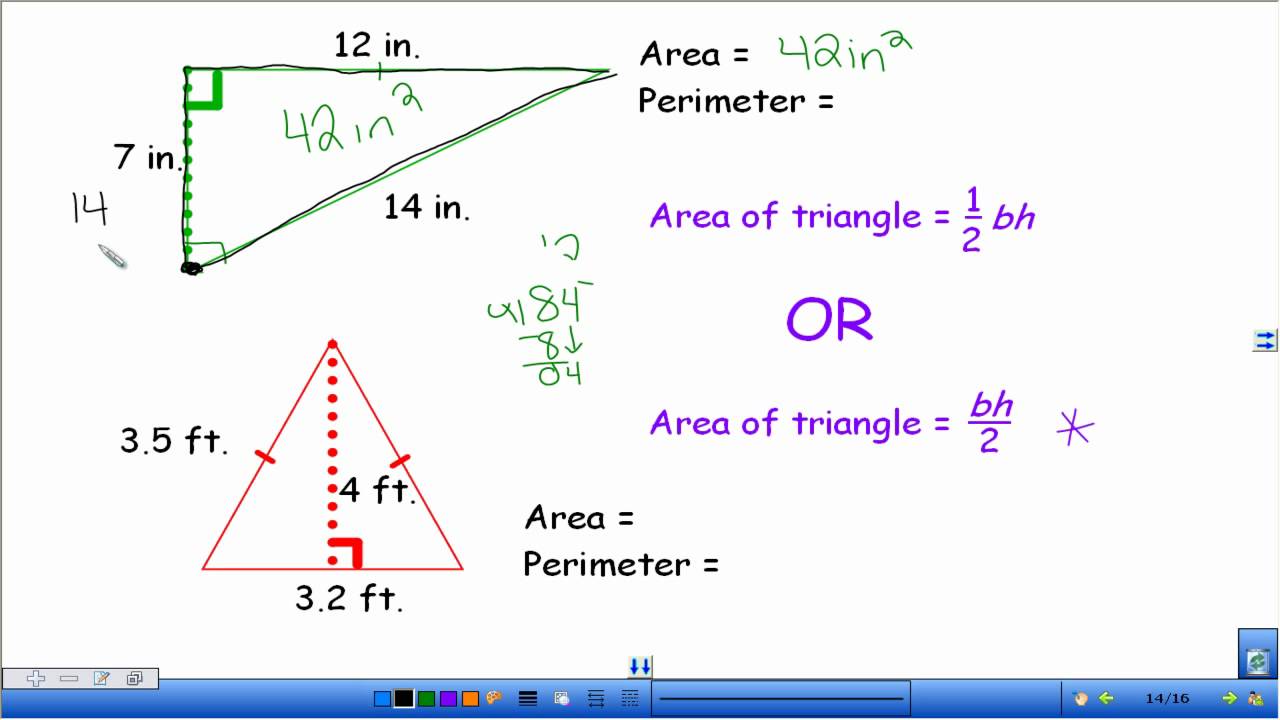
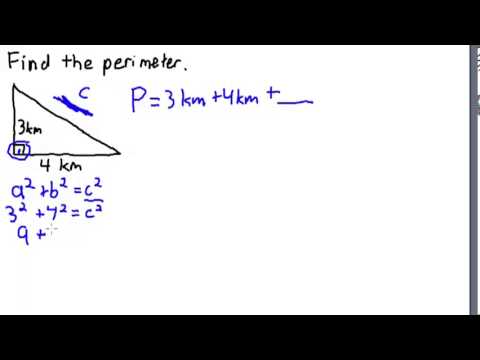
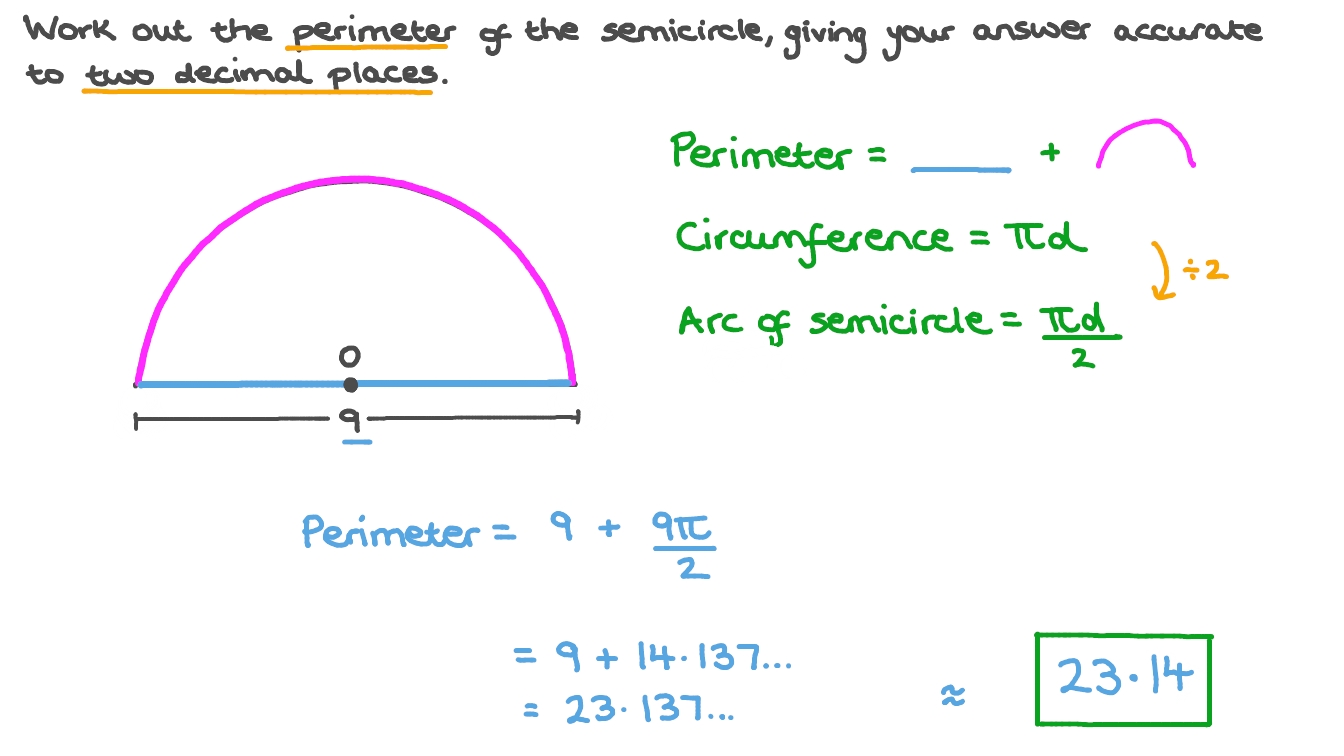
Topic area and perimeter word problems 4th grade: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on area and perimeter word problems for 4th grade! This article provides engaging exercises and practical problems to help young learners master these essential math skills. Dive in to explore formulas, definitions, and real-life applications designed to make learning both fun and effective.
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter Word Problems for 4th Grade
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Understanding Area and Perimeter
- Formulas and Definitions
- Basic Word Problems
- Rectangle Area and Perimeter Word Problems
- Triangle Area and Perimeter Word Problems
- Quadrilateral Area and Perimeter Word Problems
- Circle Area and Circumference Word Problems
- Real-Life Area and Perimeter Word Problems
- Polygon Area and Perimeter Word Problems
- Advanced Word Problems
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Practice Worksheets and Exercises
- Answer Keys and Explanations
- Interactive Online Resources
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE:
Area and Perimeter Word Problems for 4th Grade
Understanding area and perimeter is crucial for 4th-grade students as it lays the foundation for more advanced geometry concepts. Here are some engaging word problems to help students practice their skills.
Word Problem 1: Rectangular Garden
