Topic what's the perimeter of a triangle: Discover the fascinating world of geometry as we explore "What"s the Perimeter of a Triangle?" – a comprehensive guide to understanding and calculating the boundaries of these intriguing shapes.
Table of Content
- Basic Concept and Formula for Triangle Perimeter
- Perimeter Calculation for Different Types of Triangles
- Advanced Perimeter Calculations
- Practical Examples and Problem Solving
- YOUTUBE: How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
- FAQs and Common Misconceptions
- Interactive Learning Tools and Resources
- Further Reading and External Resources
Basic Concept and Formula for Triangle Perimeter
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around its edges, a fundamental concept in geometry. To calculate this, we simply add the lengths of the triangle\"s three sides. The general formula is represented as:
Perimeter (P) = a + b + c
Where:
- a, b, c are the lengths of the triangle\"s sides.
This formula applies to any triangle, regardless of its type. Let\"s break down the perimeter calculations for various types of triangles:
- Equilateral Triangle: All sides are equal, so the formula simplifies to P = 3 × a.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal. If the equal sides are \"a\" and the base is \"b\", the formula is P = 2 × a + b.
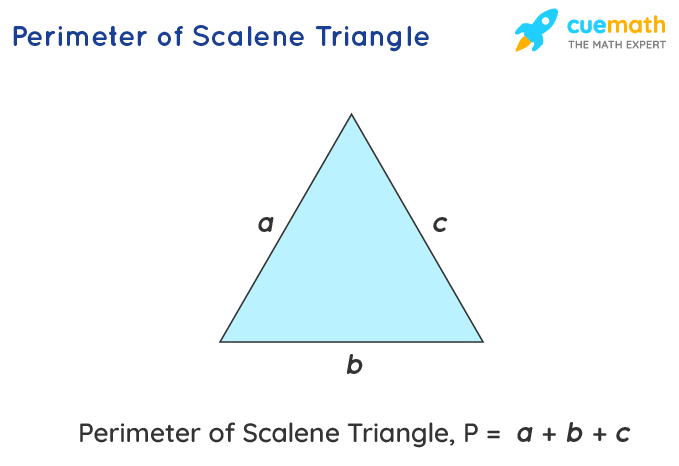
- Scalene Triangle: All sides are different. We use the standard formula P = a + b + c.
- Right Triangle: If the sides are known, apply the standard formula. If not, use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side, then calculate the perimeter.
Understanding these formulas allows for accurate measurement and application in various geometrical problems and real-world scenarios.

READ MORE:
Perimeter Calculation for Different Types of Triangles
The perimeter of a triangle varies depending on its type. Here\"s a detailed look at how to calculate the perimeter for different types of triangles:
- Equilateral Triangle: In an equilateral triangle, all sides are equal. If each side is of length \"a\", then the perimeter is simply P = 3 × a.
- Isosceles Triangle: This type has two equal sides. If the equal sides are of length \"a\" and the base is \"b\", the perimeter is calculated as P = 2 × a + b.
- Scalene Triangle: A scalene triangle has all sides of different lengths. If the sides are \"a\", \"b\", and \"c\", the perimeter is P = a + b + c.
- Right Triangle: For a right triangle, if the lengths of the two legs are \"a\" and \"b\", and the hypotenuse is \"c\", then the perimeter is P = a + b + c. If one side length is unknown, it can be found using the Pythagorean theorem.
By understanding these specific formulas, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any triangle, enhancing your problem-solving skills in geometry.

