Topic perimeter and area worksheet: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the perimeter and area worksheet! This article is designed to help you master the essential math skills needed to calculate perimeter and area for various shapes. With clear explanations, practical examples, and interactive activities, you'll find everything you need to succeed. Start your learning journey now!
Table of Content
- Perimeter and Area Worksheet
- Introduction to Perimeter and Area
- Calculating the Perimeter of Different Shapes
- Calculating the Area of Different Shapes
- Perimeter and Area Formulas
- Worked Examples
- Real-World Applications of Perimeter and Area
- Interactive Activities and Games
- Additional Resources and Worksheets
- Answers and Solutions
- Tips and Tricks for Solving Perimeter and Area Problems
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE:
Perimeter and Area Worksheet
Welcome to our comprehensive worksheet on perimeter and area! Here, you'll find a variety of problems and examples to help you master these important mathematical concepts.
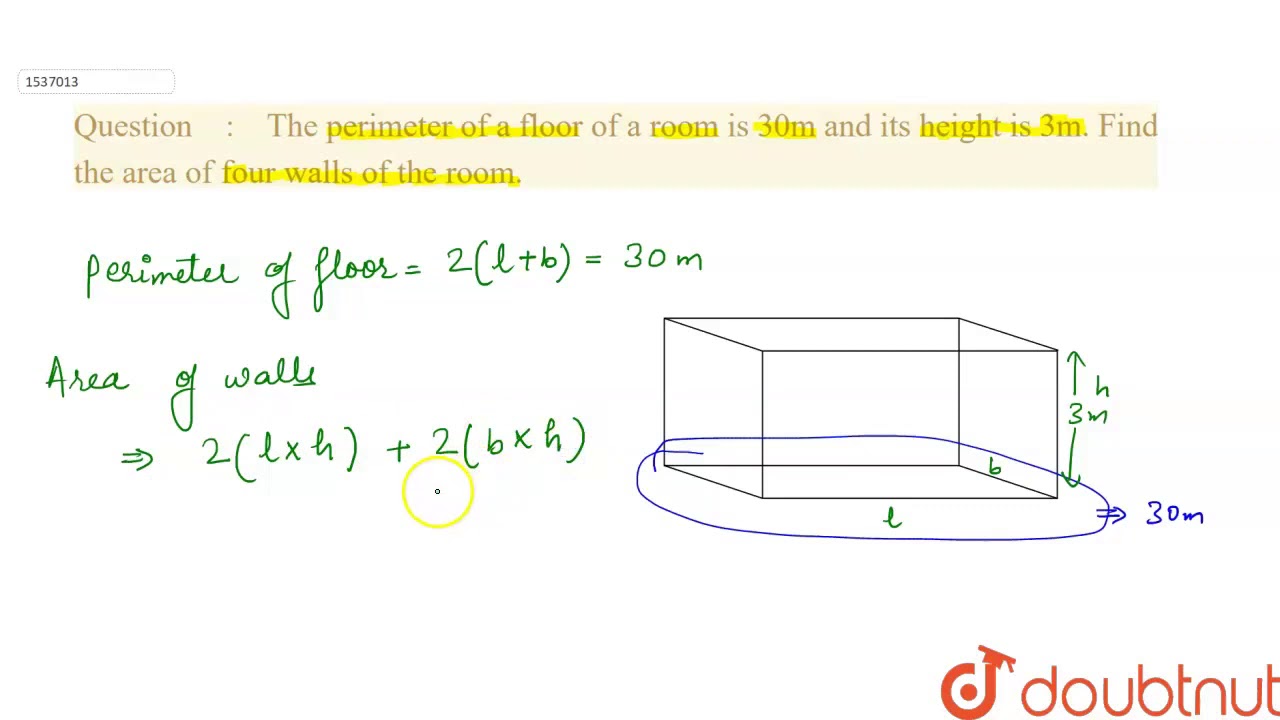
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around the edge of the shape. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides.
