Topic calculate area of irregular shape using perimeter: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to calculate the area of an irregular shape using its perimeter. In this article, we will explore various methods and provide detailed examples to help you accurately determine the area of any irregular shape. Let's dive in and make these calculations simple and effective!
Table of Content
- Calculating the Area of Irregular Shapes Using Perimeter
- Introduction
- Understanding Irregular Shapes
- Methods to Calculate Area
- Detailed Step-by-Step Examples
- Calculating Perimeter
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp, ví dụ hình chữ L, trong môn hình học với thầy J. Video phù hợp cho học sinh và người yêu toán học.
Calculating the Area of Irregular Shapes Using Perimeter
Calculating the area of irregular shapes can be challenging due to their varied sides and angles. Here, we provide a comprehensive guide to different methods used to calculate the area of irregular shapes using perimeter and other techniques.
Methods to Calculate Area of Irregular Shapes
1. Using Unit Squares
This method involves overlaying a grid of unit squares on the shape and counting the number of squares that fall within the shape. This technique works well for shapes with curved boundaries or complex outlines.
For example:
- Count each square as "1" if more than half of it lies within the shape.
- Add up the total number of unit squares to get the area.
2. Dividing the Shape into Regular Polygons
Irregular shapes can be broken down into smaller, regular shapes such as triangles, rectangles, and squares. The area of these individual shapes can then be calculated and summed up to find the total area.
For example, consider an irregular shape divided into triangles and rectangles:
Area = Area1 + Area2 + Area3
Each area can be calculated using standard formulas for triangles and rectangles.
3. Using Graph Paper
Graph paper can help in visually breaking down an irregular shape into smaller, manageable sections. By counting the full and partial squares that the shape covers, you can estimate the total area.
4. Using Coordinate Geometry
For more precision, especially with polygons, you can use coordinate geometry. This involves plotting the vertices of the shape on a coordinate plane and using the coordinates to calculate the area.
For an irregular polygon with vertices \((x_1, y_1), (x_2, y_2), \ldots, (x_n, y_n)\), the area can be calculated using the formula:
\[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \left| \sum_{i=1}^{n-1} (x_i y_{i+1} + x_n y_1) - (y_i x_{i+1} + y_n x_1) \right| \]
Conclusion
These methods provide different approaches to calculate the area of irregular shapes, depending on the tools and precision required. Whether using simple unit squares, decomposing into polygons, employing graph paper, or using coordinate geometry, you can find an accurate estimate of the area of irregular shapes.

Introduction
Calculating the area of irregular shapes using the perimeter can be a challenging yet fascinating task. Unlike regular shapes, irregular shapes do not have straightforward formulas for area calculation. However, by understanding the relationship between perimeter and area, and utilizing various methods, you can accurately determine the area of any irregular shape.
In this guide, we will cover:
- The importance of calculating the area of irregular shapes
- Different methods to approach the calculation
- Step-by-step examples to illustrate the process
By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to use the perimeter to calculate the area of irregular shapes effectively. Let's begin our journey into the world of geometry and uncover the secrets to mastering these calculations!
Understanding Irregular Shapes
Irregular shapes are geometric figures that do not conform to standard geometric rules for regular shapes like squares, rectangles, or circles. These shapes lack symmetry and have sides and angles of varying lengths and degrees. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for accurately calculating their area.
Key features of irregular shapes:
- Irregular shapes can have curved or straight sides.
- The sides and angles are not necessarily equal or uniform.
- They can be complex and varied in form.
To calculate the area of an irregular shape, we often employ methods that simplify the shape into more manageable components:
- Dividing into Regular Shapes: Break down the irregular shape into smaller regular shapes (e.g., triangles, rectangles) whose area can be calculated easily.
- Using Graph Paper: Draw the shape on graph paper and count the unit squares within the shape to estimate the area.
- Unit Square Method: Approximate the area by overlaying a grid of unit squares on the shape and counting the squares covered by the shape.
By recognizing the properties of irregular shapes and using these methods, we can simplify the process of area calculation and achieve accurate results.
Methods to Calculate Area
Calculating the area of irregular shapes can be challenging, but several methods can simplify the process. Here are some effective techniques:
Dividing into Regular Shapes
This method involves breaking down the irregular shape into a combination of simpler, regular shapes such as rectangles, triangles, and circles. The steps are as follows:
- Identify the irregular shape and sketch it on paper.
- Divide the shape into smaller, recognizable shapes.
- Calculate the area of each smaller shape using appropriate formulas:
- Rectangle: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Triangle: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Circle: \( \text{Area} = \pi \times r^2 \) (for full circles or semicircles)
- Sum up the areas of all the smaller shapes to get the total area of the irregular shape.
