiasts!
Table of Content
- Understanding the Octagon
- Basic Perimeter Formula for a Regular Octagon
- Calculating Perimeter from Side Length
- Using the Octagon Calculator Tools
- Perimeter for Irregular Octagons
- YOUTUBE: Finding the Perimeter of an Octagon
- Understanding and Using Circumradius and Inradius
- Steps to Draw a Regular Octagon
- Converting Units for Perimeter Measurement
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Understanding Internal and External Angles
Understanding the Octagon
An octagon is a geometric shape with eight sides and eight angles. In a regular octagon, all sides and angles are equal, making it a highly symmetrical shape. This symmetry lends itself to various mathematical properties, particularly in calculating its perimeter.
- Sides: A regular octagon has eight equal-length sides.
- Angles: Each interior angle in a regular octagon measures 135 degrees, while each exterior angle is 45 degrees.
- Area and Perimeter: The formulas for area and perimeter depend on the regularity and dimensions of the octagon.
- Applications: Octagons are prevalent in architecture and design, most notably seen in the shape of stop signs.
Understanding these basic characteristics is essential for calculating the perimeter, whether the octagon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles vary).
READ MORE:
Basic Perimeter Formula for a Regular Octagon
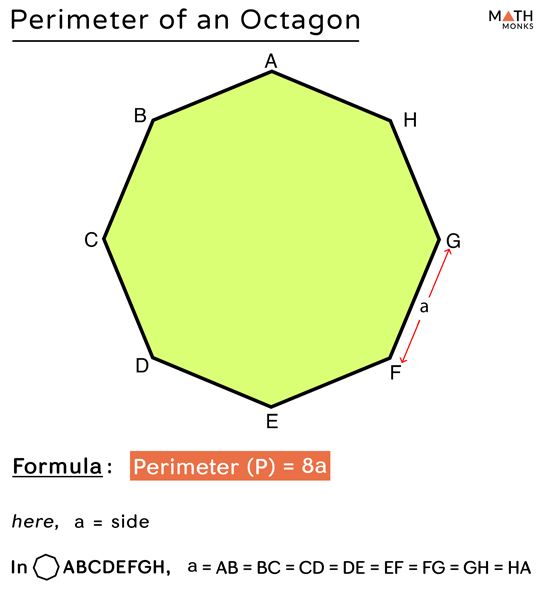
The perimeter of a regular octagon can be calculated using a simple formula. A regular octagon is a geometric figure with eight equal sides and equal angles. The basic formula to find the perimeter (P) of a regular octagon is:
Perimeter (P) = 8 × Side Length (a)
- Identify the Length of One Side: Measure or obtain the length of one side of the octagon (a).
- Apply the Formula: Multiply the length of one side by 8 (since an octagon has 8 sides).
- Calculate the Perimeter: The resulting product is the perimeter of the octagon.
This formula assumes all sides are of equal length, which is a characteristic of a regular octagon. For example, if one side of the octagon is 5 units long, the perimeter would be 8 × 5 = 40 units.
Calculating Perimeter from Side Length
Calculating the perimeter of a regular octagon is straightforward when you know the length of one side. Here\"s how you can do it:
- Measure the Side: Start by measuring the length of one side of the octagon. In a regular octagon, all sides are of equal length.
- Use the Perimeter Formula: The perimeter of a regular octagon is equal to eight times the length of one side. The formula is P = 8 × side length.
- Calculate: Multiply the length of one side by 8 to get the total perimeter of the octagon.
For example, if the length of one side is 4 units, then the perimeter would be 8 × 4 = 32 units. This method is efficient and accurate for regular octagons where all sides are of equal length.
Using the Octagon Calculator Tools
Octagon calculator tools simplify the process of calculating the perimeter of an octagon, especially when dealing with regular octagons. These tools are user-friendly and provide quick and accurate results. Here’s how to use them:
- Select a Calculator: Choose an online octagon calculator tool. Many websites offer these tools for free.
- Input Side Length: Enter the length of one side of the octagon. In regular octagons, all sides are of equal length.
- Submit for Calculation: After entering the side length, submit it for calculation. The tool will automatically apply the formula P = 8 × side length to determine the perimeter.
- Review Results: The calculated perimeter of the octagon will be displayed. Some tools might also provide additional information like area or angle measurements.
Using octagon calculator tools is particularly helpful for educational purposes, quick checks, or when working on complex projects where manual calculation can be time-consuming.
Perimeter for Irregular Octagons
The process to calculate the perimeter of an irregular octagon, which has sides of different lengths, is straightforward but requires accurate measurements of each side. Unlike regular octagons, where all sides are equal, irregular octagons have varying side lengths. Therefore, the perimeter is the sum of these lengths.
Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter:
- Measure Each Side: Start by measuring the length of each of the eight sides. It\"s crucial to be precise in these measurements for an accurate calculation.
- Record the Measurements: Write down each measurement. Label them as a, b, c, d, e, f, g, and h for ease of reference.