- For a rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
- For a square: \( P = 4s \)
- For a triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
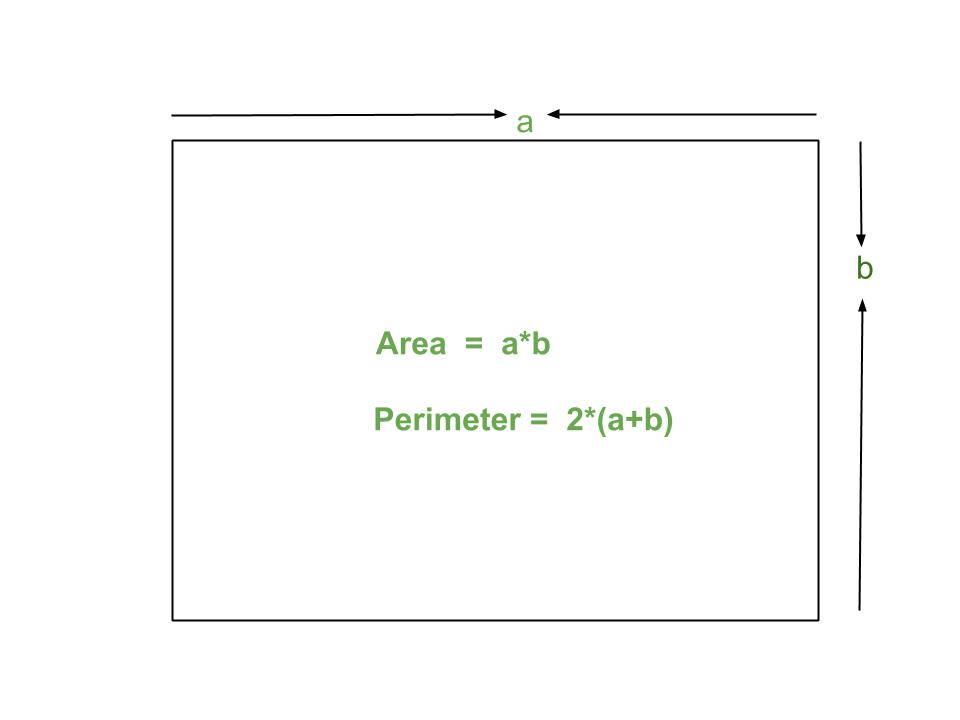
Understanding Area
The area of a shape is the amount of space inside the shape. It is calculated differently depending on the type of shape.
- For a rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- For a square: \( A = s^2 \)
- For a triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
Practice Problems
Try solving the following problems to test your understanding:
Problem 1
A rectangle has a length of 8 cm and a width of 3 cm. Calculate the perimeter and area.
- Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times 8 + 2 \times 3 = 22 \) cm
- Area: \( A = 8 \times 3 = 24 \) cm2
Problem 2
A square has a side length of 5 cm. Calculate the perimeter and area.
- Perimeter: \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \) cm
- Area: \( A = 5^2 = 25 \) cm2
Problem 3
A triangle has sides of 6 cm, 7 cm, and 8 cm. Calculate the perimeter. If the base is 6 cm and the height is 4 cm, calculate the area.
- Perimeter: \( P = 6 + 7 + 8 = 21 \) cm
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4 = 12 \) cm2
Additional Exercises
- Find the perimeter and area of a rectangle with length 10 cm and width 5 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter and area of a square with side length 12 cm.
- A triangle has a base of 9 cm and height of 6 cm. What is its area?
Answers to Additional Exercises
- Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times 10 + 2 \times 5 = 30 \) cm; Area: \( A = 10 \times 5 = 50 \) cm2
- Perimeter: \( P = 4 \times 12 = 48 \) cm; Area: \( A = 12^2 = 144 \) cm2
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 9 \times 6 = 27 \) cm2
We hope this worksheet helps you understand perimeter and area better. Keep practicing to improve your skills!

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter and Area
The concepts of perimeter and area are fundamental in geometry and are widely used in various real-world applications. Understanding these concepts helps in solving problems related to the measurement of spaces and boundaries.
Perimeter refers to the total length of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides of the shape. For example:
- Rectangle: The perimeter \(P\) of a rectangle with length \(l\) and width \(w\) is given by \(P = 2l + 2w\).
- Square: The perimeter \(P\) of a square with side length \(s\) is given by \(P = 4s\).
- Triangle: The perimeter \(P\) of a triangle with sides \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) is given by \(P = a + b + c\).
Area measures the amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape. Different shapes have different formulas for calculating their area. For example:
- Rectangle: The area \(A\) of a rectangle is given by \(A = l \times w\).
- Square: The area \(A\) of a square is given by \(A = s^2\).
