Topic how to find the perimeter of an isosceles triangle: Discover the step-by-step process for finding the perimeter of an isosceles triangle in our comprehensive guide. Whether you're a student or an enthusiast, this article will provide clear instructions, examples, and tips to master this essential geometric calculation with ease and confidence.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
- Introduction to Isosceles Triangles
- Understanding the Properties of Isosceles Triangles
- Basic Formula for Perimeter Calculation
- Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Perimeter
- Example Calculations
- Using Different Units of Measurement
- Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculations
- Additional Tips and Tricks
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
How to Find the Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
Finding the perimeter of an isosceles triangle involves summing the lengths of its sides. An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length and a third side that is different. Here is a step-by-step guide:
Step-by-Step Guide
-
Identify the lengths of the sides: Let the lengths of the two equal sides be \(a\) and the length of the base be \(b\).
-
Use the perimeter formula: The formula to find the perimeter \(P\) of an isosceles triangle is:
\[
P = 2a + b
\] -
Plug in the values: Substitute the lengths of the sides into the formula and calculate the perimeter.
For example, if the lengths of the equal sides are 5 units each and the base is 8 units:
\[
P = 2(5) + 8 = 10 + 8 = 18 \text{ units}
\]
Example Calculation
Consider an isosceles triangle with equal sides of length 7 cm each and a base of 10 cm. The perimeter can be calculated as follows:
\[
P = 2(7) + 10 = 14 + 10 = 24 \text{ cm}
\]
Additional Tips
- Make sure to use the same units for all side lengths.
- Double-check the lengths of the sides to ensure accurate calculations.
- If only the lengths of the equal sides are given and the height of the triangle, use the Pythagorean theorem to find the base first.
Using the Pythagorean Theorem
If you know the height \(h\) of the isosceles triangle and the lengths of the equal sides \(a\), you can find the base \(b\) as follows:
-
Apply the Pythagorean theorem: For one of the right triangles formed by the height:
\[
\left(\frac{b}{2}\right)^2 + h^2 = a^2
\] -
Solve for the base:
\[
b = 2 \sqrt{a^2 - h^2}
\]
Once you have the base, you can use the perimeter formula mentioned earlier.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Isosceles Triangles
An isosceles triangle is a type of triangle that has at least two sides of equal length. These two equal sides are called the legs, and the third side is known as the base. The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal. Understanding the properties of isosceles triangles is essential for calculating their perimeter and other geometric properties.
Key properties of isosceles triangles include:
- Two sides of equal length
- Two equal angles opposite the equal sides
- A unique base that is different in length from the legs
To better understand isosceles triangles, consider the following diagram:
Let the lengths of the two equal sides be denoted as \(a\), and the length of the base be denoted as \(b\). The angles opposite the equal sides are denoted as \(\alpha\), and the angle between the two equal sides is denoted as \(\beta\).
Here are the main components of an isosceles triangle:
- Legs: The two equal sides of the triangle, both labeled as \(a\).
- Base: The third side of the triangle, labeled as \(b\).
- Vertex Angle: The angle formed between the two equal sides, labeled as \(\beta\).
- Base Angles: The two angles opposite the equal sides, both labeled as \(\alpha\).
In an isosceles triangle, the perimeter \(P\) can be calculated using the formula:
\[
P = 2a + b
\]
Where \(a\) is the length of each of the equal sides and \(b\) is the length of the base. Understanding this formula and the properties of isosceles triangles will help you accurately determine their perimeter and solve related geometric problems.
Understanding the Properties of Isosceles Triangles
An isosceles triangle is a type of triangle that has two sides of equal length. These two equal sides are known as the legs, and the third side is referred to as the base. The unique properties of isosceles triangles make them a fundamental topic in geometry.
Here are some key properties of isosceles triangles:
- Equal Sides: Two sides of the triangle are of equal length.
- Equal Angles: The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal.
- Altitude: The altitude from the vertex opposite the base bisects the base and creates two right triangles.