- Add the Lengths: Calculate the perimeter by adding the lengths of all sides: P = a + b + c + d + e + f + g + h.
Example Calculation:
- If the sides of an irregular octagon measure 4 cm, 5 cm, 4.5 cm, 5.5 cm, 6 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, and 6.5 cm, then the perimeter (P) is calculated as P = 4 + 5 + 4.5 + 5.5 + 6 + 4 + 5 + 6.5 = 40.5 cm.
Remember, the accuracy of the perimeter depends on the precision of each individual measurement.
_HOOK_
Finding the Perimeter of an Octagon
Want to explore the fascinating world of shapes? Join us as we dive into the concept of perimeter! Discover the secrets behind calculating the length of a shape\'s outer edge and unravel the wonders of geometry in our captivating video.
Finding the Perimeter of a Regular Octagon
Curious about the mesmerizing beauty of symmetry and shape? Journey with us as we unravel the mysteries of regular octagons! Explore the intricate angles and precise measurements that create this remarkable shape in our captivating video. Get ready to be amazed!
Understanding and Using Circumradius and Inradius
The concepts of circumradius and inradius are pivotal in understanding the geometry of regular octagons. A regular octagon is a polygon with eight equal sides and angles, and these radii are key to determining its geometric properties.
Circumradius (Rc)
The circumradius is the radius of a circumscribed circle that passes through all eight vertices of the octagon. It can be calculated using the formula:
- Rc = a / (2 * sin(22.5°))
This formula derives from the relationship between the side length of the octagon and the angles formed at its center.
Inradius (Ri)
The inradius is the radius of an inscribed circle that touches all eight sides of the octagon. It can be found using the formula:
- Ri = a / (2 * tan(22.5°))
The inradius is effectively the apothem of the octagon and is a key measure in calculating the area of the octagon.
Application in Area and Perimeter Calculation
The inradius and circumradius can be used to calculate the area and perimeter of a regular octagon. The area can be calculated as:
- Area = 2 * a2 * (1 + √2)
Where \"a\" is the length of a side. The perimeter is simpler, being the sum of all side lengths:
- Perimeter = 8 * a
These formulas offer a straightforward way to calculate the properties of an octagon, essential in fields such as architecture and design.
Geometric Interpretation
The circumradius and inradius provide insight into the octagon\"s geometry. The circumradius corresponds to the longest diagonal of the octagon, and the inradius is aligned with the height of the octagon, demonstrating how these measures relate to the octagon\"s overall shape and size.
Practical Examples
In practical scenarios, these measurements are vital. For instance, in designing an octagonal frame, the circumradius can determine the overall size, while the inradius helps in detailing the inner space. These concepts are not just limited to octagons but apply to other polygons as well, making them fundamental in polygonal geometry.
Conclusion
Understanding the circumradius and inradius of a regular octagon is crucial for various applications, from mathematical problems to practical design and architecture. These measures help in accurately determining the size, shape, and area of the octagon, thereby facilitating precise calculations and designs.

Steps to Draw a Regular Octagon
Drawing a regular octagon, a polygon with eight equal sides and angles, can be done with a few simple steps. This guide will help you create a precise and symmetrical octagon using basic drawing tools.
- Begin by drawing a horizontal line slightly longer than the desired diameter of your octagon. This line will serve as a guide for the octagon\"s width.
- Mark a point on the line to represent the center of the octagon. Let\"s call this point O. Then, mark another point at one end of the line, representing a vertex of the octagon. We\"ll call this point A.
- Using a compass, draw a circle with point O as the center and the distance OA as the radius. This circle is the circumcircle of the octagon and will guide the placement of the vertices.
- From point A, draw a perpendicular line upwards, crossing the circumcircle at point B. This establishes one of the octagon\"s sides.
- Set the compass width to the length of the line segment OA. With the compass, draw arcs from points A and B, intersecting above and below the circumcircle.
- Draw a line through the intersection points of the arcs and the circumcircle\"s center, O. This line will intersect the circumcircle at two new points, C and D, giving you two more vertices of the octagon.
- Repeat the process using points C and D to find the remaining vertices of the octagon on the circumcircle.
- Connect the adjacent points on the circumcircle with straight lines to form the octagon.
- Refine the drawing by ensuring all sides are equal in length and angles are congruent, each measuring 135°.
With patience and precision, you can easily draw a regular octagon. This method ensures that each side and angle of the octagon is equal, creating a symmetrical and balanced shape.