- Triangle: The area \(A\) of a triangle is given by \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\), where \(b\) is the base and \(h\) is the height.
Learning to calculate the perimeter and area of various shapes is crucial for solving geometry problems effectively. These concepts also have practical applications in fields such as architecture, engineering, and everyday tasks like home improvement projects.
By practicing with worksheets and engaging in interactive activities, students can develop a strong understanding of these concepts and enhance their problem-solving skills.
Calculating the Perimeter of Different Shapes
Perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional shape. To calculate the perimeter of various shapes, you simply add the lengths of all the sides. Below are the steps for calculating the perimeter of some common shapes:
Perimeter of a Rectangle
The perimeter (P) of a rectangle is calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 2 \times (l + w) \]
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter (P) of a square is calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 4 \times s \]
where \( s \) is the length of a side.
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter (P) of a triangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
Perimeter of a Parallelogram
The perimeter (P) of a parallelogram is calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 2 \times (a + b) \]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the adjacent sides.
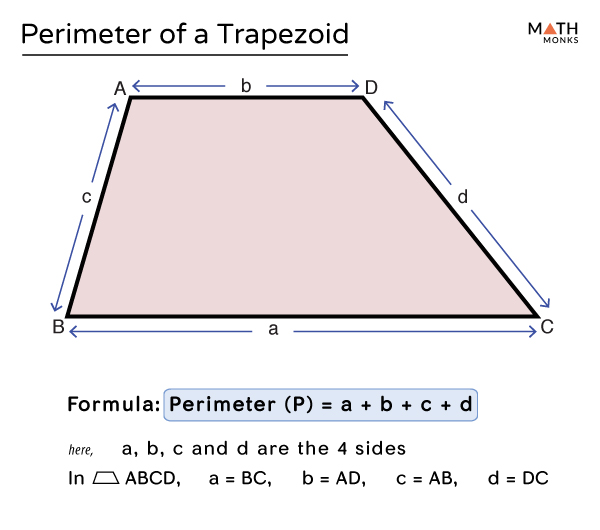
Perimeter of a Trapezoid
The perimeter (P) of a trapezoid is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides:
\[ P = a + b + c + d \]
where \( a \), \( b \), \( c \), and \( d \) are the lengths of the sides.
Perimeter of a Circle (Circumference)
The perimeter (P) of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 2 \pi r \]
where \( r \) is the radius.
Worked Example
Let's calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 8 cm and a width of 5 cm:
\[ P = 2 \times (8 \text{ cm} + 5 \text{ cm}) = 2 \times 13 \text{ cm} = 26 \text{ cm} \]
By understanding and using these formulas, you can easily determine the perimeter of any given shape. Practice with different shapes and their measurements to master perimeter calculations.
Calculating the Area of Different Shapes
Calculating the area of various geometric shapes is a fundamental skill in geometry. The area represents the amount of space enclosed within a shape's boundaries. Different shapes require different formulas to calculate their area. Here are the steps and formulas for calculating the area of some common shapes:
1. Area of a Rectangle
The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length by its width:
\( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
Example:
- Length = 8 units
- Width = 5 units
- \( \text{Area} = 8 \times 5 = 40 \, \text{square units} \)
2. Area of a Square
The area of a square is found by squaring the length of one of its sides:
\( \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \)
Example:
- Side = 6 units
- \( \text{Area} = 6^2 = 36 \, \text{square units} \)
3. Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle is calculated using the formula:
\( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
Example:
- Base = 10 units
- Height = 4 units
- \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 4 = 20 \, \text{square units} \)
4. Area of a Circle
The area of a circle is found using the formula:
\( \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
Example:
- Radius = 7 units
- \( \text{Area} = \pi \times 7^2 = 49\pi \, \text{square units} \approx 153.94 \, \text{square units} \)
5. Area of a Parallelogram
The area of a parallelogram is calculated by multiplying the base by the height:
\( \text{Area} = \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
Example:
- Base = 12 units
- Height = 5 units
- \( \text{Area} = 12 \times 5 = 60 \, \text{square units} \)
6. Area of a Trapezoid
The area of a trapezoid is found using the formula:
\( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \)
Example:
- Base 1 = 8 units
- Base 2 = 5 units
- Height = 4 units
- \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times (8 + 5) \times 4 = \frac{1}{2} \times 13 \times 4 = 26 \, \text{square units} \)
7. Area of a Rhombus
The area of a rhombus can be calculated using the lengths of its diagonals:
\( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{diagonal}_1 \times \text{diagonal}_2 \)
Example:
- Diagonal 1 = 10 units
- Diagonal 2 = 8 units
- \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 8 = 40 \, \text{square units} \)
By understanding and using these formulas, you can calculate the area of various shapes accurately and efficiently. Practicing these calculations will improve your problem-solving skills and help you apply these concepts in real-world situations.