Sarah has a rectangular garden that is 5 meters long and 3 meters wide. What is the perimeter of the garden? What is the area of the garden?
Solution:
The perimeter \(P\) of a rectangle is given by:
\[
P = 2 \times (length + width) = 2 \times (5 \, \text{m} + 3 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 8 \, \text{m} = 16 \, \text{m}
\]
The area \(A\) of a rectangle is given by:
\[
A = length \times width = 5 \, \text{m} \times 3 \, \text{m} = 15 \, \text{m}^2
\]
Word Problem 2: Classroom Floor
Mr. Johnson's classroom floor is in the shape of a rectangle. It is 8 meters long and 6 meters wide. What is the perimeter of the classroom floor? What is the area of the classroom floor?
Solution:
The perimeter \(P\) of the classroom floor is:
\[
P = 2 \times (length + width) = 2 \times (8 \, \text{m} + 6 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 14 \, \text{m} = 28 \, \text{m}
\]
The area \(A\) of the classroom floor is:
\[
A = length \times width = 8 \, \text{m} \times 6 \, \text{m} = 48 \, \text{m}^2
\]
Word Problem 3: Swimming Pool
The community center has a swimming pool that is 10 meters long and 4 meters wide. Calculate the perimeter and area of the swimming pool.
Solution:
The perimeter \(P\) of the swimming pool is:
\[
P = 2 \times (length + width) = 2 \times (10 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 14 \, \text{m} = 28 \, \text{m}
\]
The area \(A\) of the swimming pool is:
\[
A = length \times width = 10 \, \text{m} \times 4 \, \text{m} = 40 \, \text{m}^2
\]
Practice Problems
-
A rectangular park is 12 meters long and 7 meters wide. What is the perimeter and area of the park?
