Topic area and perimeter video: Discover the fascinating world of geometry with our engaging area and perimeter video. Learn to measure the size and boundaries of different shapes through step-by-step explanations and interactive examples. Perfect for students and educators alike, this video makes complex concepts simple and fun. Start mastering area and perimeter today!
Table of Content
- Understanding Area and Perimeter
- Introduction to Perimeter
- Understanding Area
- Formulas for Area and Perimeter
- Calculating the Perimeter of Various Shapes
- Calculating the Area of Different Shapes
- Real-life Applications of Area and Perimeter
- Interactive Examples and Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Summary and Review
- YOUTUBE: Xem bài hát vui nhộn về diện tích và chu vi dành cho học sinh lớp 3 và lớp 4. Học cách tính diện tích và chu vi một cách thú vị và dễ hiểu!
Understanding Area and Perimeter
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, essential for measuring the size and boundaries of 2D shapes. Below, you'll find an overview of these concepts along with methods to calculate them for various shapes.
What is Perimeter?
The perimeter is the total distance around the outside of a shape. Imagine it as the length of the fence that encloses a garden. To calculate the perimeter of a polygon, you simply add up the lengths of all its sides.
Formulas for Perimeter
- Square: \( P = 4s \) (where \( s \) is the length of a side)
- Rectangle: \( P = 2l + 2w \) (where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width)
- Triangle: \( P = a + b + c \) (where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides)
- Circle (Circumference): \( P = 2\pi r \) or \( P = \pi d \) (where \( r \) is the radius and \( d \) is the diameter)
What is Area?
Area measures the amount of space inside a shape. Think of it as the amount of paint needed to cover the surface inside the boundaries of a shape.
Formulas for Area
- Square: \( A = s^2 \) (where \( s \) is the length of a side)
- Rectangle: \( A = l \times w \) (where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width)
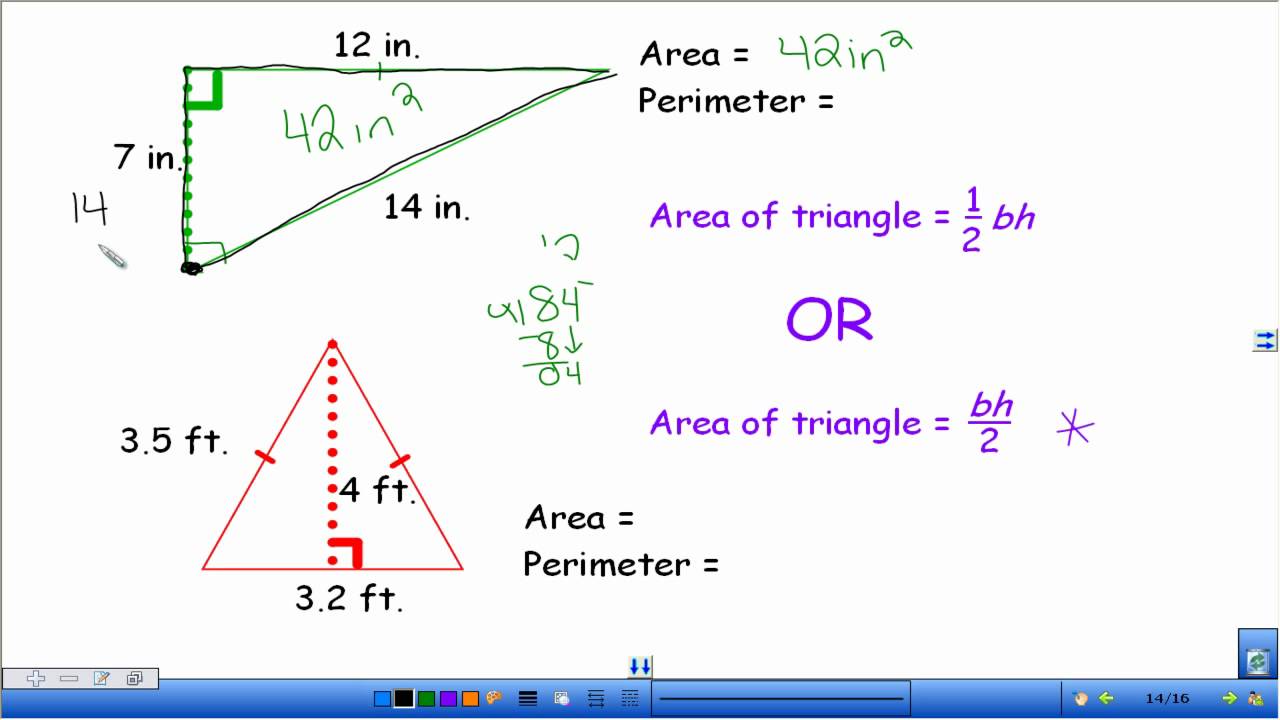
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} b \times h \) (where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height)
- Circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \) (where \( r \) is the radius)
Example Problems
Let's walk through a couple of examples to illustrate these calculations:
- Finding the Perimeter of a Rectangle: Suppose a rectangle has a length of 5 meters and a width of 3 meters. Using the formula \( P = 2l + 2w \), we get:
\[ P = 2(5) + 2(3) = 10 + 6 = 16 \text{ meters} \]
- Finding the Area of a Triangle: Suppose a triangle has a base of 4 meters and a height of 3 meters. Using the formula \( A = \frac{1}{2} b \times h \), we get:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} (4) \times (3) = 2 \times 3 = 6 \text{ square meters} \]
Applications of Area and Perimeter
Understanding area and perimeter is crucial in various real-life situations, such as:
- Calculating the amount of material needed for construction projects.
- Determining the amount of paint required to cover a surface.
- Planning the layout of a garden or a room.
Interactive Learning
For more detailed explanations and interactive learning, you can check out the following resources:
- - Comprehensive videos and exercises on area and perimeter.
