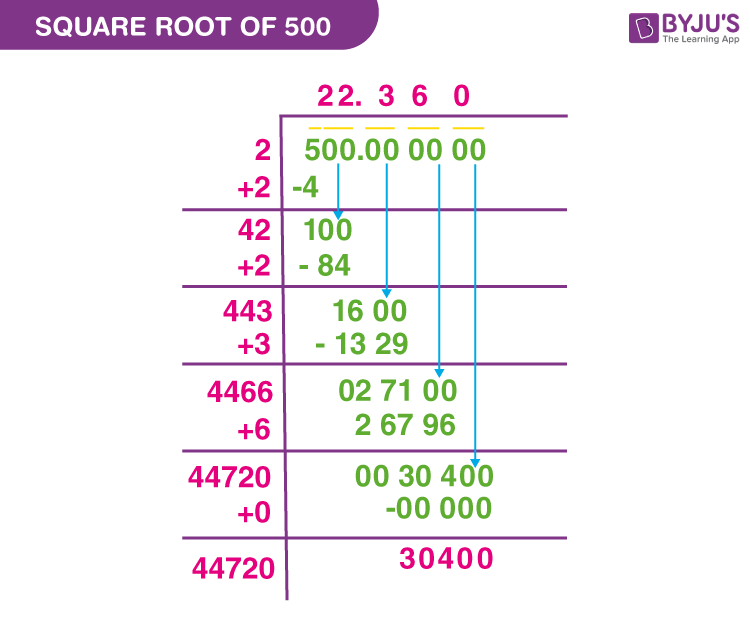
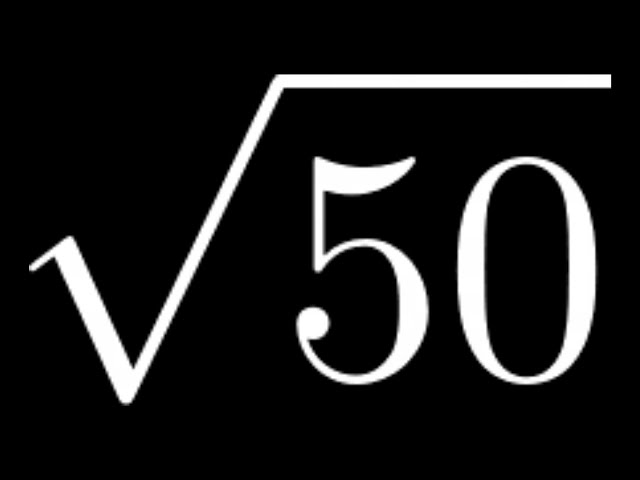Topic simplify square root 180: Learn how to simplify square root 180 effortlessly with our detailed guide. Whether you're a student tackling algebra or someone needing quick calculations, we break down the steps and methods for simplifying √180. Master the process through clear examples and practical tips, making math simpler and more understandable.
Table of Content
- Simplifying the Square Root of 180
- Introduction to Simplifying Square Root of 180
- Understanding the Concept of Square Root and Simplification
- Methods and Techniques to Simplify √180
- Step-by-Step Guide to Simplify Square Root of 180
- Examples and Practice Problems for √180 Simplification
- Applications of Simplifying Square Root of 180
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Simplifying √180
- Further Resources and Advanced Topics on Square Roots
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 180 một cách dễ hiểu và hấp dẫn.
Simplifying the Square Root of 180
The square root of 180 can be simplified by using its prime factorization. Here are the steps to simplify √180:
Steps to Simplify
- List the prime factors of 180: 2, 2, 3, 3, 5.
- Group the prime factors into pairs: (2, 2) and (3, 3).
- Each pair of prime factors can be taken out of the square root: 2 and 3.
- Multiply these factors together outside the square root: 2 * 3 = 6.
- The remaining factor (5) stays inside the square root.