Understanding these properties is essential for solving various geometric problems involving isosceles triangles. These properties also lead to specific formulas that can be used to calculate the perimeter and area of isosceles triangles.
For instance, the perimeter of an isosceles triangle can be found using the formula:
where \( a \) is the length of the two equal sides and \( b \) is the length of the base.
To calculate the area, the following formula can be used:
where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height of the triangle.
These properties and formulas make isosceles triangles an interesting and important topic in the study of geometry, providing a basis for understanding more complex shapes and theorems.
Basic Formula for Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides. For an isosceles triangle, the formula can be simplified as:
Perimeter (P) = 2a + b
Where:
- a is the length of the two equal sides.
- b is the length of the base.
To find the perimeter, follow these steps:
- Measure the lengths of the two equal sides (a).
- Measure the length of the base (b).
- Substitute these values into the formula P = 2a + b.
- Calculate the result to find the perimeter.
For example, if the lengths of the equal sides are 5 cm each and the base is 8 cm, the perimeter would be:
P = 2(5) + 8 = 10 + 8 = 18 cm
Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Perimeter
To find the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, follow these detailed steps:
-
Identify the sides: Determine the lengths of the two equal sides (let's call them \(a\)) and the base (let's call it \(b\)) of the isosceles triangle.
-
Apply the perimeter formula: The formula to calculate the perimeter \(P\) of an isosceles triangle is:
P = 2a + b -
Substitute the values: Plug in the known values of \(a\) and \(b\) into the formula. For example, if \(a = 5\) cm and \(b = 8\) cm, the calculation will be:
P = 2(5) + 8 = 10 + 8 = 18 \text{ cm} -
Sum the sides: Add the lengths of the two equal sides and the base to find the total perimeter.
Following these steps ensures that you accurately calculate the perimeter of any isosceles triangle.
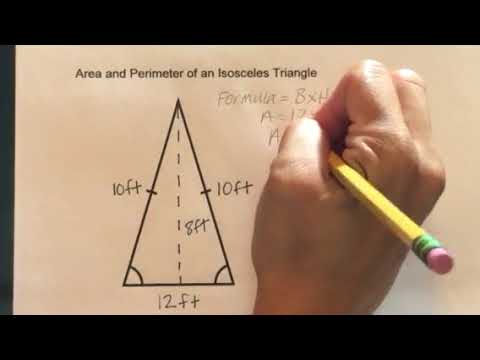
Example Calculations
To understand the calculation of the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, let's go through some examples step-by-step.
Example 1: Simple Perimeter Calculation
Given an isosceles triangle with the equal sides measuring 5 cm each and the base measuring 6 cm, we can calculate the perimeter using the formula:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
where \( a \) is the length of the equal sides and \( b \) is the base.
Substituting the given values:
\[ P = 2(5) + 6 = 10 + 6 = 16 \text{ cm} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 16 cm.
Example 2: Perimeter with Different Measurements
Consider another isosceles triangle where the equal sides are 8 cm each and the base is 10 cm. Using the same perimeter formula:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
Substituting the given values:
\[ P = 2(8) + 10 = 16 + 10 = 26 \text{ cm} \]
Thus, the perimeter of this triangle is 26 cm.
Example 3: Solving for Missing Side
In some cases, you may be given the perimeter and one side, and need to find the missing sides. For example, if the perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 24 cm and the base is 8 cm, you can find the length of the equal sides. Let's denote the equal sides as \( a \) and use the perimeter formula:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
Substituting the known values:
\[ 24 = 2a + 8 \]
Simplify and solve for \( a \):
\[ 2a = 24 - 8 \]
\[ 2a = 16 \]
\[ a = 8 \]
So, the equal sides are each 8 cm long.