- - Step-by-step guides on finding area and perimeter.
- - Engaging videos that explain these concepts with real-life examples.
- - Detailed video tutorials on perimeter.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around its edges. It's a fundamental concept in geometry and is often described as the length of the boundary enclosing a figure. For simple polygons, the perimeter is calculated by summing the lengths of all sides.
- For a rectangle, the perimeter \( P \) can be found using the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- For a square, since all sides are equal, the perimeter \( P \) is \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of a side.
- For a triangle, the perimeter \( P \) is the sum of its three sides: \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a, b, \) and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
Understanding the perimeter is crucial for practical tasks such as constructing a fence around a garden, framing a picture, or any activity requiring the measurement of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape.
Let's consider an example: suppose you have a garden in the shape of a rectangle with a length of 10 meters and a width of 5 meters. The perimeter of the garden is:
\[ P = 2(10 + 5) = 2 \times 15 = 30 \, \text{meters} \]
This means you would need 30 meters of fencing material to enclose the garden.
In cases where the shape is irregular, you can still find the perimeter by adding the lengths of all its sides. For instance, if a garden has sides measuring 7 meters, 8 meters, 5 meters, and 6 meters, the perimeter is:
\[ P = 7 + 8 + 5 + 6 = 26 \, \text{meters} \]
Perimeter calculations are not limited to simple shapes. They can also be applied to more complex polygons, where each side length is measured and summed up to find the total boundary length. This concept is essential in various real-world applications, making it a valuable skill in both academic and practical settings.
Understanding Area
The area of a shape is the amount of space inside its boundaries. It is measured in square units, such as square centimeters (\(cm^2\)), square meters (\(m^2\)), or square inches (\(in^2\)). Understanding how to calculate the area is essential for solving various real-world problems, from determining the amount of paint needed for a wall to finding the size of a plot of land.
Here's a step-by-step approach to understanding and calculating the area for different shapes:
- Area of a Rectangle: The formula to calculate the area of a rectangle is \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \). For example, if the length of a rectangle is 5 meters and the width is 3 meters, the area is \( 5 \times 3 = 15 \, m^2 \).
- Area of a Triangle: The area of a triangle is calculated using the formula \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \). If the base is 6 cm and the height is 4 cm, then the area is \( \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4 = 12 \, cm^2 \).
- Area of a Circle: The area of a circle is found with the formula \( \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \). If the radius of the circle is 7 inches, the area is \( \pi \times 7^2 \approx 153.94 \, in^2 \).
- Area of a Parallelogram: The formula for the area of a parallelogram is similar to that of a rectangle, \( \text{Area} = \text{base} \times \text{height} \). For a base of 8 meters and a height of 5 meters, the area is \( 8 \times 5 = 40 \, m^2 \).