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 180 is:
$$ \sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5} $$
Decimal Form
The decimal form of the square root of 180 is approximately:
$$ \sqrt{180} \approx 13.416 $$
Example Problems
-
Example 1: If you want to find the length of the side of a square with an area of 180 square units, you would calculate:
$$ \text{side length} = \sqrt{180} \approx 13.416 $$ units
-
Example 2: To evaluate \( \frac{\sqrt{180}}{\sqrt{45}} \):
$$ \frac{\sqrt{180}}{\sqrt{45}} = \frac{6\sqrt{5}}{3\sqrt{5}} = 2 $$
-
Example 3: To find the distance Mia walks if she goes 6 miles north and 12 miles east:
$$ \text{Distance} = \sqrt{6^2 + 12^2} = \sqrt{36 + 144} = \sqrt{180} \approx 13.416 $$ miles
Methods to Find the Square Root
There are three common methods to find the square root of a number:
- Long Division Method
- Repeated Subtraction Method
Using the Prime Factorization Method
To find the square root of 180 using the prime factorization method:
- Express 180 as a product of prime factors: \(180 = 2^2 \times 3^2 \times 5\).
- Take the square root of each pair of prime factors: \( \sqrt{180} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3^2 \times 5} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{5} \).
- Multiply the results: \( 2 \times 3 = 6 \).
- The simplified form is \( 6\sqrt{5} \).
Conclusion
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 180 is:
$$ \sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5} \approx 13.416 $$
This concludes the methods and steps to simplify the square root of 180.
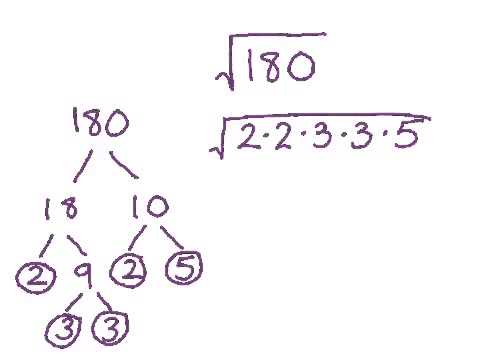
READ MORE:
Introduction to Simplifying Square Root of 180
Simplifying the square root of 180 involves finding the largest integer that can be factored out from the number under the radical sign. This process simplifies the expression while ensuring its accuracy. Let's explore the steps to simplify √180:
- Prime Factorization: Begin by determining the prime factors of 180, which are 2, 2, 3, 3, and 5.
- Pairing Factors: Group pairs of identical factors together. Here, we have (2 × 2), (3 × 3), and 5.
- Extracting Perfect Squares: Take out the square roots of the perfect square pairs. In this case, √(2 × 2) = 2, √(3 × 3) = 3.
- Combine and Simplify: Multiply the numbers obtained from the square roots. The simplified form of √180 is 6√5.
By following these steps, you can effectively simplify the square root of 180, ensuring accuracy and clarity in mathematical expressions involving radicals.
Understanding the Concept of Square Root and Simplification
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For √180, it represents a number which, when squared, equals 180.
Simplifying square roots involves finding factors of the number under the radical sign that are perfect squares, which can be extracted. This process reduces the complexity of the expression while maintaining its mathematical integrity.
- Identifying Factors: Determine the factors of 180, such as 2, 3, and 5.
- Pairing Factors: Group factors into pairs of identical numbers, such as (2 × 2), (3 × 3), and 5.
- Extracting Square Roots: Take the square root of each pair of identical factors, resulting in √(2 × 2) = 2, √(3 × 3) = 3.
- Combining Results: Multiply the extracted square roots together and simplify to obtain the final simplified form, like 6√5 for √180.
This method of simplification is essential in mathematics, enabling easier manipulation of expressions and calculations involving square roots.
Methods and Techniques to Simplify √180
There are several methods and techniques to simplify the square root of 180 effectively:
- Prime Factorization: Begin by determining the prime factors of 180, which are 2, 2, 3, 3, and 5.
- Grouping Factors: Pair the factors into groups of identical numbers, such as (2 × 2), (3 × 3), and 5.
- Extracting Square Roots: Take the square root of each group of identical factors. For instance, √(2 × 2) = 2 and √(3 × 3) = 3.
- Combining and Simplifying: Multiply the results obtained from the square roots and combine them to achieve the simplified form. In the case of √180, the simplified form is 6√5.
By following these systematic steps, you can simplify the square root of 180 efficiently and accurately, utilizing fundamental mathematical principles of factorization and square roots.