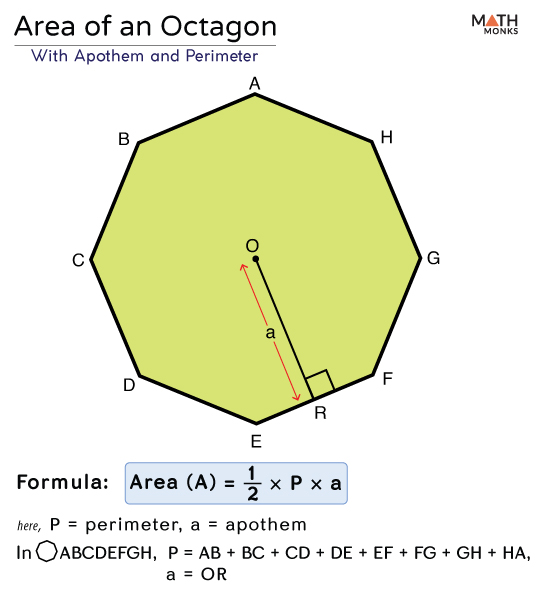
Converting Units for Perimeter Measurement
Converting the units of measurement is crucial when calculating the perimeter of an octagon, especially if the given dimensions are in different units. This section provides a comprehensive guide to unit conversion, ensuring accurate calculations.
Understanding Different Measurement Units
Common units used in measuring perimeter include millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m), inches (in), and feet (ft). Understanding how these units relate to each other is key to successful conversion.
Basic Conversion Factors
- Metric to Imperial: 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters.
- Imperial to Metric: 1 meter = 3.28084 feet.
Step-by-Step Conversion Process
- Determine the Current Unit: Identify the unit of measurement used in the given perimeter or side length.
- Select the Target Unit: Choose the unit you wish to convert to.
- Apply Conversion Factor: Use the appropriate conversion factor to translate the measurement.
- Calculate the Converted Perimeter: Multiply the original perimeter measurement by the conversion factor.
Conversion Tables for Quick Reference
| From | To | Conversion Factor |
| Inches | Centimeters | 2.54 |
| Feet | Meters | 0.3048 |
| Centimeters | Inches | 0.393701 |
| Meters | Feet | 3.28084 |
Remember, accuracy in conversion is vital for the correct calculation of the perimeter. Double-check your conversions to ensure precision.
Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding how to find the perimeter of octagons, both regular and irregular, is essential for mastering basic geometry. This section provides examples and practice problems to help reinforce this concept.
Regular Octagon Examples
- Example 1: Calculate the perimeter of a regular octagon with each side measuring 10 cm.
- Solution: Perimeter = 8 × side length = 8 × 10 cm = 80 cm.
- Example 2: A regular octagon has a perimeter of 64 ft. What is the length of one side?
- Solution: Side length = Perimeter ÷ 8 = 64 ft ÷ 8 = 8 ft.
- Example 3: Find the perimeter of a regular octagon with side lengths of 16 inches.
- Solution: Perimeter = 8 × side length = 8 × 16 inches = 128 inches.
Irregular Octagon Examples
In the case of irregular octagons, the perimeter is the sum of all side lengths.
- Example 4: Find the perimeter of an irregular octagon with side lengths of 6 cm, 16 cm, 14 cm, 20 cm, 12 cm, 8 cm, 10 cm, and 18 cm.
- Solution: Perimeter = Sum of all sides = 6 + 16 + 14 + 20 + 12 + 8 + 10 + 18 cm = 104 cm.
Practice Problems
- Calculate the perimeter of a regular octagon with each side measuring 7 feet.
- Find the length of one side of a regular octagon if its perimeter is 72 inches.
- Determine the perimeter of an irregular octagon with side lengths of 3 cm, 7 cm, 8 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, 6 cm, 10 cm, and 9 cm.
Understanding Internal and External Angles
Understanding the internal and external angles of an octagon is crucial for comprehending its geometric properties. This section will guide you through the basics of these angles in both regular and irregular octagons.
Internal Angles of an Octagon
Internal angles are the angles found inside the shape. In a regular octagon, all internal angles are equal.
- Total Sum of Internal Angles: The sum of all internal angles in any octagon is 1080°.
- Individual Internal Angle in a Regular Octagon: Since all internal angles in a regular octagon are equal, each angle measures 135° (1080° divided by 8).
External Angles of an Octagon
External angles are the angles formed between any side of the octagon and the extended line of its adjacent side.
- Total Sum of External Angles: The sum of all external angles for any polygon is always 360°.
- Individual External Angle in a Regular Octagon: Since the sum of the internal and external angle at each vertex is 180°, and each internal angle in a regular octagon is 135°, each external angle is 45° (180° - 135°).
Irregular Octagons
In an irregular octagon, the internal and external angles are not equal. However, the total sum of internal angles remains 1080°, and the total sum of external angles remains 360°.
Calculating Angles
- For Regular Octagons: Use the standard measures of 135° for each internal angle and 45° for each external angle.
- For Irregular Octagons: Measure each angle individually with a protractor. Ensure that the total of internal angles adds up to 1080° and the total of external angles adds up to 360°.
Understanding these angles is essential for various applications, including architectural design, graphic design, and mathematics.
Mastering the calculation of an octagon\"s perimeter enriches your understanding of geometry, serving as a stepping stone to more complex mathematical concepts and real-world applications. Embark on this fascinating journey and unlock the secrets of octagonal shapes!
_HOOK_