- Area of Trapezoids: To find the area of a trapezoid, use the formula \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \). If base1 is 6 cm, base2 is 4 cm, and height is 5 cm, the area is \( \frac{1}{2} \times (6 + 4) \times 5 = 25 \, cm^2 \).
By practicing these calculations and understanding the properties of each shape, you can develop a strong foundation in geometry and apply these concepts effectively in various situations.
Formulas for Area and Perimeter
Understanding the formulas for area and perimeter is crucial in geometry. These formulas help in calculating the boundaries and spaces of various shapes. Here are some key formulas:
Rectangle
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(l + w) \)
- Area: \( A = l \times w \)
Square
- Perimeter: \( P = 4s \)
- Area: \( A = s^2 \)
Triangle
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
Circle
- Perimeter (Circumference): \( P = 2 \pi r \)
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
Parallelogram
- Perimeter: \( P = 2(a + b) \)
- Area: \( A = b \times h \)
Trapezoid
- Perimeter: \( P = a + b + c + d \)
- Area: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (b_1 + b_2) \times h \)
Composite Shapes
For composite shapes, decompose them into basic shapes like rectangles, triangles, etc., calculate their individual areas, and then sum them up. The perimeter is calculated by adding the outer boundary lengths.
Calculating the Perimeter of Various Shapes
Calculating the perimeter of different shapes involves adding the lengths of all the sides. Here is a detailed guide on how to calculate the perimeter for various common shapes:
- Square: The perimeter of a square is the sum of the lengths of all four sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, you can calculate it using the formula \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side.
- Rectangle: To find the perimeter of a rectangle, add the lengths of all four sides. The formula is \( P = 2l + 2w \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
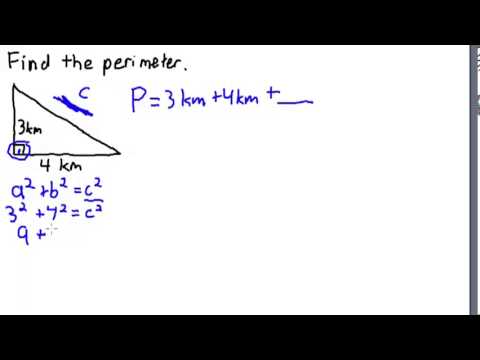
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. If the sides are \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), then the perimeter is \( P = a + b + c \).
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle is known as the circumference. It can be calculated using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
- Polygon: For a polygon, add up the lengths of all its sides. If a polygon has \( n \) sides with lengths \( s_1, s_2, ..., s_n \), then the perimeter is \( P = s_1 + s_2 + ... + s_n \).
Here are step-by-step examples for clarity:
- Square Example:
- Side length (\( s \)) = 5 units
- Perimeter (\( P \)) = \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units
- Rectangle Example:
- Length (\( l \)) = 8 units, Width (\( w \)) = 3 units
- Perimeter (\( P \)) = \( 2 \times 8 + 2 \times 3 = 16 + 6 = 22 \) units
- Triangle Example:
- Sides (\( a, b, c \)) = 3 units, 4 units, 5 units
- Perimeter (\( P \)) = \( 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) units
- Circle Example:
- Radius (\( r \)) = 7 units
- Circumference (\( C \)) = \( 2\pi \times 7 \approx 2 \times 3.14159 \times 7 \approx 43.98 \) units
- Irregular Polygon Example:
- Sides (\( s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4, s_5 \)) = 5 units, 7 units, 3 units, 4 units, 6 units
- Perimeter (\( P \)) = \( 5 + 7 + 3 + 4 + 6 = 25 \) units
Understanding the concept of perimeter is crucial for solving various practical problems, from fencing a garden to framing a picture.

Calculating the Area of Different Shapes
Understanding how to calculate the area of various shapes is essential in geometry. Here are detailed steps and formulas for different shapes:
Rectangles and Squares
The area of a rectangle or square can be calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width}
\]
For a square, since all sides are equal:
\[
\text{Area} = \text{side}^2
\]
Triangles
The area of a triangle is given by:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}
\]
For right triangles, the base and height are the two perpendicular sides.