Using Graph Paper
Graph paper can be an effective tool for estimating the area of an irregular shape. Follow these steps:
- Place the irregular shape on graph paper.
- Count the number of full squares within the shape.
- For partial squares, estimate the area covered by the shape. Count a square if more than half of it is covered, otherwise ignore it.
- Sum the number of full and estimated partial squares to determine the total area.
Unit Square Method
This method is similar to using graph paper but is more precise for complex shapes. The steps are:
- Overlay the shape with a grid of unit squares (squares with an area of one square unit each).
- Count the number of unit squares that fall completely within the shape.
- Estimate the area of partially covered squares. Sum the fully covered squares and add the estimated area of partial squares.
- The total gives an approximation of the area of the irregular shape.
By employing these methods, you can accurately calculate the area of irregular shapes, aiding in various practical applications such as construction, land measurement, and design.
Detailed Step-by-Step Examples
Example 1: Simple Irregular Shape
Let's calculate the area of a simple irregular shape by dividing it into smaller, regular shapes.
- Define the Shape: Consider an irregular shape that can be divided into two rectangles.
- Divide into Regular Shapes:
- Rectangle 1: 3 cm by 4 cm
- Rectangle 2: 2 cm by 3 cm
- Apply Appropriate Formulas:
- Area of Rectangle 1: \( A_1 = 3 \times 4 = 12 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Area of Rectangle 2: \( A_2 = 2 \times 3 = 6 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Sum the Areas:
Total Area: \( A = A_1 + A_2 = 12 + 6 = 18 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Example 2: Complex Irregular Shape
Now let's tackle a more complex shape by dividing it into a combination of triangles and rectangles.
- Define the Shape: Consider an irregular shape that can be divided into one triangle and two rectangles.
- Divide into Regular Shapes:
- Triangle: Base = 4 cm, Height = 3 cm
- Rectangle 1: 2 cm by 5 cm
- Rectangle 2: 3 cm by 4 cm
- Apply Appropriate Formulas:
- Area of Triangle: \( A_1 = \frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 3 = 6 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Area of Rectangle 1: \( A_2 = 2 \times 5 = 10 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Area of Rectangle 2: \( A_3 = 3 \times 4 = 12 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Sum the Areas:
Total Area: \( A = A_1 + A_2 + A_3 = 6 + 10 + 12 = 28 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Example 3: Using Unit Squares
For shapes with curves or very irregular boundaries, use the unit square method.
- Overlay a grid of unit squares (e.g., 1 cm²) on the shape.
- Count fully covered squares and estimate partially covered squares.
- Fully covered squares: 15
- Partially covered squares: Estimate to 8
- Calculate the Area:
Total Area: \( 15 + 0.5 \times 8 = 15 + 4 = 19 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Example 4: Using the Shoelace Formula
For a more mathematical approach, use the shoelace formula to find the area of a polygon by its vertices.
- List the coordinates of the vertices: (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ..., (xn, yn)
- Apply the Shoelace Formula:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \left| \sum_{i=1}^{n-1} (x_i y_{i+1} - y_i x_{i+1}) + (x_n y_1 - y_n x_1) \right|
\] - Calculate for a given shape with vertices (1, 2), (3, 5), (5, 4), (4, 1):
- Sum 1: \(1 \cdot 5 + 3 \cdot 4 + 5 \cdot 1 + 4 \cdot 2 = 5 + 12 + 5 + 8 = 30\)
- Sum 2: \(2 \cdot 3 + 5 \cdot 5 + 4 \cdot 4 + 1 \cdot 1 = 6 + 25 + 16 + 1 = 48\)
- Area: \(\frac{1}{2} |30 - 48| = \frac{1}{2} \times 18 = 9 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
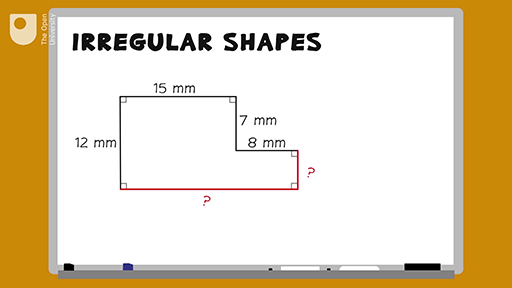
Calculating Perimeter
The perimeter of an irregular shape is the total distance around its outer edges. To calculate the perimeter, you need to measure the length of each side and then sum these lengths.
Definition and Importance
Perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of a shape. For irregular shapes, this involves adding up the lengths of all the sides, which may vary in length. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is crucial for various applications such as determining the fencing required for a plot of land or the frame length for a piece of art.