Perimeter and Area Formulas
Understanding the formulas for calculating the perimeter and area of different shapes is crucial in solving geometry problems. Here, we will outline the key formulas for various common shapes.
Perimeter Formulas
- Square: \( P = 4s \) where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \) where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter.
Area Formulas
- Square: \( A = s^2 \) where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- Rectangle: \( A = lw \) where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2}bh \) where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \) where \( r \) is the radius.
- Parallelogram: \( A = bh \) where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Trapezoid: \( A = \frac{1}{2}(b_1 + b_2)h \) where \( b_1 \) and \( b_2 \) are the lengths of the parallel sides and \( h \) is the height.
These formulas are the building blocks for solving various geometry problems involving perimeter and area. By understanding and memorizing these formulas, students can approach problems with confidence and accuracy.
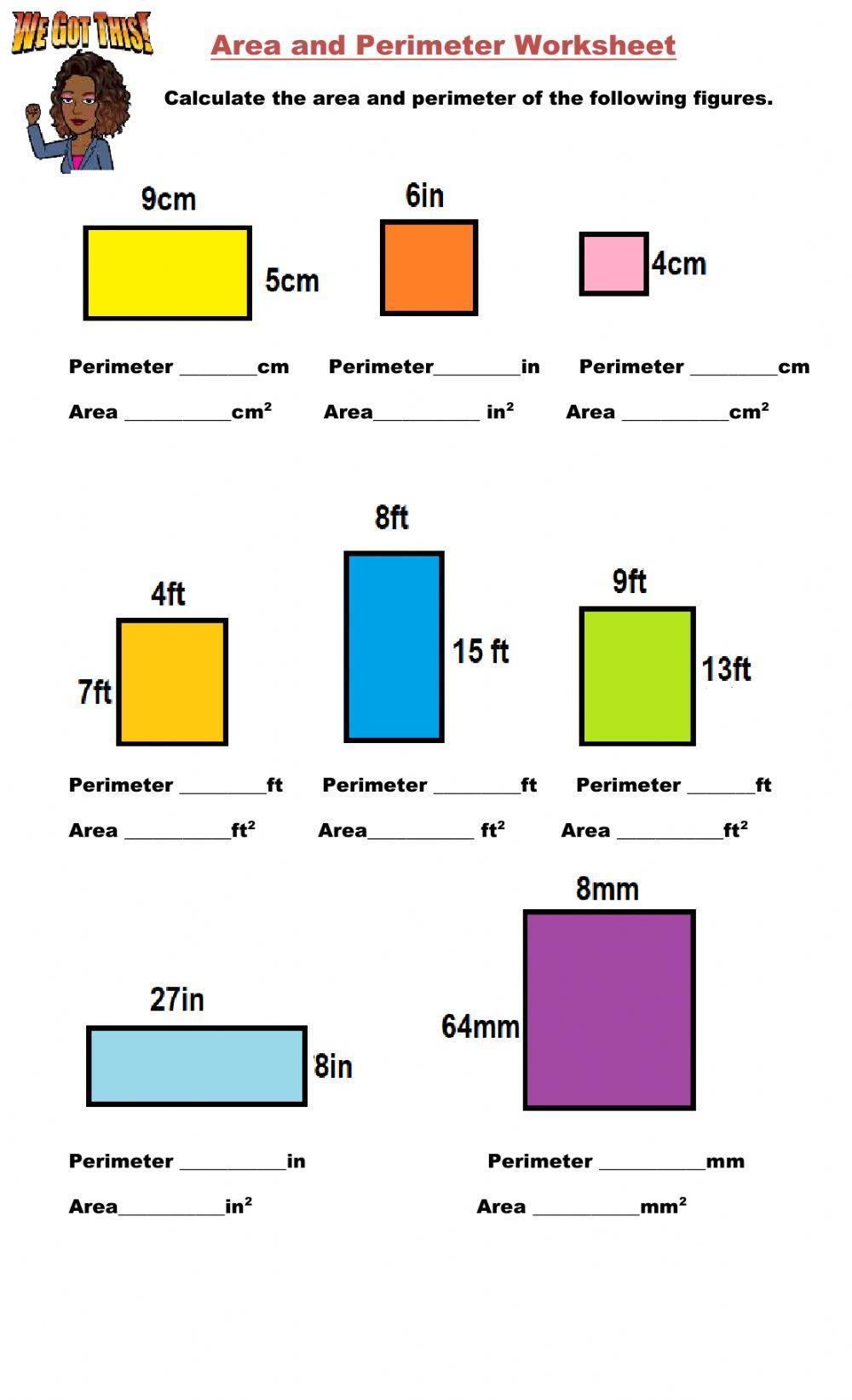
Worked Examples
In this section, we will go through several worked examples to help you understand how to calculate the perimeter and area of various shapes. Each example will provide a step-by-step solution to demonstrate the methods and formulas used.