Advanced Perimeter Calculations
For more complex scenarios in triangle geometry, advanced methods are used to calculate the perimeter. These include situations where not all side lengths are known, or the triangle is defined by angles and a side. Here are some advanced methods:
- Using the Law of Sines: This is particularly useful in an ASA (Angle-Side-Angle) scenario. If two angles and the side between them are known, use the Law of Sines to find the missing sides and then add them to find the perimeter.
- Using the Law of Cosines: Helpful in a SAS (Side-Angle-Side) scenario. Calculate the length of the unknown side using the Law of Cosines and then sum up all sides for the perimeter.
- Trigonometric Calculations: When dealing with right triangles and certain known angles, trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) can be used to find missing side lengths before calculating the perimeter.
These advanced calculations require a good understanding of trigonometry and are essential for solving complex problems in higher-level geometry.
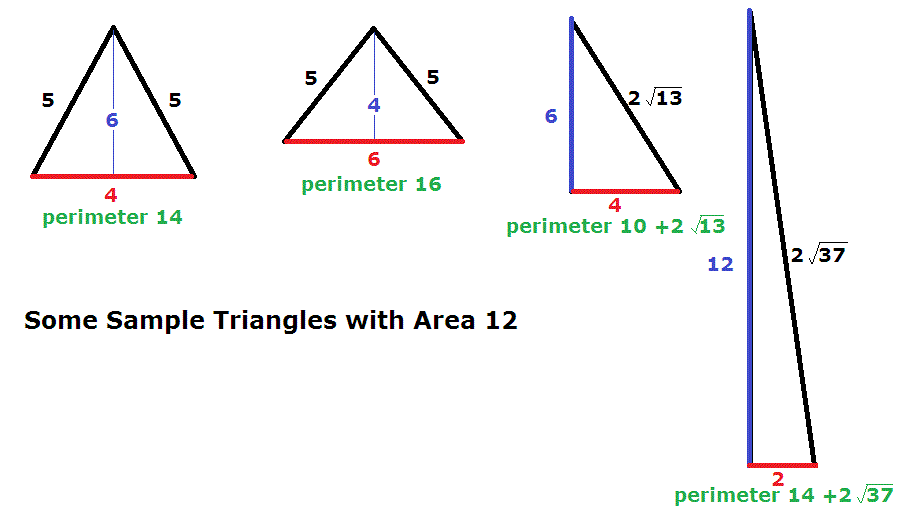
Practical Examples and Problem Solving
Applying perimeter calculations to real-world scenarios enhances understanding. Here are some practical examples and problems for a comprehensive grasp of calculating the perimeter of triangles:
- Example 1 - Equilateral Triangle: Consider a flower bed shaped like an equilateral triangle with each side measuring 4 meters. Calculate its perimeter. Solution: Since all sides are equal, the perimeter P = 3 × 4 = 12 meters.
- Example 2 - Isosceles Triangle: A triangular park has two sides of 150 meters each and a base of 200 meters. Find the perimeter. Solution: P = 2 × 150 + 200 = 500 meters.
- Example 3 - Scalene Triangle: In a triangular field, the sides measure 70m, 80m, and 90m. What is the perimeter? Solution: Simply add the sides, P = 70 + 80 + 90 = 240 meters.
- Example 4 - Right Triangle: A right-angled triangle has legs of 3m and 4m. Calculate its perimeter. Solution: First, find the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem (5m). Then, P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 meters.
These examples cover various types of triangles, providing a practical approach to mastering perimeter calculations.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Discover the fascinating world of perimeter measurements with our educational video! Learn how to calculate the total distance around a shape and unlock the secrets of perimeter in just a few minutes.\"
FAQs and Common Misconceptions
In learning about the perimeter of triangles, certain questions frequently arise, along with some common misconceptions. Addressing these can clarify and deepen your understanding:
- FAQ 1: Can the perimeter of a triangle be the same as its area? While numerically possible, it\"s important to understand that perimeter and area are different concepts. Perimeter measures the boundary length, while area measures the surface covered.
- FAQ 2: Is the perimeter of a right triangle always an integer? Not necessarily. The perimeter depends on the side lengths, which can be non-integer values, especially when using the Pythagorean theorem.
- FAQ 3: Can two triangles with the same perimeter have different shapes? Yes, triangles with the same perimeter can vary in shape and size, as long as the sum of their sides remains constant.
- Misconception 1: The longest side of a triangle greatly influences its perimeter. While the longest side contributes to the total length, the perimeter is the sum of all sides. Shorter sides collectively can influence the perimeter significantly.
- Misconception 2: Calculating the perimeter of a triangle always requires knowing all side lengths. Not always. For isosceles and equilateral triangles, knowing the lengths of certain sides is sufficient due to their symmetric properties.
- Misconception 3: The perimeter of a triangle is twice its area. This is not a universal truth. The relationship between the area and perimeter of a triangle varies depending on the triangle\"s dimensions.
Understanding these FAQs and misconceptions helps in avoiding common errors and deepens the conceptual grasp of triangle geometry.

_HOOK_
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
\"Are you curious about triangles and their properties? Dive into our engaging video where we explore the different types of triangles, their angles, and sides, and unravel the mysteries of these versatile shapes.\"
Interactive Learning Tools and Resources
To enhance the learning experience for the concept of triangle perimeters, several interactive tools and resources are available. These tools make learning engaging and cater to various learning styles:
- Online Triangle Perimeter Calculators: These calculators allow you to input the sides or angles of a triangle to automatically calculate its perimeter. They are ideal for quick checks and understanding the impact of different dimensions.
- Geometry Learning Apps: Many mobile apps offer interactive lessons and quizzes on triangle perimeters and other geometry topics, suitable for learners at different levels.
- Interactive Geometry Software: Programs like GeoGebra provide a dynamic way to visualize and manipulate triangles, helping to understand the relationship between side lengths and perimeters.
- Educational Videos: Numerous educational platforms host video tutorials that explain triangle perimeters visually, often with real-life examples.
- Geometry Worksheets and Printables: For hands-on practice, printable worksheets with problems and puzzles on triangle perimeters can be highly beneficial.
- Online Geometry Forums: These forums are places to ask questions, share knowledge, and learn from others\" experiences and explanations about various geometry problems, including triangle perimeters.
Using these interactive tools and resources can make learning about triangle perimeters both fun and effective.

READ MORE:
Further Reading and External Resources
For those interested in delving deeper into the topic of triangle perimeters and related concepts in geometry, numerous resources are available. Here are some recommendations for further reading and external resources:
- Geometry Textbooks: Comprehensive textbooks offer detailed explanations, diagrams, and practice problems on triangle perimeters and other geometric concepts.
- Online Educational Websites: Websites like Khan Academy, Coursera, and edX provide courses and tutorials on geometry that cover triangle perimeters extensively.
- Scientific Journals: For advanced learners, journals in mathematics and education often publish research papers and articles on geometric theories and teaching methodologies.
- Educational Blogs and Articles: Numerous blogs and online articles provide insights, tips, and interesting facts about geometry, making learning more engaging.
- Interactive Geometry Tools: Explore tools like Desmos or GeoGebra for an interactive and visual approach to understanding triangle perimeters and other geometric properties.
- YouTube Channels: Channels dedicated to mathematics education often have playlists or videos specifically addressing geometry and triangle perimeters.
- Mathematics Forums and Online Communities: Engaging in discussions with fellow learners and experts can provide valuable insights and answers to specific questions.
These resources are excellent for expanding your knowledge and understanding of geometry, providing both foundational learning and more advanced exploration.
In conclusion, understanding the perimeter of a triangle is a key step in mastering geometry, opening doors to fascinating mathematical explorations and practical applications in everyday life.