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the perimeter of an irregular shape, follow these steps:
- Identify and Measure Each Side: Carefully measure the length of each side of the shape.
- Write Down Each Measurement: Record each side length to avoid confusion.
- Add the Lengths Together: Sum all the recorded lengths to get the total perimeter.
Here’s an example calculation for an irregular triangle:
- Side 1: 5 mm
- Side 2: 8 mm
- Side 3: 10 mm
The perimeter \( P \) is calculated as:
\[ P = 5 \, \text{mm} + 8 \, \text{mm} + 10 \, \text{mm} = 23 \, \text{mm} \]
For an irregular pentagon with sides 13 m, 13 m, 7 m, 8 m, and 9 m, the calculation would be:
- Side 1: 13 m
- Side 2: 13 m
- Side 3: 7 m
- Side 4: 8 m
- Side 5: 9 m
The perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 13 \, \text{m} + 13 \, \text{m} + 7 \, \text{m} + 8 \, \text{m} + 9 \, \text{m} = 50 \, \text{m} \]
These steps can be applied to any irregular shape to find its perimeter accurately.
Remember to cross off each side as you add it to ensure no side is omitted or counted twice, especially for shapes with many sides.
Common Mistakes and Tips
Calculating the area of irregular shapes can be challenging and prone to errors. Here are some common mistakes to avoid and tips to ensure accurate measurements:
Common Calculation Errors
- Incorrect Shape Breakdown: Failing to accurately divide the irregular shape into smaller, familiar shapes can lead to incorrect area calculations.
- Overlapping Areas: Ensure that the smaller shapes do not overlap, as this can result in double-counting certain areas.
- Measurement Inaccuracies: Inaccurate measurements of the sides or angles of the shapes can lead to significant errors in the final area calculation.
- Wrong Formulas: Using incorrect formulas for the individual shapes will lead to wrong results. Always double-check the formulas you are using.
- Omitting Units: Forgetting to include or convert units can cause mistakes, especially when combining areas of different shapes.
Tips for Accurate Measurements
- Use Clear Definitions: Clearly define the boundaries of the irregular shape before starting the calculation process.
- Break Down Complex Shapes: Divide the irregular shape into simpler geometric shapes such as triangles, rectangles, or circles. This simplifies the calculation process.
- Double-Check Measurements: Always measure sides and angles accurately. Use tools like rulers, protractors, and graph paper for precision.
- Apply Correct Formulas: Use the correct area formulas for each geometric shape. For example:
- Area of a rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Area of a triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
- Area of a circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Check for Overlaps: Ensure that the shapes do not overlap. If they do, adjust the calculations to avoid double-counting any areas.
- Use Technology: Utilize software tools or online calculators for complex shapes. They can help verify manual calculations and reduce errors.
- Practice and Review: Regular practice with different shapes and reviewing your calculations can help you avoid common pitfalls and improve accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the area of an irregular shape?
The area of an irregular shape is the amount of space it covers. Unlike regular shapes, irregular shapes do not have a standard formula for calculating their area. Instead, they are often broken down into smaller, regular shapes for calculation.
-
How do you find the area of an irregular shape?
To find the area of an irregular shape, you can break it down into smaller, regular shapes such as rectangles, triangles, or circles. Calculate the area of these smaller shapes and sum them up. More advanced techniques include the method of dissection or the Monte Carlo method.
-
What is the difference between a regular shape and an irregular shape?
A regular shape has a standard formula for calculating its area, such as a square or a circle. An irregular shape does not have a standard formula and often needs to be decomposed into smaller, regular shapes to determine its area.
-
What is dissection in math?
Dissection in math is a method of finding the area of a shape by dividing it into smaller, manageable shapes. This method is especially useful for irregular shapes, which can be divided into regular shapes like triangles, rectangles, and squares to calculate the area.
-
What is the Monte Carlo method in math?
The Monte Carlo method is a statistical technique that uses random sampling to estimate mathematical values, such as the area of a shape. This method is useful for complex or irregular shapes where traditional methods are difficult to apply.
-
Why is calculating the area of irregular shapes important?
Calculating the area of irregular shapes is important in various real-life applications, such as determining the amount of material needed for a project or the space available in a given area. It helps in effective space management and resource allocation.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp, ví dụ hình chữ L, trong môn hình học với thầy J. Video phù hợp cho học sinh và người yêu toán học.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán với Thầy J
Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi và diện tích của các hình không đều, giúp bạn nắm vững phương pháp và áp dụng vào thực tế.
Chu vi và Diện tích của Các Hình Không Đều