Example 1: Perimeter of a Rectangle
Given a rectangle with a length of 8 cm and a width of 5 cm:
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Step 2: Substitute the given values into the formula: \( P = 2(8 + 5) \)
- Step 3: Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 2 \times 13 = 26 \, \text{cm} \)
Example 2: Area of a Rectangle
Given a rectangle with a length of 10 m and a width of 4 m:
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the area of a rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Step 2: Substitute the given values into the formula: \( A = 10 \times 4 \)
- Step 3: Calculate the area: \( A = 40 \, \text{m}^2 \)
Example 3: Perimeter of a Triangle
Given a triangle with sides of lengths 7 cm, 10 cm, and 5 cm:
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the perimeter of a triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Step 2: Substitute the given values into the formula: \( P = 7 + 10 + 5 \)
- Step 3: Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 22 \, \text{cm} \)
Example 4: Area of a Triangle
Given a triangle with a base of 6 cm and a height of 9 cm:
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the area of a triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Step 2: Substitute the given values into the formula: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 9 \)
- Step 3: Calculate the area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 54 = 27 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Example 5: Perimeter of a Circle
Given a circle with a radius of 3 m:
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the perimeter (circumference) of a circle: \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Step 2: Substitute the given value into the formula: \( C = 2\pi \times 3 \)
- Step 3: Calculate the circumference: \( C = 6\pi \approx 18.85 \, \text{m} \)
Example 6: Area of a Circle
Given a circle with a diameter of 10 cm:
- Step 1: Calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{\text{diameter}}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Step 2: Identify the formula for the area of a circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Step 3: Substitute the radius into the formula: \( A = \pi \times 5^2 \)
- Step 4: Calculate the area: \( A = 25\pi \approx 78.54 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Example 7: Perimeter of an Irregular Polygon
Given an irregular polygon with side lengths of 4 cm, 6 cm, 3 cm, and 5 cm:
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the perimeter of a polygon: \( P = \sum_{i=1}^{n} a_i \) where \( a_i \) are the side lengths
- Step 2: Add the lengths of all sides: \( P = 4 + 6 + 3 + 5 \)
- Step 3: Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 18 \, \text{cm} \)
Example 8: Area of a Parallelogram
Given a parallelogram with a base of 8 m and a height of 5 m:
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the area of a parallelogram: \( A = \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Step 2: Substitute the given values into the formula: \( A = 8 \times 5 \)
- Step 3: Calculate the area: \( A = 40 \, \text{m}^2 \)
Real-World Applications of Perimeter and Area
Understanding the concepts of perimeter and area is crucial not only in academic settings but also in real-world applications. Here are some practical examples of how these concepts are used in everyday life:
-
Interior Design:
Interior designers use perimeter and area calculations to determine how much paint is needed for walls, the amount of flooring required, and the placement of furniture. For example, calculating the area of a room helps in estimating the amount of carpet or tiles needed.
-
Architecture and Construction:
Architects and builders use these calculations to design and construct buildings. They determine the perimeter of land plots for fencing and the area of spaces for various construction needs, ensuring efficient use of materials and space.
-
Landscaping:
Landscapers calculate the perimeter to outline garden beds and the area to decide how much soil, mulch, or grass seed is needed. This helps in planning the layout of gardens, parks, and outdoor spaces.