-
A rectangular rug is 9 meters long and 5 meters wide. Find its perimeter and area.
-
A book cover is 11 centimeters long and 6 centimeters wide. Calculate the perimeter and area of the book cover.
Table of Formulas
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | \(P = 2 \times (length + width)\) | \(A = length \times width\) |
| Square | \(P = 4 \times side\) | \(A = side^2\) |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is essential for solving various word problems in geometry. These concepts help us measure and describe the size and boundaries of different shapes, which is crucial in many real-life situations.
Perimeter: The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its sides. To find the perimeter, you simply add up the lengths of all the sides. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides:
- Perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (length + width) \)
Area: The area of a shape is the amount of space it covers. Different shapes have different formulas for calculating the area. For example, the area of a rectangle is found by multiplying its length by its width:
- Area of a rectangle: \( A = length \times width \)
To illustrate, consider a soccer field that is 100 meters long and 50 meters wide. The perimeter is the total distance around the field, which would be:
- Perimeter: \( P = 2 \times (100 + 50) = 2 \times 150 = 300 \) meters
The area, which is the space covered by the field, would be:
- Area: \( A = 100 \times 50 = 5000 \) square meters
Understanding these basic formulas and concepts allows students to solve various word problems related to area and perimeter. They can apply these formulas to find the measurements needed for projects such as fencing a garden, painting a wall, or laying out a floor plan.
Additionally, learning to break down complex shapes into simpler ones can help solve more difficult problems. For example, dividing an irregular shape into rectangles or other common shapes makes it easier to calculate the total area or perimeter.
Understanding Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is fundamental in mathematics, especially for solving word problems. Let's break down these concepts step by step to ensure a clear understanding.
Perimeter:
The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. To calculate the perimeter, you simply add the lengths of all the sides. Here are a few examples:
- For a rectangle, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as: \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \).
- For a square, since all sides are equal, the perimeter \( P \) is: \( P = 4 \times \text{side length} \).
- For a triangle, the perimeter \( P \) is the sum of all its sides: \( P = a + b + c \).
Area:
The area is the amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape. Each shape has its own formula for calculating area. Here are a few examples:
- For a rectangle, the area \( A \) is: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \).
- For a square, the area \( A \) is: \( A = \text{side length}^2 \).
- For a triangle, the area \( A \) is: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
Let's look at some specific examples to further illustrate these concepts:
- Example 1: Rectangle
- If a rectangle has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters, its perimeter is calculated as: \[ P = 2 \times (8 \, \text{meters} + 5 \, \text{meters}) = 2 \times 13 \, \text{meters} = 26 \, \text{meters} \] and its area is: \[ A = 8 \, \text{meters} \times 5 \, \text{meters} = 40 \, \text{square meters} \]
- Example 2: Triangle
- If a triangle has a base of 6 meters and a height of 4 meters, its area is calculated as: \[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \, \text{meters} \times 4 \, \text{meters} = 12 \, \text{square meters} \] If the sides of the triangle are 3 meters, 4 meters, and 5 meters, then its perimeter is: \[ P = 3 \, \text{meters} + 4 \, \text{meters} + 5 \, \text{meters} = 12 \, \text{meters} \]
Understanding these basic principles is essential for solving more complex word problems involving area and perimeter. By practicing with different shapes and their respective formulas, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and build a strong foundation in geometry.
Formulas and Definitions
Understanding the formulas and definitions for area and perimeter is essential for solving word problems effectively. Here are the key concepts and formulas you need to know:
Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. It is the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
- Rectangle: The perimeter \(P\) of a rectangle is calculated by the formula: \[ P = 2 \times (length + width) \]
- Square: The perimeter \(P\) of a square is calculated by the formula: \[ P = 4 \times side \]
- Triangle: The perimeter \(P\) of a triangle is the sum of its three sides: \[ P = side_1 + side_2 + side_3 \]
- Circle (Circumference): The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference \(C\), is calculated by: \[ C = 2 \times \pi \times radius \]
Area
The area of a shape is the amount of space inside its boundaries. Different shapes have different formulas for calculating area.
- Rectangle: The area \(A\) of a rectangle is calculated by: \[ A = length \times width \]
- Square: The area \(A\) of a square is calculated by: \[ A = side \times side = side^2 \]
- Triangle: The area \(A\) of a triangle is calculated by: \[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \]
- Circle: The area \(A\) of a circle is calculated by: \[ A = \pi \times radius^2 \]
Example Calculations
Let's go through an example for better understanding:
- Rectangle: If a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units:
- Perimeter: \[ P = 2 \times (5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16 \text{ units} \]
- Area: \[ A = 5 \times 3 = 15 \text{ square units} \]
- Circle: If a circle has a radius of 4 units:
- Circumference: \[ C = 2 \times \pi \times 4 = 8\pi \approx 25.12 \text{ units} \]
- Area: \[ A = \pi \times 4^2 = 16\pi \approx 50.24 \text{ square units} \]
By understanding these formulas and how to apply them, you can confidently solve various area and perimeter word problems.