Example 4: Using Pythagorean Theorem
If an isosceles triangle has a base of 6 cm and the equal sides are each 5 cm, you can also verify the perimeter calculation using the Pythagorean theorem. First, find the height \( h \) of the triangle:
\[ h = \sqrt{a^2 - \left(\frac{b}{2}\right)^2} \]
Substitute the values \( a = 5 \) and \( b = 6 \):
\[ h = \sqrt{5^2 - \left(\frac{6}{2}\right)^2} \]
\[ h = \sqrt{25 - 9} \]
\[ h = \sqrt{16} \]
\[ h = 4 \]
Now, calculate the perimeter again to confirm:
\[ P = 2(5) + 6 = 16 \text{ cm} \]
This confirms our previous calculation that the perimeter is indeed 16 cm.
Using Different Units of Measurement
When calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, it's important to ensure that all measurements are in the same unit. Here's a step-by-step guide to using different units of measurement:
- Convert All Sides to the Same Unit: Ensure that all sides (two equal sides and the base) are measured in the same unit (e.g., all in centimeters, meters, inches, etc.).
- Use a Consistent Formula: The basic formula for the perimeter of an isosceles triangle is
P = 2a + b , wherea is the length of the two equal sides andb is the base. - Convert the Perimeter If Necessary: Once you have the perimeter calculated, you can convert it to the desired unit of measurement if it differs from the unit used for side measurements.
For example, if the sides are given in centimeters and you need the perimeter in meters, divide the total perimeter by 100 (since 1 meter = 100 centimeters).
| Example: | Given sides of the triangle are 5 cm, 5 cm, and 8 cm. To find the perimeter in meters: |
| Step 1: | Calculate the perimeter in centimeters: |
| Step 2: | Convert the perimeter to meters: |
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate and convert the perimeter of an isosceles triangle using different units of measurement.
Advanced Perimeter Calculation Techniques
Calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle can be straightforward, but there are advanced techniques that can be applied to solve more complex problems or to improve accuracy. Below are some advanced methods:
- Using the Distance Formula: For an isosceles triangle with vertices at specific coordinates, you can use the distance formula to calculate the lengths of the sides. The distance formula is given by:
- Utilizing Trigonometric Functions: In cases where you have the angle and one side, you can use trigonometric identities to find the other sides. For example:
- Using the Law of Cosines:
- Using the Law of Cosines:
- Application of Heron's Formula: For an isosceles triangle with side lengths known, Heron's formula can be used to find the area first, and then the sides can be deduced:
These advanced techniques can enhance your understanding and ability to calculate the perimeter of isosceles triangles in various contexts, ensuring greater precision and versatility in problem-solving.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, there are several common mistakes to be aware of. Avoiding these errors can ensure accurate and efficient calculations:
- Incorrect Identification of Equal Sides: Always confirm which sides of the triangle are equal. In an isosceles triangle, two sides are of equal length, and the third side is different.
- Incorrect Formula Application: Ensure that you are using the correct formula: \( P = 2a + b \), where \(a\) is the length of the equal sides, and \(b\) is the base.
- Unit Mismatch: Make sure all side lengths are in the same unit before performing the calculation. Converting all measurements to a common unit avoids errors.
- Misinterpreting the Triangle Type: Ensure you are working with an isosceles triangle. Sometimes, it can be confused with other types like equilateral or scalene, which have different properties and formulas.
- Ignoring the Pythagorean Theorem: When given the height and base, remember to use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the equal sides if not directly provided.
- Incorrect Angle Assumptions: Do not assume incorrect angles. In a right isosceles triangle, use the correct properties and relationships, especially when dealing with angles and the Pythagorean Theorem.
- Calculation Errors: Double-check your arithmetic to avoid simple addition or multiplication errors that can affect the final perimeter calculation.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls, you can ensure more accurate and reliable calculations of the perimeter of an isosceles triangle.