Parallelograms
The area of a parallelogram is similar to that of a rectangle:
\[
\text{Area} = \text{base} \times \text{height}
\]
Note that the height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite side.
Trapezoids
The area of a trapezoid is calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height}
\]
where \(\text{base}_1\) and \(\text{base}_2\) are the lengths of the two parallel sides.
Circles
The area of a circle is given by the formula:
\[
\text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2
\]
where \(\pi\) (pi) is approximately 3.14159.
Composite Shapes
For composite shapes, divide the shape into simpler shapes, calculate the area for each, and then sum the areas:
- Identify the simple shapes within the composite shape.
- Calculate the area of each simple shape.
- Add the areas together to find the total area.
Interactive Examples and Practice Problems
- Use interactive tools to visualize how changing dimensions affect the area.
- Practice problems with varying levels of difficulty to reinforce understanding.
Common Mistakes and Tips
When calculating areas, common mistakes include not using perpendicular height for triangles and parallelograms or confusing the formulas. Double-check the dimensions and ensure you use the correct formula for each shape.
With these detailed steps and practice, calculating the area of different shapes becomes an easy and systematic process.
Real-life Applications of Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is not only essential in mathematics but also in various real-world scenarios. Here are some examples of how these concepts are applied in daily life:
-
Construction and Architecture:
In construction, calculating the area and perimeter of plots, rooms, and buildings is crucial. For example, determining the area helps in estimating the amount of materials needed for flooring or painting. The perimeter is important for planning the lengths of walls and fencing around properties.
-
Gardening and Landscaping:
When designing gardens or parks, perimeter measurements are used to outline boundaries and install fences. Calculating the area helps in planning the layout, including where to plant different species and how much soil or turf is needed.
-
Fencing and Security:
In security, the perimeter of a property determines the length of fencing or walls required to secure it. This is important for residential properties, farms, and even national borders.
-
Urban Planning:
Urban planners use perimeter and area calculations to design efficient road networks, allocate spaces for parks, and plan the layout of residential and commercial areas to optimize land use and improve accessibility.
-
Sports:
In sports, the dimensions of playing fields and tracks are defined using perimeter and area measurements. For instance, a football field's boundary lines and the space within it are precisely measured to meet official standards.
-
Art and Fashion:
Artists and fashion designers use these measurements to create patterns and designs. For example, tailoring a dress involves calculating the fabric area, while framing a picture requires knowing the perimeter to cut the frame material accurately.
-
Astronomy:
Astronomers use area and perimeter calculations to measure orbits and distances between celestial bodies, aiding in the understanding of planetary motions and the structure of the universe.
These examples illustrate the broad applicability of area and perimeter in various fields, highlighting their importance beyond the classroom. Mastery of these concepts can help solve practical problems and make informed decisions in everyday life.
Interactive Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding and mastering the concepts of area and perimeter is crucial for solving real-world problems. Here are some interactive examples and practice problems to help reinforce these concepts.
Perimeter Problems
-
Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 6 cm, 8 cm, and 9 cm.
Solution: \(P = 6 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm} + 9 \, \text{cm} = 23 \, \text{cm}\)
-
Calculate the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 9 inches and a width of 4 inches.
Solution: \(P = 2 \times (9 \, \text{in} + 4 \, \text{in}) = 26 \, \text{in}\)
-
Determine the perimeter of a regular octagon with each side measuring 7 meters.
Solution: \(P = 8 \times 7 \, \text{m} = 56 \, \text{m}\)
Area Problems
-
Find the area of a square with each side measuring 5 inches.
Solution: \(A = 5 \, \text{in} \times 5 \, \text{in} = 25 \, \text{in}^2\)
-
A rectangular yard has a length of 16 meters and a width of 3 meters. Calculate its area.
Solution: \(A = 16 \, \text{m} \times 3 \, \text{m} = 48 \, \text{m}^2\)
-
Find the area of a parallelogram with a base of 9 cm and a height of 5 cm.
Solution: \(A = 9 \, \text{cm} \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 45 \, \text{cm}^2\)
Interactive Practice
-
Interactive Problem 1: Margo wants to build a rectangular fence around her garden using 24 meters of wood. What dimensions will give Margo the largest area?
Solution: The dimensions 6 meters by 6 meters will give the largest area of \(36 \, \text{m}^2\).