Basic Word Problems
Solving basic word problems involving area and perimeter helps students understand the practical applications of these concepts. Here are a few examples to illustrate how to approach these problems step-by-step:
-
Rectangle Perimeter Problem:
John wants to build a fence around his rectangular garden which is 8 meters long and 5 meters wide. How much fencing material does he need?
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2(l + w) \).
- Step 2: Plug in the values for length (\( l \)) and width (\( w \)): \( P = 2(8 + 5) \).
- Step 3: Calculate the result: \( P = 2(13) = 26 \) meters.
John needs 26 meters of fencing material.
-
Rectangle Area Problem:
Sarah wants to plant grass in her rectangular backyard which is 10 meters long and 6 meters wide. What is the area she needs to cover?
- Step 1: Identify the formula for the area of a rectangle: \( A = l \times w \).
- Step 2: Plug in the values for length (\( l \)) and width (\( w \)): \( A = 10 \times 6 \).
- Step 3: Calculate the result: \( A = 60 \) square meters.
Sarah needs to cover an area of 60 square meters.
-
Composite Shape Problem:
A playground is made up of a rectangular area that is 15 meters long and 10 meters wide, and a semicircular area with a diameter of 10 meters. What is the total area of the playground?
- Step 1: Calculate the area of the rectangle: \( A_{\text{rect}} = 15 \times 10 = 150 \) square meters.
- Step 2: Calculate the radius of the semicircle: \( r = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \) meters.
- Step 3: Calculate the area of the semicircle: \( A_{\text{semi}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi (5^2) = \frac{1}{2} \pi \times 25 = 12.5 \pi \approx 39.27 \) square meters.
- Step 4: Add the areas of the rectangle and the semicircle: \( A_{\text{total}} = 150 + 39.27 \approx 189.27 \) square meters.
The total area of the playground is approximately 189.27 square meters.
By practicing these types of problems, students can develop a better understanding of how to apply the formulas for area and perimeter to solve real-world scenarios.
Rectangle Area and Perimeter Word Problems
Understanding how to solve word problems involving the area and perimeter of rectangles is an essential skill for 4th graders. Below are some examples and steps to guide students through these problems.
Example 1: Finding the Area
Let's start with a simple problem. Suppose you have a rectangle with a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. To find the area of the rectangle, use the formula:
\[ \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \]
Step-by-step:
- Identify the length and width of the rectangle.
- Multiply the length by the width:
- \[ 8 \, \text{meters} \times 5 \, \text{meters} = 40 \, \text{square meters} \]
So, the area of the rectangle is 40 square meters.
Example 2: Finding the Perimeter
Now, let's find the perimeter of the same rectangle. The formula for the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
Step-by-step:
- Identify the length and width of the rectangle.
- Add the length and width together:
- \[ 8 \, \text{meters} + 5 \, \text{meters} = 13 \, \text{meters} \]
- Multiply the result by 2:
- \[ 2 \times 13 \, \text{meters} = 26 \, \text{meters} \]
So, the perimeter of the rectangle is 26 meters.
Word Problem Practice
Try solving these word problems on your own:
- A rectangle has a length of 12 meters and a width of 7 meters. What is the area?
- A rectangle has a length of 9 meters and a width of 6 meters. What is the perimeter?
- If the area of a rectangle is 54 square meters and the width is 6 meters, what is the length?
Solution Steps
For each problem, follow these steps:
- Write down the given information.
- Choose the correct formula (area or perimeter).
- Plug in the known values.
- Solve for the unknown value.
These problems help students practice and reinforce their understanding of the relationship between the length, width, area, and perimeter of rectangles.
Triangle Area and Perimeter Word Problems
Understanding the area and perimeter of triangles is essential for solving various word problems. Here, we'll explore the formulas and provide examples to help 4th graders grasp these concepts.
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length around the triangle. To find the perimeter, simply add the lengths of all three sides. The formula is:
\( P = a + b + c \)
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
Example Problem
Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 5 cm, 7 cm, and 9 cm.
Solution:
- Step 1: Identify the lengths of the sides: \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = 7 \) cm, \( c = 9 \) cm
- Step 2: Add the lengths: \( P = 5 + 7 + 9 \)
- Step 3: Calculate the sum: \( P = 21 \) cm
The perimeter of the triangle is 21 cm.
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle can be found using the formula:
\( A = \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \)
where the base is one side of the triangle, and the height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
Example Problem
Find the area of a triangle with a base of 6 cm and a height of 4 cm.