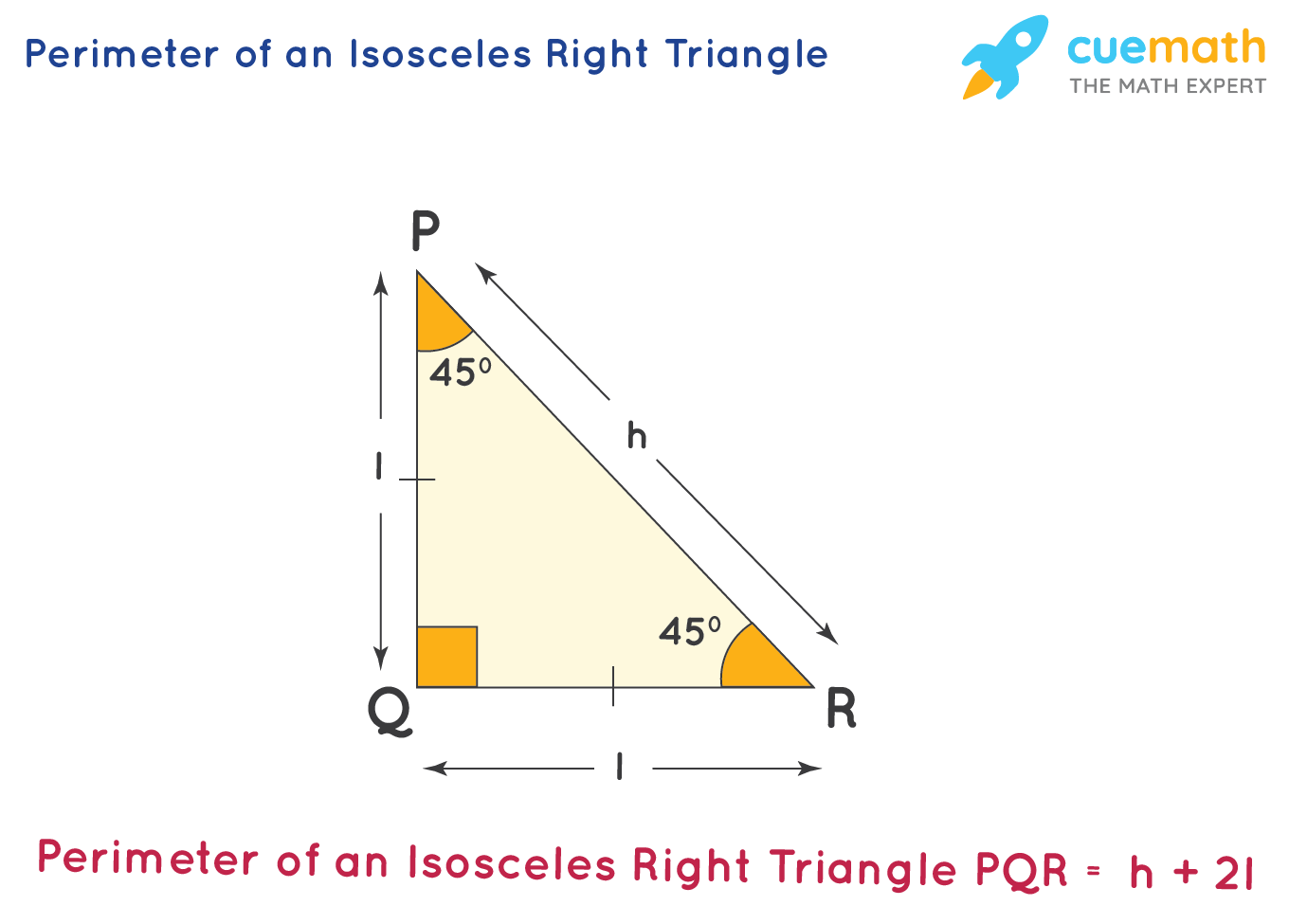
Practical Applications of Perimeter Calculations
The perimeter of an isosceles triangle has a variety of practical applications across different fields. Understanding these applications not only underscores the importance of perimeter calculations but also highlights the versatility of this geometric concept in real-world scenarios.