Step-by-Step Guide to Simplify Square Root of 180
Simplifying the square root of 180 involves expressing the number in its simplest radical form. Follow these steps to simplify √180:
- Prime Factorization: Begin by finding the prime factors of 180.
- 180 is divisible by 2: \( 180 \div 2 = 90 \)
- 90 is divisible by 2: \( 90 \div 2 = 45 \)
- 45 is divisible by 3: \( 45 \div 3 = 15 \)
- 15 is divisible by 3: \( 15 \div 3 = 5 \)
- 5 is a prime number.
- Grouping the Factors: Group the prime factors into pairs.
- \( 2^2 \) forms one pair.
- \( 3^2 \) forms another pair.
- 5 remains unpaired.
- Extracting Square Roots: For each pair of factors, take one factor out of the square root.
- \( \sqrt{2^2} = 2 \)
- \( \sqrt{3^2} = 3 \)
- Combine the Results: Multiply the extracted factors and place the unpaired factor inside the square root.
- \( 2 \times 3 = 6 \)
- Therefore, \( \sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5} \).
Thus, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{180} \) is \( 6\sqrt{5} \).
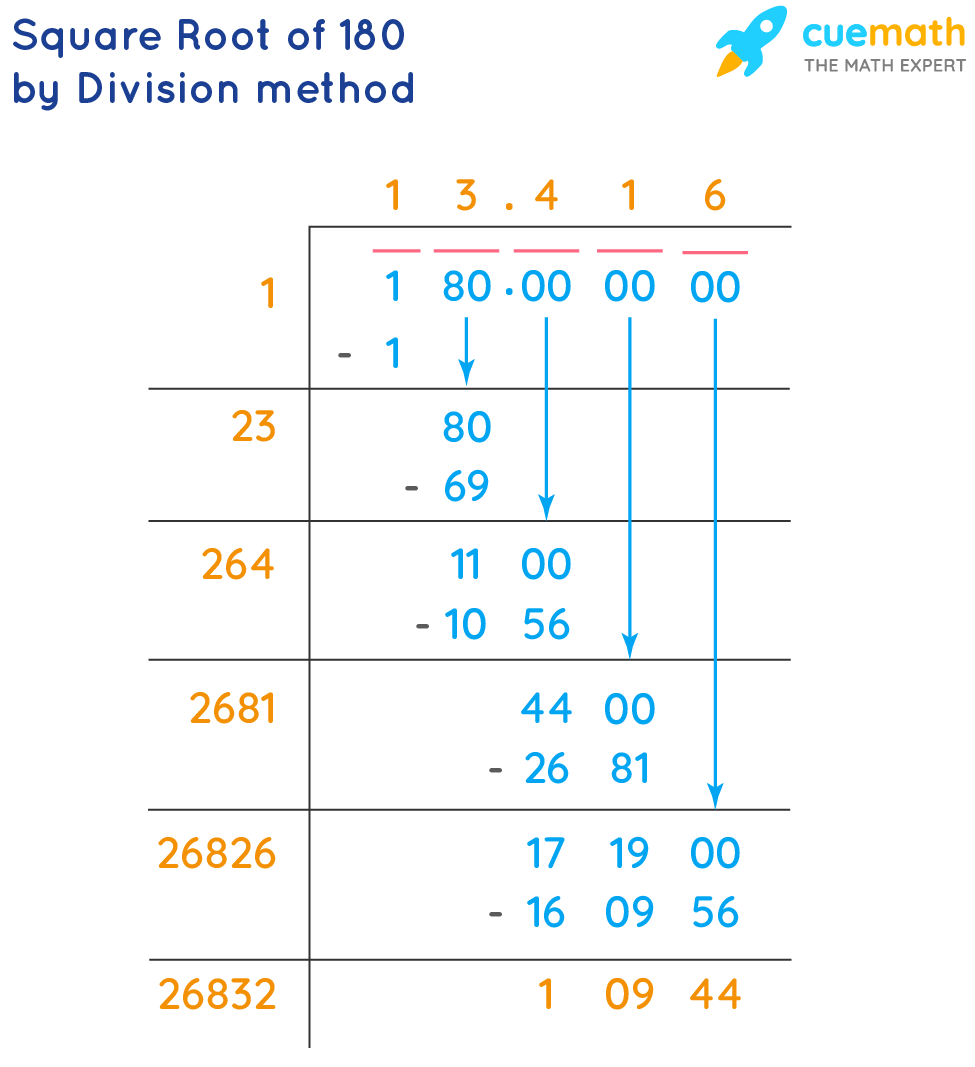
Examples and Practice Problems for √180 Simplification
Here are some examples and practice problems to help you understand and practice the simplification of √180:
Example 1: Basic Simplification
Given: \( \sqrt{180} \)
- Prime factorize 180: \( 180 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 5 \)
- Group the factors into pairs: \( 180 = (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 5 \)
- Rewrite under the square root: \( \sqrt{180} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 5} \)
- Simplify by taking the square root of the pairs: \( \sqrt{180} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{5} \)
- Result: \( \sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5} \)
Example 2: Word Problem
Sally has plans to decorate one wall of her room by putting borders along the top. If the square wall measures about 180 square feet, what is the length of the border she needs for the decor to the nearest tenth?