Solution:
- Step 1: Identify the base and height: \( base = 6 \) cm, \( height = 4 \) cm
- Step 2: Substitute into the formula: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4 \)
- Step 3: Calculate the area: \( A = 12 \) cm²
The area of the triangle is 12 cm².
Practice Problems
1. A triangle has sides measuring 8 cm, 10 cm, and 12 cm. What is the perimeter?
- Solution: \( P = 8 + 10 + 12 = 30 \) cm
2. A triangle has a base of 10 cm and a height of 5 cm. What is the area?
- Solution: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 5 = 25 \) cm²
Quadrilateral Area and Perimeter Word Problems
Quadrilaterals are four-sided polygons with various shapes like squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and rhombuses. Each type of quadrilateral has unique properties that help in calculating its area and perimeter. Here are some common word problems involving quadrilaterals:
1. Square Word Problems
Problem: A square garden has a side length of 8 meters. What is the perimeter and area of the garden?
Solution: The perimeter of a square is calculated by \( P = 4 \times \text{side length} \). Therefore, \( P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \) meters. The area is calculated by \( A = \text{side length}^2 \). Hence, \( A = 8^2 = 64 \) square meters.
2. Rectangle Word Problems
Problem: A rectangular field is 15 meters long and 10 meters wide. What is the perimeter and area of the field?
Solution: The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \). Therefore, \( P = 2 \times (15 + 10) = 50 \) meters. The area is calculated by \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \). Hence, \( A = 15 \times 10 = 150 \) square meters.
3. Parallelogram Word Problems
Problem: A parallelogram has a base of 12 meters and a height of 5 meters. What is the area of the parallelogram?
Solution: The area of a parallelogram is calculated by \( A = \text{base} \times \text{height} \). Therefore, \( A = 12 \times 5 = 60 \) square meters.
4. Trapezoid Word Problems
Problem: A trapezoid has bases of 8 meters and 5 meters with a height of 4 meters. What is the area of the trapezoid?
Solution: The area of a trapezoid is calculated by \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \). Therefore, \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (8 + 5) \times 4 = \frac{1}{2} \times 13 \times 4 = 26 \) square meters.
5. Rhombus Word Problems
Problem: A rhombus has diagonals of 10 meters and 6 meters. What is the area of the rhombus?
Solution: The area of a rhombus is calculated by \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{diagonal}_1 \times \text{diagonal}_2 \). Therefore, \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 6 = 30 \) square meters.
Circle Area and Circumference Word Problems
Understanding the area and circumference of a circle is essential for solving various real-life word problems. Here, we will explore different problems involving circles, how to approach them, and the formulas needed to find solutions.
Formulas to Remember
- Area of a Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Circumference of a Circle: \( C = 2 \pi r \)
Example Problems
Problem 1: A bicycle wheel has a radius of 0.35 meters. Calculate the distance the wheel covers in one revolution.
- Find the circumference using \( C = 2 \pi r \).
- \( C = 2 \times \pi \times 0.35 \)
- \( C = 2.2 \) meters
- Thus, the wheel covers 2.2 meters in one revolution.
Problem 2: A circular garden has a diameter of 10 meters. What is the area of the garden?
- First, find the radius by dividing the diameter by 2.
- Radius \( r = 10 / 2 = 5 \) meters.
- Use the area formula \( A = \pi r^2 \).
- \( A = \pi \times 5^2 \)
- \( A = 25 \pi \)
- Approximating \(\pi\) as 3.14, \( A \approx 78.5 \) square meters.
Problem 3: A park's circular pathway has a circumference of 150 meters. Find the radius of the pathway.
- Use the circumference formula \( C = 2 \pi r \).
- Solve for \( r \): \( 150 = 2 \pi r \).
- \( r = \frac{150}{2 \pi} \).
- \( r \approx \frac{150}{6.28} \).
- \( r \approx 23.9 \) meters.
Tips for Solving Circle Problems
- Always identify whether the problem provides the diameter or the radius.
- Remember to use the correct units for your answers.
- For word problems, translate the words into mathematical equations.

Real-Life Area and Perimeter Word Problems
Applying the concepts of area and perimeter to real-life scenarios helps students understand the practical uses of these mathematical skills. Here are some word problems that involve real-life situations:
-
Problem 1: Jane wants to put a fence around her rectangular garden that measures 15 meters in length and 10 meters in width. Calculate the perimeter of the garden to determine how much fencing material she needs.
Solution:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width}) = 2 \times (15 \, \text{m} + 10 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 25 \, \text{m} = 50 \, \text{m}
\] -
Problem 2: A rectangular playground is being covered with grass sod. The playground is 20 meters long and 12 meters wide. Calculate the area of the playground to determine how much grass sod is needed.