-
Sports Fields:
Designing sports fields involves calculating the perimeter for fencing and the area for the playing surface. For instance, the area of a soccer field is used to ensure it meets official dimensions, while the perimeter helps in planning the boundary lines.
-
Real Estate:
Real estate professionals use these measurements to appraise properties, determining the value based on the area of the land and buildings. Accurate perimeter measurements are also important for legal descriptions of property boundaries.
-
Art and Design:
Artists and designers often create works that require precise calculations of area and perimeter. For example, creating a mosaic or designing a mural involves calculating the area to determine the number of tiles or the amount of paint required.
By understanding and applying the concepts of perimeter and area, individuals can solve practical problems, optimize resources, and make informed decisions in various fields.
Interactive Activities and Games
Engaging students with interactive activities and games can make learning about perimeter and area fun and effective. Here are some activities and games designed to enhance understanding of these concepts:
- Geoboard Activities: Use virtual geoboards to create shapes and calculate their perimeter and area. Students can manipulate bands to form various polygons and use tools to measure their dimensions. This hands-on activity helps in visualizing and understanding the properties of shapes. .
- Area and Perimeter Games: Websites like Turtle Diary offer a variety of games where students can practice calculating the area and perimeter of different shapes. These games often include timed challenges and levels that progressively increase in difficulty, making learning both competitive and enjoyable. .
- Interactive Worksheets: Utilize online worksheets that provide immediate feedback. Students can solve problems related to perimeter and area and get instant results, allowing them to learn from their mistakes and improve their skills continuously.
- Math Puzzles and Challenges: Incorporate puzzles that require calculating the perimeter and area to solve. These challenges enhance problem-solving skills and help students apply mathematical concepts in various contexts.
- Classroom Activities: Set up physical activities where students measure the perimeter and area of objects in the classroom or schoolyard. This real-world application reinforces their understanding and shows the practical use of these measurements.
By incorporating these interactive activities and games, students will not only learn about perimeter and area but also develop a love for mathematics through engaging and enjoyable experiences.
Additional Resources and Worksheets
Here are some excellent resources and worksheets to help you further explore and practice calculating the perimeter and area of various shapes. These resources are designed to cater to different learning levels and include printable worksheets, interactive activities, and detailed solution keys.
Downloadable Worksheets
- - These worksheets come with answer keys and are available for various grades, ensuring that students can study at their own pace and understand the concepts thoroughly.
- - Customizable worksheets that can be tailored to different variables, providing endless quality problems for classroom or home use.
- - A wide range of worksheets focusing on different shapes and concepts, including irregular shapes, polygons, and critical thinking problems.
- - Worksheets with problems creating rectangles with the same area but different perimeters, and vice versa, helping students understand the relationship between area and perimeter.
Interactive Activities and Online Resources
- - Interactive activities where students can practice calculating the area and perimeter of various shapes, with options to label all sides for more complex problems.
- - Online platform offering interactive perimeter and area problems, providing instant feedback and detailed explanations to help students improve their skills.
- - Comprehensive lessons and exercises on perimeter and area, including video tutorials and practice problems.
Grade-Specific Worksheets
Practice Problems and Solution Keys
- - A comprehensive collection of geometry worksheets, including perimeter and area practice problems with detailed solutions.
- - Printable worksheets that provide step-by-step solutions for perimeter and area problems, catering to different grade levels.

Answers and Solutions
Here are the detailed answers and solutions to the perimeter and area worksheet problems:
1. Finding the Perimeter and Area of Various Shapes
-
Square:
- Perimeter: \( P = 4a \)
- Area: \( A = a^2 \)
- Example: For a square with side length \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \):
- Perimeter: \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
- Area: \( A = 5^2 = 25 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
-
Rectangle:
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(L + B) \)
- Area: \( A = L \times B \)
- Example: For a rectangle with length \( L = 8 \, \text{cm} \) and breadth \( B = 4 \, \text{cm} \):
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(8 + 4) = 24 \, \text{cm} \)
- Area: \( A = 8 \times 4 = 32 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
-
Circle:
- Perimeter (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Example: For a circle with radius \( r = 7 \, \text{cm} \):
- Perimeter: \( C = 2 \pi \times 7 = 44 \, \text{cm} \)
- Area: \( A = \pi \times 7^2 = 154 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
2. Solved Problems
-
Problem 1: A wire is bent in the form of a circle with a radius of 28 cm. The wire is then re-bent to form a square. Find the side of the square.