Solution:
- Calculate the side length of the wall: \( \text{side} = \sqrt{180} \approx 13.416 \)
- Round to the nearest tenth: \( \text{side} \approx 13.4 \)
The length of the border Sally needs is 13.4 feet.
Example 3: Simplifying a Radical Expression
Given: \( \frac{\sqrt{180}}{\sqrt{45}} \)
- Simplify the numerator and the denominator: \( \sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5} \) and \( \sqrt{45} = 3\sqrt{5} \)
- Rewrite the expression: \( \frac{6\sqrt{5}}{3\sqrt{5}} \)
- Cancel out the common factors: \( \frac{6\sqrt{5}}{3\sqrt{5}} = \frac{6}{3} = 2 \)
Result: \( \frac{\sqrt{180}}{\sqrt{45}} = 2 \)
Practice Problems
- Simplify \( \sqrt{200} \)
- Evaluate \( \frac{\sqrt{180}}{\sqrt{20}} \)
- Find the smallest number by which 180 must be multiplied to get a perfect square. Determine the square root of the resulting perfect square.
Try solving these problems using the methods and techniques outlined above. Practice makes perfect!
Applications of Simplifying Square Root of 180
The simplified square root of 180, which is \(6\sqrt{5}\), has various practical applications in different fields. Here are some key areas where this knowledge is beneficial:
- Geometry and Trigonometry:
In geometry, the simplified form \(6\sqrt{5}\) is useful for calculating lengths of sides in various shapes, especially when dealing with areas and volumes that involve square roots.
- For example, in a right triangle where one leg is 6 units and the other leg is 12 units, the hypotenuse can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem:
\(c = \sqrt{6^2 + 12^2} = \sqrt{36 + 144} = \sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5}\).
- For example, in a right triangle where one leg is 6 units and the other leg is 12 units, the hypotenuse can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem:
- Physics:
Square roots often appear in physics equations, particularly in those involving wave functions, distances, and energies. Simplifying \(\sqrt{180}\) to \(6\sqrt{5}\) can make calculations more straightforward.
- For instance, in calculating the distance between two points in a coordinate system, if the distance squared is 180, the distance would be \(6\sqrt{5}\).
- Engineering:
Engineers use square roots to solve problems related to material strength, electrical currents, and other measurements. Simplifying these roots can help in more accurate and faster computations.
- An example is in stress analysis, where the stress value derived from complex equations might include \(\sqrt{180}\), which simplifies to \(6\sqrt{5}\) for easier interpretation and application.
- Computer Science:
Algorithms involving square roots can benefit from simplified forms to improve efficiency and accuracy, especially in graphics and simulations where precise calculations are crucial.
- For example, in graphics programming, calculating distances and angles may require the use of square roots, where having a simplified form like \(6\sqrt{5}\) can optimize the code.
- Finance:
In financial calculations, square roots appear in risk assessment models, options pricing, and statistical analyses. Simplifying these expressions can aid in clearer and quicker financial decisions.
- For instance, when analyzing the volatility of stock prices, the simplified form \(6\sqrt{5}\) might emerge in the variance or standard deviation calculations.