Solution:
\[
\text{Area} = \text{Length} \times \text{Width} = 20 \, \text{m} \times 12 \, \text{m} = 240 \, \text{m}^2
\] -
Problem 3: Sam is designing a rectangular swimming pool that is 25 feet long and 10 feet wide. He needs to tile the bottom of the pool. Calculate the area that needs to be tiled.
Solution:
\[
\text{Area} = \text{Length} \times \text{Width} = 25 \, \text{ft} \times 10 \, \text{ft} = 250 \, \text{ft}^2
\] -
Problem 4: A farmer wants to create a rectangular pen for his animals. The pen is 50 meters long and 30 meters wide. Calculate the perimeter of the pen.
Solution:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width}) = 2 \times (50 \, \text{m} + 30 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 80 \, \text{m} = 160 \, \text{m}
\]
By solving these problems, students can see how area and perimeter are used in everyday life, helping them grasp the importance and utility of these mathematical concepts.
Polygon Area and Perimeter Word Problems
Polygons are multi-sided shapes with more than four sides. In this section, we will solve perimeter word problems for both regular and irregular polygons. Understanding how to find the perimeter of polygons is a crucial skill in geometry.
Regular Polygons
A regular polygon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles of equal measure. To find the perimeter of a regular polygon, use the following formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = \text{number of sides} \times \text{length of one side}
\]
Example Problem:
Solve the perimeter of a regular hexagon (6-sided polygon) with each side measuring 5 cm.
- Identify the number of sides: \( n = 6 \).
- Measure the length of one side: \( s = 5 \) cm.
- Apply the formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = n \times s \).
- Calculate the result: \( \text{Perimeter} = 6 \times 5 = 30 \) cm.
Therefore, the perimeter of the hexagon is 30 cm.
Irregular Polygons
An irregular polygon has sides of different lengths. To find the perimeter of an irregular polygon, simply add the lengths of all its sides.
Example Problem:
Find the perimeter of an irregular pentagon with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm.
- List the side lengths: 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm.
- Add the lengths: \( 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 \).
- Calculate the sum: \( 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 25 \) cm.
Therefore, the perimeter of the pentagon is 25 cm.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a regular octagon with each side measuring 8 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of an irregular polygon with sides measuring 2 m, 3.5 m, 4 m, 6 m, and 7.5 m.
Understanding and Applying the Concepts
Practicing these problems helps students understand the basic concept of perimeter and its application to different polygon shapes. This skill is not only crucial for geometry but also for solving real-life problems involving fencing, framing, and other measurements.
Advanced Word Problems
In this section, we will tackle some challenging area and perimeter word problems that require a deeper understanding of geometry and arithmetic operations. These problems are designed to help 4th graders develop their problem-solving skills and apply what they have learned to real-world scenarios.
-
Problem 1: The Garden Fence
Sarah wants to build a rectangular fence around her garden. The garden's length is 15 meters, and the width is 8 meters. She needs to determine the total length of the fence required to enclose the garden completely.
Solution:
- Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle using the formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \).
- Substitute the given values: \( P = 2(15 \, \text{m} + 8 \, \text{m}) \).
- Simplify the expression: \( P = 2 \times 23 \, \text{m} = 46 \, \text{m} \).
- Sarah needs 46 meters of fencing to enclose her garden.
-
Problem 2: The Swimming Pool
A rectangular swimming pool is 25 meters long and 10 meters wide. Calculate the area of the pool and the length of the border needed if a 1-meter wide path is to be constructed around it.
Solution:
- Calculate the area of the pool using the formula: \( A = l \times w \).
- Substitute the given values: \( A = 25 \, \text{m} \times 10 \, \text{m} = 250 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- For the border, first calculate the new dimensions including the path: \( l' = 25 \, \text{m} + 2 \times 1 \, \text{m} = 27 \, \text{m} \) and \( w' = 10 \, \text{m} + 2 \times 1 \, \text{m} = 12 \, \text{m} \).
- Calculate the perimeter of the new dimensions: \( P = 2(l' + w') = 2(27 \, \text{m} + 12 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 39 \, \text{m} = 78 \, \text{m} \).
- The total border length needed is 78 meters.
-
Problem 3: The Composite Shape
A playground consists of a rectangular area 30 meters long and 20 meters wide, and a semicircular area with a diameter equal to the width of the rectangle. Find the total area of the playground.
Solution:
- Calculate the area of the rectangle: \( A_{\text{rect}} = l \times w = 30 \, \text{m} \times 20 \, \text{m} = 600 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Calculate the radius of the semicircle: \( r = \frac{w}{2} = \frac{20 \, \text{m}}{2} = 10 \, \text{m} \).
- Calculate the area of the semicircle: \( A_{\text{semi}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi (10 \, \text{m})^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi \times 100 \, \text{m}^2 = 50 \pi \, \text{m}^2 \approx 157 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Find the total area by adding the areas: \( A_{\text{total}} = A_{\text{rect}} + A_{\text{semi}} = 600 \, \text{m}^2 + 157 \, \text{m}^2 = 757 \, \text{m}^2 \).