Architecture and Engineering
In architecture and engineering, the isosceles triangle is often used to design and construct stable structures. For instance, the symmetrical properties of isosceles triangles provide balance and support in the construction of roofs, trusses, and bridges. Calculating the perimeter is essential in determining the materials needed and ensuring the structural integrity of these designs.
Art and Design
Artists and designers frequently utilize isosceles triangles to create visually appealing compositions. The balanced proportions and symmetry of these triangles are employed in various art forms, including sculptures, paintings, and graphic designs. Knowing the perimeter helps in creating precise and proportionate works of art.
Surveying and Navigation
Surveyors and navigators use the principles of isosceles triangles in triangulation methods to measure distances and map out areas. The perimeter calculations are crucial in determining the exact distances between points, which is vital for accurate mapping and navigation, including GPS technology.
Physics and Engineering Applications
In physics and engineering, isosceles triangles are used to analyze forces and vectors. They help in resolving forces into their components and calculating angles in mechanical systems. For example, in optics, the perimeter can be important when designing lenses and prisms that rely on triangular shapes.
Educational and Problem-Solving Tools
Isosceles triangles are a fundamental part of mathematics education. They serve as examples to teach various geometric principles, such as congruence and similarity. Students often solve problems involving the perimeter of isosceles triangles to develop their problem-solving skills and understanding of geometric concepts.
Nature and Science
In nature, isosceles triangles can be observed in the structures of crystals and biological forms. Scientists study these shapes to understand various natural phenomena. For instance, the perimeter calculations can help in determining the growth patterns of certain crystals or the structural properties of biological tissues.
Understanding the practical applications of perimeter calculations in isosceles triangles enriches our appreciation of geometry and its relevance to everyday life. Whether in constructing buildings, creating art, or exploring scientific phenomena, the principles of isosceles triangles continue to play a crucial role in diverse fields.
Additional Tips and Tricks
When calculating the perimeter of an isosceles triangle, consider the following tips and tricks to ensure accuracy and efficiency:
- Double-check side lengths: Ensure that you correctly identify the lengths of the two equal sides and the base. Misidentifying these can lead to incorrect calculations.
- Use consistent units: Make sure all side lengths are in the same unit of measurement before performing any calculations.
- Verify given information: If the problem provides angles or other properties, use them to confirm the sides' lengths.
- Utilize geometric properties: Remember that in an isosceles triangle, the two equal sides are opposite the two equal angles. This can help in verifying that the triangle is indeed isosceles.
- Apply the Pythagorean theorem when necessary: For isosceles right triangles, use the relationship between the hypotenuse and the legs to find missing side lengths.
- Check for special cases: If the isosceles triangle is also a right triangle, use the formula \( P = h + 2 \times \frac{h}{\sqrt{2}} \) to quickly find the perimeter.
- Practice with different examples: Work on various problems involving isosceles triangles to become familiar with different scenarios and formulas.
By following these tips and practicing regularly, you can improve your ability to accurately and efficiently calculate the perimeter of isosceles triangles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the perimeter of an isosceles triangle is essential for solving various geometric problems. The unique properties of isosceles triangles, such as having two equal sides and two equal angles, make them a fundamental concept in geometry. Calculating the perimeter involves using the simple formula:
where \( b \) is the base and \( a \) is the length of the equal sides. This knowledge can be applied in numerous practical scenarios, from designing architectural structures to solving complex mathematical problems.
By mastering the techniques for perimeter calculation, you not only enhance your mathematical skills but also gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and symmetry of geometric shapes. We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical tools to confidently tackle any problems involving the perimeter of isosceles triangles.
Keep practicing, exploring, and applying these concepts to discover the wide array of applications that geometry offers. With a solid understanding of isosceles triangles, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the fascinating world of mathematics with confidence and precision.
Làm thế nào để tìm diện tích và chu vi của một tam giác cân