-
Interactive Problem 2: A rectangular table has a length that is twice its width. If the perimeter is 24 feet, find the dimensions of the table.
Solution: Let the width be \(x\). Then the length is \(2x\). The perimeter equation is \(2(x + 2x) = 24\). Solving for \(x\), we get \(x = 4 \, \text{ft}\) and \(2x = 8 \, \text{ft}\). So, the dimensions are 4 feet by 8 feet.
Practice Exercises
Here are additional practice exercises for you to try:
| Problem | Answer Box |
|---|---|
| Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 12 meters and a width of 7 meters. | P = meters |
| Calculate the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 6 cm. | A = cm² |
Use the answers provided to check your solutions and ensure you understand each step of the process. These interactive examples and practice problems will help solidify your understanding of area and perimeter.
Common Mistakes and Tips
Understanding area and perimeter can be challenging for students. Here are some common mistakes and tips to avoid them:
- Mistake: Confusing Area and Perimeter
Students often mix up area and perimeter. Perimeter is the distance around a shape, while area is the space inside it.
- Tip: Use visual aids and hand motions to differentiate. For perimeter, trace the outline with your finger. For area, shade the inside of the shape.
- Mistake: Incorrect Units
Forgetting to use square units for area or using the wrong units entirely.
- Tip: Emphasize that area is measured in square units (e.g., cm2, m2) and perimeter in linear units (e.g., cm, m).
- Mistake: Incorrect Formula Application
Using the wrong formulas or applying them incorrectly, especially for complex shapes.
- Tip: Memorize and understand the formulas. For rectangles, P = 2(l + w) and A = l × w. Practice with various shapes to reinforce learning.
- Mistake: Overlooking Composite Shapes
Struggling with shapes that are combinations of basic shapes.
- Tip: Break down composite shapes into simpler parts, calculate the area or perimeter for each, and then sum them up.
- Mistake: Not Double-Checking Work
Errors can often be caught by reviewing calculations and ensuring all steps were followed correctly.
- Tip: Always double-check your work. Verify each step and ensure units and calculations are correct.
By being aware of these common mistakes and using these tips, students can improve their understanding and accuracy when calculating area and perimeter.

Summary and Review
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is crucial in both academic and real-life applications. Here, we summarize the key points and provide a quick review of what we've covered.
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around the outside of the shape. It's like the length of the fence surrounding a yard.
- Area: The area of a shape is the amount of space inside the shape. Think of it as the surface covered by the shape, such as the grass inside the fence.
Formulas
Here are the basic formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of common shapes:
| Shape | Perimeter Formula | Area Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Square | P = 4s | A = s2 |
| Rectangle | P = 2l + 2w | A = l × w |
| Triangle | P = a + b + c | A = ½ b × h |
| Circle | C = 2πr | A = πr2 |
| Trapezoid | P = a + b + c + d | A = ½ (b1 + b2) × h |
Key Concepts
- Additivity of Area: The area of a composite shape can be found by summing the areas of its simpler component shapes.
- Units: Area is measured in square units (e.g., cm2, m2), while perimeter is measured in linear units (e.g., cm, m).
Common Mistakes and Tips
- Confusing Perimeter and Area: Remember, perimeter is the boundary length, while area is the space inside.
- Incorrect Unit Usage: Ensure that all measurements are in the same units before calculating.
Interactive Examples and Practice Problems
Practicing with interactive examples and problems helps solidify understanding. Websites like Khan Academy and Math Goodies offer valuable resources for practice and further learning.
By mastering these concepts, you can apply them effectively in various practical scenarios, such as planning a garden layout, flooring a house, or any task requiring measurement of space and boundaries.
Xem bài hát vui nhộn về diện tích và chu vi dành cho học sinh lớp 3 và lớp 4. Học cách tính diện tích và chu vi một cách thú vị và dễ hiểu!
Bài Hát Về Diện Tích Và Chu Vi Cho Trẻ Em | Lớp 3 - Lớp 4
READ MORE:
Xem video 'Chu Vi Quanh Khu Vực' của The Bazillions để học về diện tích và chu vi. Video này giúp học sinh hiểu rõ hơn về cách tính diện tích và chu vi một cách thú vị.
"Chu Vi Quanh Khu Vực" của The Bazillions