- The total area of the playground is approximately 757 square meters.
These advanced word problems challenge students to think critically and apply multiple mathematical concepts. Practice solving similar problems to enhance your skills and confidence in handling complex scenarios.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Learning how to solve area and perimeter word problems is a fundamental skill in math, especially for 4th graders. However, there are some common mistakes that students often make. Understanding these mistakes and knowing how to avoid them can help students improve their problem-solving skills.
Common Mistakes
- Confusing Perimeter and Area: One of the most common mistakes is confusing the concepts of perimeter and area. Perimeter refers to the total distance around a shape, while area refers to the amount of space inside the shape.
- Incorrect Formula Application: Another frequent error is using the wrong formula. For example, students might use the formula for perimeter when they need to find the area, or vice versa.
- Incorrect Unit Usage: Forgetting to use or incorrectly using units (e.g., square meters for area and meters for perimeter) can lead to incorrect answers.
- Calculation Errors: Simple arithmetic errors in addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division can also cause mistakes in the final answer.
- Misinterpretation of the Problem: Not fully understanding the problem or misinterpreting the question can lead to incorrect approaches and solutions.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
- Understand the Definitions: Clearly understand the definitions of perimeter and area. Perimeter is the sum of all sides of a shape, while area is the space within the shape.
- Memorize the Formulas: Ensure you know the correct formulas:
- Perimeter of a rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (l + w) \)
- Area of a rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Perimeter of a square: \( P = 4 \times s \)
- Area of a square: \( A = s^2 \)
- Use Units Correctly: Always include the correct units in your answers and ensure they match the quantities you're calculating.
- Double-Check Your Work: Recheck your calculations to avoid arithmetic errors. It can help to work through the problem step-by-step and verify each part.
- Draw Diagrams: Visualizing the problem by drawing a diagram can help in understanding and solving the problem correctly.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, students can improve their accuracy and confidence in solving area and perimeter word problems.

Practice Worksheets and Exercises
Practicing area and perimeter word problems is crucial for reinforcing the concepts learned in 4th grade. Below are some detailed worksheets and exercises designed to help students apply their knowledge in a variety of contexts.
Worksheet 1: Basic Perimeter and Area
- Solve for the perimeter and area of given rectangles and squares.
- Include diagrams where students can label dimensions.
- Example Problem: A rectangle has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. Calculate the perimeter and area.
Worksheet 2: Complex Shapes
- Break down complex shapes into simpler ones to calculate the total area and perimeter.
- Include irregular shapes that can be divided into rectangles and triangles.
- Example Problem: Divide an L-shaped figure into two rectangles and find the total area and perimeter.
Worksheet 3: Real-Life Scenarios
- Apply area and perimeter calculations to real-life situations like fencing a garden or tiling a floor.
- Encourage students to visualize and draw the problems.
- Example Problem: A garden is 10 meters long and 6 meters wide. How much fencing is needed to enclose it?
Worksheet 4: Mixed Operations
- Include problems that require both area and perimeter calculations.
- Incorporate word problems where students need to find missing dimensions.
- Example Problem: The perimeter of a rectangle is 26 meters. If the length is 8 meters, find the width and area.
Worksheet 5: Challenge Problems
- Provide advanced problems for students who need an extra challenge.
- Include problems involving multiple steps and conversions between units.
- Example Problem: A rectangular park measures 50 meters by 30 meters. If a pathway of 2 meters width runs all around inside the park, calculate the area of the pathway.
Answer Keys
Each worksheet comes with a detailed answer key to help students check their work and understand their mistakes. Encourage students to review the answer keys after completing the exercises to ensure they grasp the concepts fully.
Answer Keys and Explanations
Having clear and detailed answer keys along with explanations is crucial for students to understand their mistakes and learn the correct methods to solve area and perimeter problems. Below are comprehensive solutions to some common types of problems you may encounter in worksheets.
Example 1: Rectangle Area
Problem: A rectangle has a length of 12 meters and a width of 8 meters. Find the area.
Solution:
- Identify the formula for the area of a rectangle: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Substitute the given values into the formula: \( A = 12 \, \text{meters} \times 8 \, \text{meters} \)
- Calculate the product: \( A = 96 \, \text{square meters} \)
Answer: The area of the rectangle is 96 square meters.
Example 2: Perimeter of a Square
Problem: Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 cm.
Solution:
- Identify the formula for the perimeter of a square: \( P = 4 \times \text{side length} \)
- Substitute the given value into the formula: \( P = 4 \times 5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Calculate the product: \( P = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
Answer: The perimeter of the square is 20 cm.
Example 3: Area of a Triangle
Problem: A triangle has a base of 10 meters and a height of 5 meters. Find the area.