Overall, simplifying the square root of 180 to \(6\sqrt{5}\) not only makes the number more manageable but also enhances the precision and clarity of various mathematical and practical applications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Simplifying √180
Simplifying the square root of 180 can be tricky, and there are common mistakes that students often make. Being aware of these errors can help ensure accurate simplification.
- Ignoring Prime Factorization: Always start by breaking down 180 into its prime factors. Skipping this step can lead to incorrect simplifications.
Example: \(180 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 5\)
- Forgetting to Simplify Perfect Squares: After finding the prime factors, identify and simplify the perfect squares.
Example: Recognize that \(2 \times 2 = 4\) and \(3 \times 3 = 9\) are perfect squares.
So, \(\sqrt{180} = \sqrt{4 \times 9 \times 5} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{5} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{5} = 6\sqrt{5}\).
- Mistaking Non-Perfect Squares for Perfect Squares: Ensure the factors you pull out are indeed perfect squares.
Example: Incorrectly simplifying \( \sqrt{180} \) as \(\sqrt{36 \times 5} = \sqrt{36} \times \sqrt{5} = 6\sqrt{5}\) is correct, but mistaking \(\sqrt{72}\) for \(\sqrt{36} \times \sqrt{2}\) is incorrect since 72 is not a product of these factors.
- Overlooking Remaining Factors: After simplifying the perfect squares, ensure no factor is left inside the square root unnecessarily.
Example: After extracting \(\sqrt{4} = 2\) and \(\sqrt{9} = 3\), ensure \(\sqrt{5}\) remains inside as \(5\) is not a perfect square.
- Arithmetic Errors: Be cautious of simple multiplication and division errors while simplifying.
Example: \(\sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5}\), ensure the multiplication \(2 \times 3 = 6\) is performed correctly.
- Misinterpreting the Final Form: Ensure the simplified form is expressed correctly.
Example: Always express \(\sqrt{180}\) in simplest form as \(6\sqrt{5}\), and not leave intermediate steps in the answer.
Avoiding these common mistakes can help ensure accurate and simplified expressions for square roots.
Further Resources and Advanced Topics on Square Roots
Understanding and simplifying square roots can open the door to a variety of advanced mathematical concepts and applications. Here are some resources and advanced topics to explore further:
1. Advanced Methods for Simplifying Square Roots
For those looking to deepen their understanding, consider exploring different methods of simplifying square roots:
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down the number into its prime factors can help simplify the square root more efficiently.
- Long Division Method: This method provides an accurate way to find the square root by hand.
- Newton's Method: An iterative approach to finding increasingly accurate approximations of square roots.
2. Real-World Applications
Simplified square roots have numerous applications in various fields:
- Geometry: Calculating distances, areas, and volumes often involves square roots.
- Physics: Understanding wave functions, quantum mechanics, and other phenomena.
- Engineering: Simplified square roots are used in stress analysis, material properties, and more.
3. Interactive Learning Tools
Use these online tools to practice and improve your skills in simplifying square roots:
- : Offers interactive lessons and problems for practice.
- : Provides clear explanations and examples.
- : Features calculators and step-by-step guides for simplification.
4. Advanced Topics in Square Roots
Once you are comfortable with basic simplifications, explore these advanced topics:
- Surds: Understand and work with irrational roots that cannot be simplified further.
- Complex Numbers: Learn about the square roots of negative numbers and their applications.
- Fractional Exponents: Delve into how square roots relate to exponents and logarithms.
5. Challenging Problems and Exercises
Test your skills with these challenging exercises:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{200} \) and express it in simplest form.
- Find the smallest number by which 180 must be multiplied to get a perfect square. Determine the square root of the perfect square obtained.
- Evaluate \( \sqrt{180} + 2\sqrt{45} \) in its simplest form.
6. Further Reading and Courses
Consider the following books and courses for an in-depth understanding:
- Books: "Principles of Mathematics" by Allendoerfer and Oakley, "Precalculus" by David Lippman.
- Online Courses: Khan Academy's Algebra and Precalculus courses, Coursera's Mathematics for Machine Learning.

Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 180 một cách dễ hiểu và hấp dẫn.
Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai 180
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính căn bậc hai của số 180 một cách dễ hiểu và hấp dẫn.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 180