Solution:
- Perimeter of the circle: \( P = 2\pi r = 2 \times 22/7 \times 28 = 176 \, \text{cm} \)
- Perimeter of the square: \( 4a = 176 \, \text{cm} \)
- Side of the square: \( a = 176 / 4 = 44 \, \text{cm} \)
-
Problem 2: The area of a right triangle is 28 cm2. One of its perpendicular sides exceeds the other by 10 cm. Find the length of the longest perpendicular side.
Solution:
- Let the length of the shorter perpendicular be \( x \) cm, then the length of the longer perpendicular is \( x + 10 \) cm.
- Area: \( \frac{1}{2} \times x \times (x + 10) = 28 \)
- Solve: \( x^2 + 10x - 56 = 0 \)
- Roots: \( x = 4 \) (since length cannot be negative)
- Longest perpendicular side: \( x + 10 = 14 \, \text{cm} \)
3. Detailed Solutions to Worksheet Problems
For more detailed solutions to specific worksheet problems, refer to the provided resources. These solutions include step-by-step instructions to help you understand the process of solving perimeter and area problems:
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 9 Perimeter and Area (NCERT Solutions Guru)
- Practice problems and detailed solutions available at Byju's and Cuemath
Tips and Tricks for Solving Perimeter and Area Problems
Mastering perimeter and area calculations can be much easier with a few helpful tips and tricks. Here are some effective strategies:
- Understand the Basics: Always start by reviewing the basic formulas for perimeter and area of common shapes (rectangles, squares, triangles, circles). For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is P = 2(l + w) and the area is A = l × w.
- Use Visual Aids: Drawing shapes and labeling the sides can help you visualize the problem better. For perimeter, trace the outline of the shape, and for area, shade or count the unit squares inside.
- Break Down Complex Shapes: For composite figures, break them down into simpler shapes, calculate the area or perimeter of each part, and then sum them up. For example, a complex figure can be divided into rectangles and triangles.
- Memorize Key Formulas: Make sure to memorize key formulas and understand when to use them. For example, the area of a triangle is A = 1/2 × base × height and the circumference of a circle is C = 2πr.
- Check Units: Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before performing calculations. Convert units if necessary to avoid errors in your final answer.
- Practice Estimation: Estimation can be a useful skill. For example, if you know the approximate size of a square foot, you can better gauge the area of larger spaces by comparing.
- Use Mnemonics: Mnemonics can help remember formulas. For instance, remember "Perimeter" with "PE RIM ETER" to think about the rim or edge, and "Area" with "Are-a" to think about the space inside.
- Double-Check Your Work: After solving a problem, always double-check your calculations and ensure all steps follow logically. Look out for common mistakes like missing units or incorrect formula application.
- Apply Real-World Problems: Practice with real-world problems to understand the application of perimeter and area. For example, calculate the fencing needed for a garden (perimeter) or the paint required for a wall (area).
- Interactive Tools: Utilize online tools and interactive games that reinforce these concepts through engaging activities.
By following these tips and consistently practicing, you can improve your ability to solve perimeter and area problems efficiently and accurately.
Conclusion and Summary
In this worksheet, we have explored the fundamental concepts of perimeter and area, key aspects of geometry that are essential for understanding and solving real-world problems involving various shapes and figures. Let's recap the main points covered:
- Perimeter: The perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in linear units such as meters, centimeters, or inches. Key formulas include:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Square: \( P = 4a \)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Circle (Circumference): \( C = 2\pi r \)
- Area: The area is the measure of the space inside a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in square units such as square meters, square centimeters, or square inches. Key formulas include:
- Rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Square: \( A = a^2 \)
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
- Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
Understanding and applying these formulas allows us to solve various practical problems, from calculating the amount of material needed to build a fence to determining the area of a room for flooring. As you practice more, you will become proficient in quickly identifying the appropriate formulas and applying them accurately to different shapes.
We hope this worksheet has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of perimeter and area, helping you build a strong foundation in geometry. Continue practicing with the provided problems and explore real-world applications to reinforce your skills. Remember, mastering these concepts will not only help you in math but also in many everyday tasks.
Thank you for working through this worksheet. Keep exploring and enjoying the fascinating world of mathematics!
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán Học với Mr. J
READ MORE:
Bài Hát về Diện Tích và Chu Vi cho Trẻ Em | Lớp 3 - 4