Solution:
- Identify the formula for the area of a triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Substitute the given values into the formula: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \, \text{meters} \times 5 \, \text{meters} \)
- Calculate the product: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 50 \, \text{square meters} \)
- Divide the product by 2: \( A = 25 \, \text{square meters} \)
Answer: The area of the triangle is 25 square meters.
Example 4: Composite Shapes
Problem: Find the area of a composite shape consisting of a rectangle (10m by 6m) and a semicircle with a diameter of 6m.
Solution:
- Calculate the area of the rectangle: \( A_{\text{rectangle}} = 10 \, \text{m} \times 6 \, \text{m} = 60 \, \text{square meters} \)
- Calculate the radius of the semicircle: \( r = \frac{6 \, \text{m}}{2} = 3 \, \text{m} \)
- Calculate the area of the full circle: \( A_{\text{circle}} = \pi \times r^2 = \pi \times 3^2 = 9\pi \, \text{square meters} \)
- Calculate the area of the semicircle: \( A_{\text{semicircle}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 9\pi = 4.5\pi \, \text{square meters} \approx 14.14 \, \text{square meters} \)
- Add the areas of the rectangle and semicircle: \( A_{\text{total}} = 60 \, \text{square meters} + 14.14 \, \text{square meters} \approx 74.14 \, \text{square meters} \)
Answer: The area of the composite shape is approximately 74.14 square meters.
Example 5: Perimeter of a Composite Shape
Problem: Find the perimeter of a shape consisting of a rectangle (12m by 4m) and an attached semicircle with a diameter of 4m.
Solution:
- Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle (excluding the side where the semicircle is attached): \( P_{\text{rectangle}} = 12 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m} + 12 \, \text{m} = 28 \, \text{m} \)
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle: \( C_{\text{circle}} = \pi \times d = \pi \times 4 \, \text{m} = 4\pi \, \text{m} \approx 12.57 \, \text{m} \)
- Calculate the perimeter of the semicircle: \( P_{\text{semicircle}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 4\pi = 2\pi \, \text{m} \approx 6.28 \, \text{m} \)
- Add the perimeters: \( P_{\text{total}} = 28 \, \text{m} + 6.28 \, \text{m} \approx 34.28 \, \text{m} \)
Answer: The perimeter of the composite shape is approximately 34.28 meters.
Interactive Online Resources
Interactive online resources are excellent tools for enhancing the learning experience and making math fun for 4th graders. These resources provide dynamic ways to engage with area and perimeter problems, allowing students to practice and reinforce their skills through various activities and games. Below are some valuable interactive resources that can be utilized:
- Khan Academy:
Khan Academy offers a comprehensive unit on area and perimeter for 4th graders. It includes video lessons, practice exercises, and quizzes to help students master the concepts. The platform's interactive nature allows students to learn at their own pace and receive immediate feedback on their progress.
- Online Math Learning:
Online Math Learning provides interactive worksheets that challenge students with area and perimeter word problems. These worksheets come with hints and solutions, helping students to understand their mistakes and learn from them. The step-by-step explanations make it easy for students to follow along and grasp the concepts.
- Math Center:
Math Center offers a variety of interactive resources tailored for 4th-grade students. These include games, quizzes, and step-by-step practice exercises that make learning area and perimeter engaging. The platform also allows students to create their own learning paths, ensuring that they focus on areas where they need the most improvement.
Using these interactive online resources, students can enjoy a more engaging and effective learning experience. Encourage them to explore these tools and incorporate them into their regular study routines for better understanding and retention of area and perimeter concepts.
Conclusion and Summary
As we conclude our exploration of area and perimeter word problems for 4th graders, it's important to reflect on the key concepts and skills we've developed. Understanding area and perimeter is crucial as these measurements are widely used in various real-life applications, from designing a garden to planning the layout of a room.
Throughout this guide, we've covered:
- The basic definitions and differences between area and perimeter.
- Formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of different shapes including rectangles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles.
- Step-by-step approaches to solving word problems involving these measurements.
- Common mistakes students often make and how to avoid them.
- Practice worksheets and exercises to reinforce learning.
To further enhance your learning, we've provided interactive online resources where you can practice more problems and track your progress.
In summary, mastering the concepts of area and perimeter not only helps in academic success but also prepares students for practical tasks in everyday life. Keep practicing, and remember to visualize problems, break them down into manageable steps, and double-check your work to avoid errors.
We hope this guide has been informative and helpful. Happy learning!

Toán Lớp 4: Bài Toán Diện Tích và Chu Vi 4
READ MORE:
Học cách giải các bài toán về diện tích và chu vi trong chương trình Lớp 4 theo chuẩn Common Core. Video hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu, phù hợp cho học sinh và giáo viên.
Diện Tích và Chu Vi Bài Toán | Lớp 4 | Common Core